LML 6.6 Duramax Engine Diagram: Layout & Component Guide
An LML 6.6 Duramax engine diagram provides a visual map of the V8 diesel’s architecture, highlighting critical parts like the turbocharger, injectors, and sensors. It is an essential tool for identifying components during maintenance, ensuring every torque spec is followed, and locating wiring paths to the ECU for complex electrical troubleshooting.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides a visual reference for all mechanical and electrical components in the LML system.
- Crucial for identifying the fuel system layout including the CP4 pump and injectors.
- Ensures safety by detailing high-pressure lines and sensitive electrical connections.
- Speeds up repairs by matching visual parts to their corresponding diagnostic code results.
- Essential for locating wiring harness paths when tracing sensor communication errors.
Navigating the complexities of a modern diesel powerplant requires precision, and having a reliable lml 6.6 duramax engine diagram is the foundation of any successful repair or maintenance project. Whether you are tracking down a persistent leak, replacing a worn-out component, or simply trying to understand the inner workings of your heavy-duty truck, a high-quality diagram acts as your roadmap. This specific engine, known for its robust power and advanced emissions systems, features a dense layout that can be intimidating without visual guidance. In this guide, we will break down the primary systems shown in the diagram, explain how to interpret technical schematics, and provide actionable steps to use this information for effective troubleshooting and upkeep.
Understanding the LML 6.6 Duramax Engine Layout
The LML 6.6 Duramax engine, utilized in heavy-duty trucks between 2011 and 2016, represents a significant evolution in diesel technology. When looking at a comprehensive lml 6.6 duramax engine diagram, the first thing you will notice is the 90-degree V8 block architecture. The diagram typically highlights the “valley” of the engine, where the variable geometry turbocharger (VGT) is centrally located. This design is crucial for heat management and efficient exhaust gas routing.
The diagram further breaks down the engine into several critical subsystems. First is the high-pressure common rail fuel system, which includes the CP4.2 injection pump and the piezo-electric fuel injectors. Unlike earlier models, the LML diagram shows a complex network of return lines and a ninth injector (hydrocarbon injector) used specifically for the Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) regeneration process. Understanding this layout is essential because the fuel system operates at pressures exceeding 29,000 PSI, requiring absolute precision during any disassembly.
Another key feature of the diagram is the electrical architecture. You will find the ECU (Engine Control Unit) positioned to manage a vast array of sensors. These sensors monitor everything from exhaust gas temperatures (EGT) to fuel rail pressure. The diagram will also illustrate the OBD-II interface connection, which is the gateway for your diagnostic tools to communicate with the ECU. By studying the visual locations of these sensors, you can more easily identify which component corresponds to a specific diagnostic code when your check engine light illuminates on the dashboard.
The LML Duramax was the first in its lineage to incorporate Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) technology, which requires Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF). A full engine diagram will include the fluid lines and the DEF injector located in the exhaust stream, separate from the main engine block.
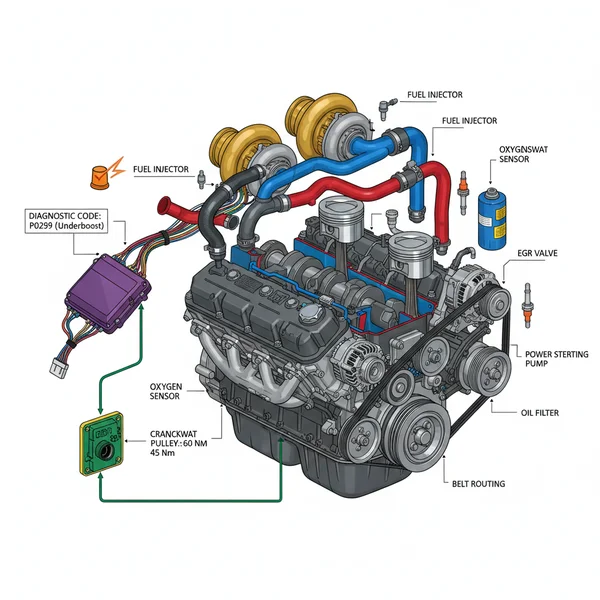
Visual Representation of the LML 6.6 Duramax Engine highlighting the Turbocharger, Fuel Rail, ECU placement, Accessory Belt Routing, and Coolant Passages.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the Engine Diagram

Interpreting a technical lml 6.6 duramax engine diagram involves more than just looking at pictures; it requires a systematic approach to match the drawing to the physical reality under your hood. Follow these steps to effectively utilize the diagram for your mechanical tasks.
Step 1: Orient the Perspective
Before turning a wrench, determine the orientation of the diagram. Most automotive diagrams use “Front of Engine” (where the cooling fan sits) and “Rear of Engine” (where the transmission attaches) as primary markers. Locate the accessory belt on the diagram to establish the front-facing view.
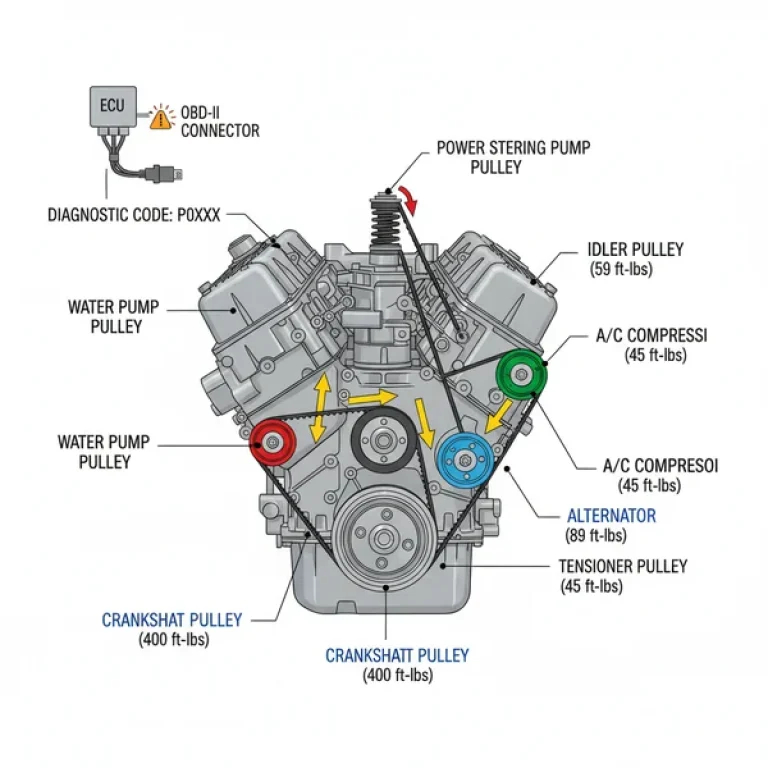
Step 2: Trace the Accessory Belt Path
One of the most common uses for a diagram is replacing the accessory belt. Trace the line on the diagram that weaves through the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump. Note the position of the tensioner pulley; the diagram will show you which direction the tensioner must move to release the belt.
Step 3: Map the Coolant Flow
Efficient coolant flow is vital for preventing the LML from overheating, especially when towing. Use the diagram to identify the upper and lower radiator hoses, the bypass pipe, and the heater core lines. The diagram helps you locate the two thermostats housed in a single housing—a unique feature of the Duramax that ensures rapid warming and stable operating temperatures.
Step 4: Locate the ECU and Sensor Network
If you are dealing with an electrical issue, find the ECU on the diagram. From there, you can trace the wiring harness to various sensors like the Crankshaft Position Sensor or the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor. This is particularly helpful when a diagnostic code points to a circuit error, allowing you to check the physical integrity of the wires and connectors.
Step 5: Identify the Timing Assembly
While the LML uses a gear-driven system for many components, people often look for a timing chain or belt. In this engine, the diagram will show the heavy-duty timing gears located behind the front cover. Understanding how the crankshaft gear meshes with the camshaft gear is essential for any internal engine repair, such as a camshaft replacement.
Step 6: Utilize Torque Specifications
A high-quality lml 6.6 duramax engine diagram often includes or references a torque spec table. As you identify a bolt on the diagram (such as a manifold bolt or a fuel injector hold-down), cross-reference it with the manufacturer’s torque requirements. Using the correct torque is non-negotiable for diesel engines to prevent leaks or catastrophic metal fatigue.
The LML fuel system maintains extremely high pressure even after the engine is turned off. Always allow the system to depressurize for at least 10 minutes and consult your diagram to identify the high-pressure lines before attempting any fuel system service.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with the LML
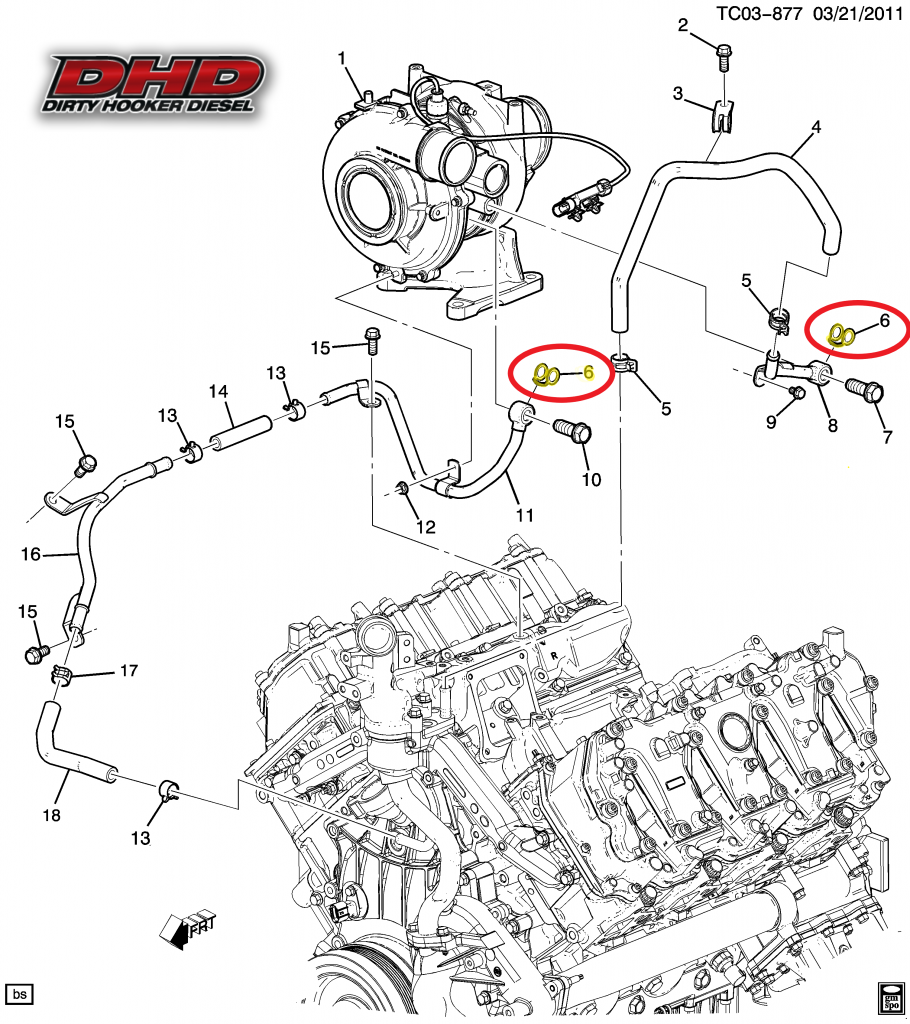
The LML is a workhorse, but it is not without its specific vulnerabilities. Utilizing your lml 6.6 duramax engine diagram can help you pinpoint the source of common problems quickly.
One frequent issue is the failure of the CP4.2 high-pressure fuel pump. When this pump fails, it can send metal shavings throughout the entire fuel system. The diagram allows you to see the path the fuel takes from the pump to the rails and then to the injectors, helping you realize why a total system flush is required if contamination occurs.
Another common problem is related to the emissions system. If your check engine light comes on with a diagnostic code like P20EE (SCR NOx Catalyst Efficiency), the diagram will help you locate the NOx sensors and the DEF injector. By tracing these components, you can check for DEF crystallization or sensor soot-fouling before deciding to replace expensive parts.
Finally, cooling system leaks can be elusive. Using the diagram to follow the coolant flow allows you to check common leak points such as the turbocharger coolant lines or the water pump weep hole, which are often hidden from plain sight.
- ✓ Fuel System: Watch for P0087 (Low Fuel Rail Pressure) codes.
- ✓ Emissions: Monitor DPF soot levels via the OBD-II port.
- ✓ Turbocharger: Check for oil leaks at the VGT actuator shown in the diagram.
Maintenance Tips and Best Practices
To keep your LML 6.6 Duramax running at peak performance, regular maintenance guided by a proper diagram is essential. Here are some pro tips to extend the life of your engine.
Always use a high-quality fuel additive that improves lubricity. The CP4 pump found in the LML diagram relies heavily on the fuel itself for lubrication, and modern ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) can sometimes be “dryer” than the pump prefers.
First, pay close attention to the accessory belt. Inspect it every 30,000 miles for glazing, cracks, or “chunking.” A failure here can lead to an immediate loss of power steering and alternator function, leaving you stranded. Use your diagram to ensure the replacement belt is routed exactly as intended, as an incorrect routing can spin the water pump backward, causing rapid overheating.
Second, maintain the integrity of the ECU connections. Diesel engines vibrate significantly, which can lead to harness chafing. Periodically use your lml 6.6 duramax engine diagram to identify where the wiring harness is secured to the engine block and check for signs of wear. Applying a small amount of dielectric grease to sensor connectors can prevent moisture intrusion and the phantom diagnostic code issues that often follow.
Lastly, never skip a coolant flush. Over time, the chemistry of the coolant breaks down, which can lead to cavitation in the water pump and erosion of the internal coolant flow passages. Refer to the torque spec for the drain plugs and thermostat housing bolts to ensure a leak-free seal after service. Investing in high-quality, manufacturer-approved fluids will save you thousands of dollars in long-term repair costs.
By combining the visual clarity of an lml 6.6 duramax engine diagram with a disciplined maintenance schedule, you ensure that your truck remains a reliable asset for years to come. Whether you are clearing a check engine light or performing a total overhaul, the diagram is your most valuable tool in the garage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is LML 6.6 Duramax engine diagram?
An LML 6.6 Duramax engine diagram is a technical illustration that maps out the physical layout and connections of the 2011-2016 GM diesel engine. It identifies the location of the turbocharger, fuel rails, and cooling system, helping mechanics navigate the complex engine bay for repairs, part replacements, or general maintenance tasks.
How do you read LML 6.6 Duramax engine diagram?
To read the diagram, start by identifying the front of the engine, usually indicated by the cooling fan or serpentine belt. Follow the lines representing wiring or fluid paths from the central ECU to individual sensors. Use the legend to decode symbols for electrical grounds, connectors, and fluid flow directions.
What are the parts of LML 6.6 Duramax?
The primary parts include the high-pressure CP4 fuel pump, common rail injectors, variable geometry turbocharger (VGT), and the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system. The diagram also highlights the Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) components and the complex wiring harness that facilitates communication between engine sensors and the onboard computer system.
Why is ECU important?
The ECU, or Engine Control Unit, acts as the brain of the Duramax engine. It processes data from dozens of sensors to manage fuel timing, boost pressure, and emissions. Understanding its location on a diagram is vital when troubleshooting electrical failures that prevent the vehicle from starting or running efficiently.
What is the difference between LML and LMM diagrams?
The LML diagram features a more advanced fuel system and additional emissions components compared to the earlier LMM version. Specifically, the LML includes the DEF injection system and a different high-pressure fuel pump layout. These diagrams are not interchangeable because the wiring harness and sensor locations differ significantly between generations.
How do I use LML 6.6 Duramax engine diagram?
Use the diagram as a spatial guide when a diagnostic code indicates a sensor failure. By locating the specific sensor on the map, you can trace the wiring back to the ECU to check for breaks. It also helps in identifying which components must be removed to reach buried parts.