If you’re looking for a Ford 2G Alternator Wiring Diagram, you’ve come to the right place. Here at Automotive wiring diagram HQ we have compiled a list of the most popular electrical wiring diagrams for Ford vehicles from various years and models. This collection of schematics will help you get your car or truck’s electrical system up and running in no time.
Whether you’re working on a classic Mustang or a brand new F-150, our collection of Ford alternator wiring diagrams has everything you need to get your vehicle’s electrical system up and running. From simple charging system circuits to more complex computer controlled setups, we’ve got all the info you need to get things going. So take a look through our selection and find the perfect diagram for your ride.
If you’re looking for a Ford 2G Alternator Wiring Diagram, you’ve come to the right place. Here at EasyEngineering, we make it our mission to provide the best possible engineering diagrams and schematics to our readers. In this blog post, we’ll be providing a free downloadable diagram for a Ford 2G Alternator Wiring Diagram.
This particular diagram covers the following vehicles:
1995-2005 Ford Crown Victoria
2003-2005 Ford E-150 Van
2003-2005 Ford E-250 Van
2003-2005 Ford E-350 Van
Credit: vb.foureyedpride.com
What are the Three Wires on a Ford Alternator?
The three wires on a Ford alternator are the positive (red), negative (black), and field (blue) wires. The positive wire goes to the battery and provides power to charge it. The negative wire goes to the engine block or chassis and provides a path for the current to flow back to the alternator.
The field wire goes to the “exciter” winding on the alternator, which creates a magnetic field that causes the alternator to generate electricity.
What are the Wires on a 2 Wire Alternator?
An alternator is a device that generates alternating current (AC) by using a rotating magnetic field. The most common type of alternator is the two-wire alternator, which has two windings: a primary winding and a secondary winding. The primary winding is typically made of thicker wire than the secondary winding.
The reason for this is that the primary winding carries more current than the secondary winding.
The two wires on a two-wire alternator are the positive and negative terminals of the AC output. The positive terminal is typically marked with a plus sign (+), while the negative terminal is typically marked with a minus sign (-).
These terminals are usually located at the back of the alternator.
The purpose of the primary winding is to create a strong magnetic field, while the purpose of the secondary winding is to convert this magnetic field into AC current.
What is a 2G Alternator?
An alternator is an electrical device that converts mechanical energy into alternating current (AC) electrical energy. Alternators are used in a wide variety of applications, including automotive, marine, and aircraft power generation. Two-stage generators are similar to alternators, but they have two sets of windings instead of just one.
The 2G designation on an alternator indicates that it is a two-stage generator.
How do 2G Alternators Work?
2G alternators have two sets of windings: a field winding and an armature winding.
The field winding is typically excited by direct current (DC), while the armature winding is supplied with AC from the rectifier/regulator output. When the engine is running, the crankshaft turns the rotor which spins the field magnets past the stationary armature coils. This induces a voltage in the armature coils which drives the current through the external circuit.
The advantage of using a 2G over a 1G alternator is that the 2G can produce more power at lower engine speeds than a 1G. This makes them ideal for applications where low speed operation is common, such as in marine or aircraft engines. Additionally, 2G alternators tend to be more rugged and durable than their 1G counterparts since they have fewer moving parts.
If you’re looking for an alternator for your next project, be sure to consider a 2G model!
What Wires Go Where on Alternator?
If you’re looking to wire up an alternator, there are a few things you need to know. First off, alternators have three main wires coming out of them – the battery terminal, the ground terminal, and the field terminal. The battery terminal is where you’ll connect the positive (+) cable from your battery.
The ground terminal is where you’ll connect a negative (-) cable from your engine block or chassis. And finally, the field terminal is where you’ll connect a small gauge wire that will provide power to the field coil inside the alternator.
Now that you know which terminals go where, let’s talk about how to actually wire up an alternator.
If you’re working with a new alternator (or one that has been rewound), it’s important to start by connecting the ground terminal first. This will help prevent any accidental shorts when connecting the other two wires. Once the ground wire is in place, go ahead and connect the battery cable next.
Make sure this connection is nice and tight – loose connections can cause all sorts of problems down the road. Finally, attach the field wire last. This completes the electrical circuit and allows power to flow through to charge your battery!
As always, be careful when working with electricity – it can be dangerous if not done properly! If you’re unsure about anything, make sure to consult with a professional mechanic before proceeding.
Ford 2G Alternator Wiring
Ford 1G to 2G Alternator Conversion
If you have a Ford 1G (first generation) alternator in your vehicle, you may be considering upgrading to a 2G (second generation) alternator. There are several benefits to doing this conversion, including increased amperage output and better charging at low RPMs.
To do the conversion, you will need a few tools and parts, including a drill, tap set, die grinder, large socket or wrench for the main nut, and an impact gun for the smaller bolts.
You will also need a 2G stator (the part of the alternator that produces electricity), pulley, and regulator. Once you have all of your supplies gathered, follow these steps:
1. Remove the old 1G alternator from your vehicle.
This will require disconnecting the battery terminals and unbolting the alternator from its mounting bracket.
2. Install the new 2G stator into the housing where the old 1G stator was located. You may need to slightly enlarge the holes with your die grinder in order for everything to fit properly.
3. Reattach all of the wiring connectors to their appropriate locations on the new 2G alternator. Make sure everything is snug and secure before moving on to step 4!
4. Install the new 2G pulley onto the shaft of the alternator using either a large socket or wrench.
.5 Finally, bolt everything back into place using your impact gun (for smaller bolts) or drill/tap set (for larger bolts). Reconnect your battery terminals and start up your engine – if everything has been done correctly, you should now have an upgraded 2G alternator powering your car!
Ford 2G to 3G Alternator Wiring
If you are looking to upgrade your Ford Alternator from a 2G to a 3G, there are a few things you will need to know. The first is that the 3G alternator is not a direct bolt on replacement for the 2G. You will need an adapter bracket, which can be found at most auto parts stores.
The second thing you need to know is that the 3G has a higher output than the 2G, so if you are running any kind of high-performance accessories, you may want to upgrade your electrical system as well.
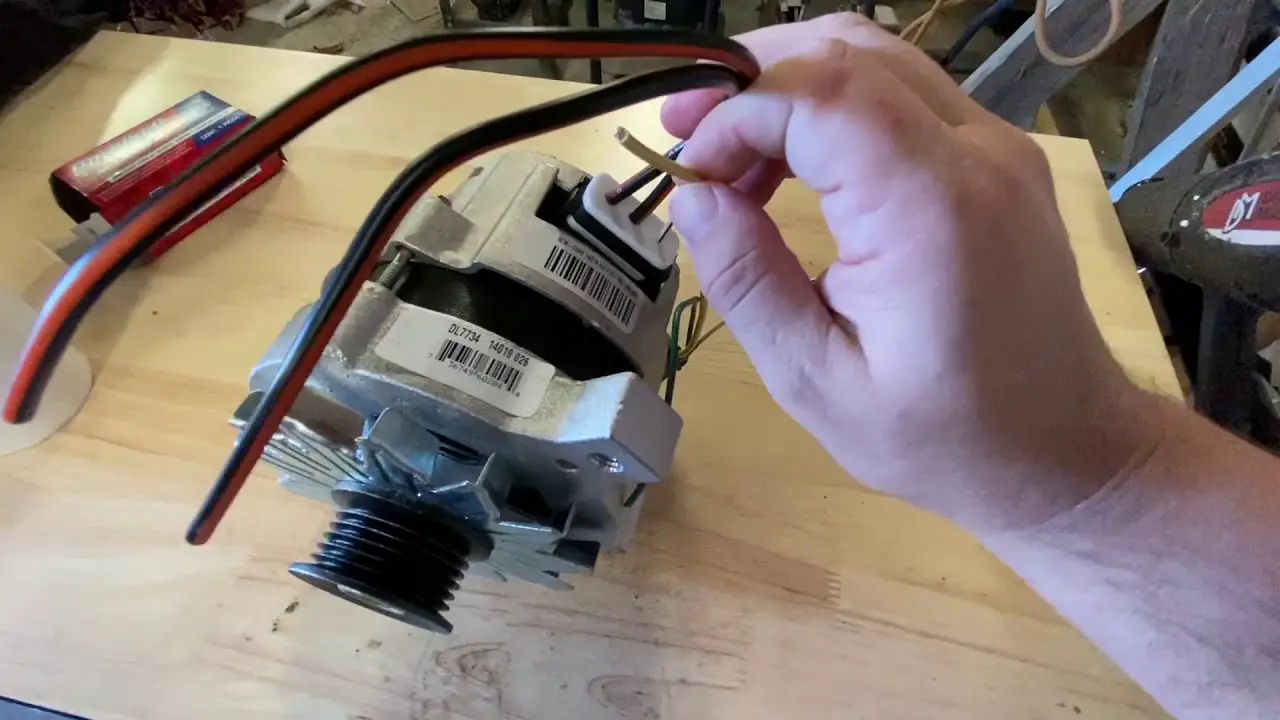
Ford 2G Alternator Pigtail
If your Ford 2G Alternator is anything like mine was, the pigtail connector that plugs into the back of it is probably corroded and in need of replacement. The good news is that this is a fairly easy repair that you can do yourself with just a few tools.
First, start by disconnecting the negative battery terminal to avoid any short circuits.
Next, locate the two wires that connect to the back of the alternator (one should be red and the other should be black). Using a wire cutter, carefully cut away any corrosion on both wires.
Now it’s time to splice in the new pigtail connector.
I like to use soldered butt connectors for this job, but you could also use crimp connectors if you prefer. Just make sure whatever method you use provides a secure connection. Once both wires are connected to the new pigtail, tuck everything neatly into place and reconnect the negative battery terminal.
That’s all there is too it! This simple repair will ensure that your alternator continues to function properly for years to come.
Conclusion
If you’re looking for a Ford 2G Alternator Wiring Diagram, you’ve come to the right place. Here at AutoZone, we carry a wide variety of alternators for your specific vehicle so you can rest assured knowing that you’re getting the best possible fit. Plus, our helpful staff is always on hand to answer any questions and help with installation.






