Leer Truck Cap Parts Diagram: Identification and Repair
A Leer truck cap parts diagram provides a visual breakdown of the shell’s configuration, including gas props, mounting hardware, and window seals. Understanding this system allows owners to identify specific replacement components accurately, ensuring the structure remains weather-tight and secure throughout its lifespan on your vehicle’s bed.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides clear visualization of all hardware and mounting components.
- Crucial for identifying the correct serial number for part compatibility.
- Helps ensure all seals are intact for a weather-tight structure.
- Facilitates regular inspection of gas struts and handle mechanisms for wear.
- Allows users to order precise replacement parts from authorized dealers.
Owning a Leer truck cap adds immense utility and security to your pickup, but maintaining that functionality requires a clear understanding of its intricate assembly. Whether you are tackling a leak, replacing a shattered window, or upgrading your locking mechanism, a comprehensive leer truck cap parts diagram serves as your essential roadmap for repair and maintenance. Having the correct schematic is the difference between a seamless DIY fix and a frustrating afternoon of trial and error. This article provides a detailed exploration of the components that make up the Leer system, helping you identify every bolt, seal, and strut. You will learn how to interpret complex layouts, select the right replacement parts, and ensure your truck cap remains weather-tight and secure for years to come.
Before ordering any parts from a diagram, locate the serial number of your Leer cap. This is usually found on a silver or black sticker on the interior roof or near the rear door. This number ensures the configuration matches your specific model year and bed size.
Decoding the Leer Truck Cap Parts Diagram
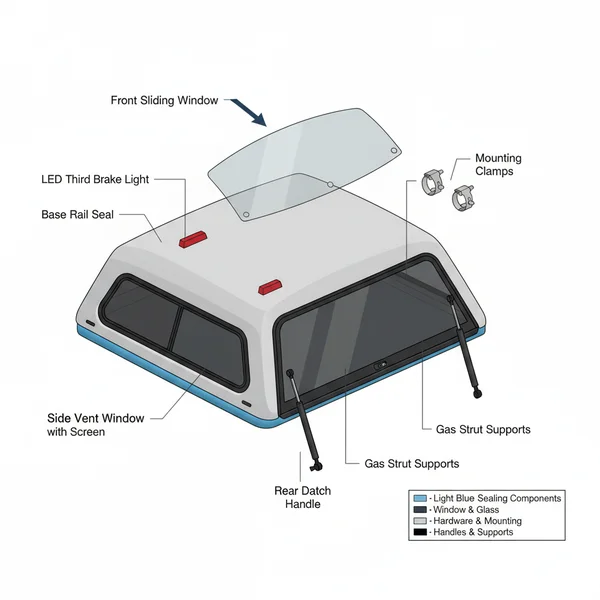
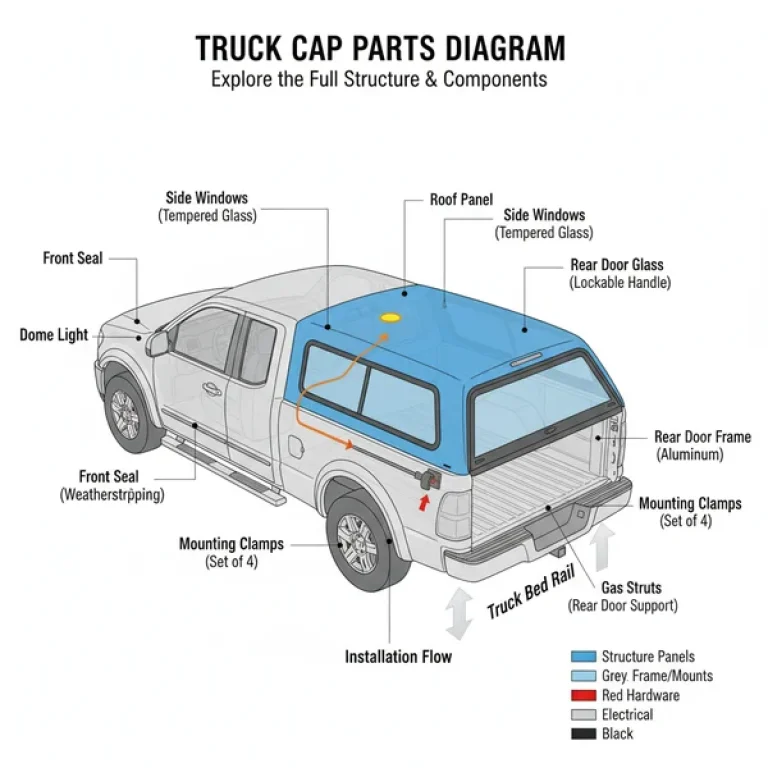
A standard leer truck cap parts diagram is a multi-layered configuration that breaks the unit down into four primary categories: the structural shell, the window system, the rear door assembly, and the mounting hardware. The layout is typically presented in an “exploded view,” which shows how individual pieces relate to one another in three-dimensional space. Understanding this visual breakdown is the first step toward successful troubleshooting.
The structural shell is the fiberglass or aluminum body. In the diagram, you will see the reinforcement points where the roof can support racks and the base rail where the cap meets the truck bed. The window system is often the most complex part of the layout. Depending on your model, the diagram will detail side “win-doors,” sliding glass, or fixed panes. Each window component includes the glass itself, the outer frame, the internal trim ring, and the rubber gasket or “bulb seal” that prevents moisture from entering the cab.
The rear door assembly is a high-traffic system that includes the rear glass, the door frame (often called the “bottom metal”), hinges, and gas struts. The gas struts, or lift props, are measured by length and poundage of pressure, both of which are critical specifications found in the technical layout. Finally, the mounting system consists of J-clamps or C-clamps that secure the cap to the bed rails without the need for drilling. The diagram will also illustrate the electrical configuration, specifically the wiring harness for the third brake light and any interior LED lighting.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: Exploded view of a Leer Truck Cap showing rear door, gas struts, side windows, and mounting clamps with alphabetical labels A-L]
Step-by-Step Guide to Interpreting and Using the Diagram

Reading a technical layout can be intimidating if you aren’t familiar with automotive schematics. However, by following a logical progression, you can use a leer truck cap parts diagram to perform professional-grade repairs. Use the following steps to navigate the system configuration.
- ✓ Step 1: Identify the View Orientation – Most diagrams show the cap from a three-quarter rear perspective. Identify the front (cab side) and the rear (tailgate side) to ensure you are looking at the correct window or hinge side.
- ✓ Step 2: Locate the Part Index – Match the numbered or lettered callouts on the diagram to the parts list at the bottom. This list will provide the official “Component Name” and often the Leer OEM part number.
- ✓ Step 3: Analyze the Fastener System – Look closely at how the components are joined. Diagrams will distinguish between rivets, T-bolts, and hex screws. Knowing the fastener type tells you exactly which tools to bring to the job.
- ✓ Step 4: Assess the Seal Interface – Check the layout for “soft parts” like the bulb seal or the base seal. These are represented by thin lines running along the edges of the windows and the bottom rail.
- ✓ Step 5: Verify the Electrical Path – If you are fixing a light, follow the dotted lines in the diagram that represent the wiring system. This shows where the wires enter the fiberglass shell and how they connect to the truck’s battery or brake light circuit.
- ✓ Step 6: Execute the Disassembly – Using the diagram as a guide, remove parts in the reverse order of their assembly. For example, to replace a window, the diagram will show that the interior trim ring must be removed before the exterior glass can be pushed out.
When replacing gas struts, never replace just one. Even if only one side is failing, the other is likely near its end of life. Replacing them in pairs ensures balanced pressure on the rear door, preventing the glass from twisting or shattering due to uneven stress.
To perform these tasks effectively, you will generally need a basic toolkit:
- ✓ Socket set (specifically 9/16″ for most clamps)
- ✓ Phillips and flat-head screwdrivers
- ✓ Torx bit set (for newer locking mechanisms)
- ✓ Silicone-based lubricant
- ✓ Non-marring trim removal tools
Always wear eye protection when working with gas struts or tempered glass. Gas struts are under high pressure and can cause injury if the mounting points fail during installation. Additionally, tempered glass is designed to shatter into small pieces if stressed, which can be dangerous for your eyes.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with the Parts Diagram

Even the most robust Leer caps encounter wear and tear over time. The most frequent issues involve water intrusion and mechanical failure of the rear door. By referencing the leer truck cap parts diagram, you can pinpoint the exact failure point.
Water Leaks: If you notice moisture in the truck bed, the diagram helps you identify which seal has failed. Most leaks occur at the “bulb seal” on the rear door or the “base seal” between the cap and the truck bed. The diagram shows how these seals are seated; if the seal appears flattened or cracked, it is no longer providing the necessary compression.
Lock and Latch Failures: If the rear handle turns but the door doesn’t open, the internal cables or rotary latches are likely disconnected. The parts diagram illustrates the connection between the center handle and the side latches. Often, a small set-screw has come loose, which can be easily identified and tightened once you see the internal layout of the handle assembly.
Sagging Rear Door: If the door hits your head or won’t stay up, the gas struts are the culprit. The diagram will specify the poundage (e.g., 40 lbs or 60 lbs). Installing struts with too much pressure can crack the fiberglass mounting points, while too little pressure will fail to hold the door open.
Tips and Best Practices for Component Longevity
To avoid frequent reliance on the leer truck cap parts diagram, proactive maintenance is key. Treating your truck cap as a precision system rather than a “set it and forget it” accessory will save you hundreds of dollars in replacement parts.
1. Lubrication is Vital: Use a dry graphite lubricant for the lock cylinders and a silicone spray for the rubber seals. Avoid oil-based lubricants on the seals, as they can cause the rubber to degrade and swell, leading to a poor fit.
2. Check Mounting Clamps Regularly: The vibration of the road can cause J-clamps to loosen over time. Every 5,000 miles, use your socket set to ensure the clamps are tight. A loose cap can shift, damaging both the truck’s paint and the cap’s base seal.
3. Clean the Tracks: For caps with sliding windows, dirt and grit can act as sandpaper against the window felt. Clean the tracks with compressed air or a soft brush to ensure the windows slide smoothly and the seals remain intact.
4. Protect the Finish: Treat the fiberglass shell like the rest of your truck’s paint. Use a high-quality automotive wax to protect the gel coat from UV damage. When the finish oxidizes, it can become brittle, making the mounting points for hardware more prone to stress cracks.
5. OEM vs. Aftermarket: While aftermarket gas struts or handles may be cheaper, using OEM parts listed in the leer truck cap parts diagram ensures that the tolerances are correct. OEM parts are designed to fit the specific curvature of the fiberglass, providing a more reliable seal and a longer lifespan.
By understanding the system layout and keeping a copy of the leer truck cap parts diagram handy, you transform from a passive owner into a capable technician. Whether it is a simple seal replacement or a complex door realignment, having the right information ensures your truck cap remains a valuable asset to your vehicle’s utility and appearance. Consistent maintenance and a clear understanding of the component configuration are the keys to a lifetime of worry-free use.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Leer truck cap parts diagram?
A Leer truck cap parts diagram is a schematic representing the internal and external layout of the canopy. It illustrates how each component, such as the rear glass, mounting rails, and wiring harness, integrates into the overall system. This visual aid is essential for identifying specific hardware for repairs or maintenance.
How do you read Leer truck cap parts diagram?
Reading the diagram involves matching the numbered callouts on the illustration to a corresponding parts list. Focus on the exploded view to see the internal structure and how various fasteners secure the shell to the bed rails. This configuration reveals hidden components like T-handle linkages and third brake light wiring.
What are the parts of Leer truck cap?
The primary parts include the fiberglass or aluminum shell, side windows, rear door glass, and gas props. Crucial structural elements include the base seal, C-clamps or mounting rails, and the locking handle system. Electrical components like the interior dome light and brake light are also part of the system.
Why is the gas prop component important?
The gas prop component is vital because it supports the weight of the rear glass when open. If these struts fail, the door won’t stay upright, posing a safety risk. Identifying the correct pressure rating on the diagram ensures the replacement props maintain the integrity of the lift system configuration.
What is the difference between a cap and a tonneau?
While both cover the truck bed, a truck cap is a tall structure that matches the cab height, providing large enclosed volume. In contrast, a tonneau cover is a flat system that sits flush with the bed rails. The parts diagram for a cap is significantly more complex than a tonneau.
How do I use Leer truck cap parts diagram?
Use the diagram to troubleshoot leaks or mechanical failures by locating the specific seal or hinge involved. Once identified, use the part numbers from the layout to source genuine replacements. It serves as a blueprint for disassembling and reassembling the unit during major maintenance or restoration projects.