Hydraulic Dump Trailer Wiring Diagram: Installation Guide
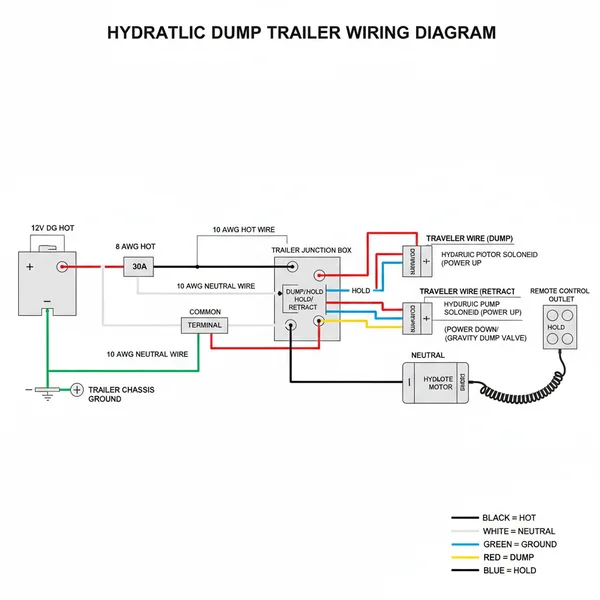
A hydraulic dump trailer wiring diagram maps the electrical path between the battery, solenoid, and pump motor. It shows how the hot wire provides power while the ground wire completes the circuit. The schematic helps identify the traveler wire and common terminal connections necessary for the remote control to operate the lift.
📌 Key Takeaways
- The diagram identifies the primary connection between the battery and the solenoid.
- Correct grounding is the most critical factor for preventing pump motor failure.
- Always use a circuit breaker or fuse on the main hot wire for fire safety.
- Color-coding helps distinguish between up and down traveler wire signals.
- Use this diagram when installing a new remote or replacing a faulty solenoid.
Navigating the electrical system of a heavy-duty piece of equipment can be a daunting task, but a clear hydraulic dump trailer wiring diagram is the ultimate roadmap to success. Whether you are building a new trailer from scratch, replacing an old pump, or troubleshooting a mysterious failure in the lifting mechanism, understanding how current flows from your battery to the hydraulic motor is essential. This comprehensive guide is designed to demystify the complex web of cables, solenoids, and switches. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough grasp of component functions, wire sizing requirements, and the step-by-step process required to ensure your dump trailer operates safely and reliably every time you hit the switch.
Most modern hydraulic dump trailers operate on a 12V DC system. While the colors of the wires may vary slightly by manufacturer, the fundamental logic of the circuit remains consistent: a high-amperage power circuit for the motor and a low-amperage control circuit for the remote.
Understanding the Core Components of the Wiring Diagram
A standard hydraulic dump trailer wiring diagram is divided into two primary circuits: the high-current power circuit and the low-current control circuit. To read the diagram effectively, you must first identify the key players. At the heart of the system is the 12V deep-cycle battery, which provides the necessary voltage to move heavy loads. From the battery, a heavy-duty hot wire (usually red) connects to the large common terminal on the starter solenoid. This solenoid acts as a high-capacity relay, allowing a small switch to control a massive amount of electrical energy without melting the switch or the operator’s hand.
The ground wire (usually black or green) is equally important. In many dump trailer setups, the pump motor is grounded directly back to the battery negative terminal to ensure maximum efficiency, although some systems use the trailer frame as a chassis ground. When examining the diagram, you will notice a series of smaller wires known as traveler wire sets. These wires run from the handheld remote control to the small trigger terminals on the solenoid. In a power-up/gravity-down system, you will have one traveler wire for the “up” function. In a power-up/power-down system, you will have two—one for each direction.
The solenoid itself often features a brass screw or specialized post for these smaller connections. These terminals receive the signal from the remote, closing the internal contactor and allowing the high-amperage current to reach the hydraulic pump motor. While “neutral wire” is a term more common in AC residential wiring, in the context of a DC trailer, it refers to the return path or the negative side of the control coil, which must be properly grounded for the solenoid to click into action.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A detailed visual schematic showing a 12V battery connected to a dual-terminal solenoid, leading to a hydraulic pump motor. The diagram includes a 3-wire remote control with labeled Up/Down buttons, a circuit breaker on the main positive line, and clear color-coding for Power (Red), Ground (Black), and Control (Blue/Yellow). Labels indicate the Gauge of wire (2 AWG for power, 14 AWG for control).]
Variations in these diagrams usually occur based on the type of pump. A single-acting pump (gravity down) requires fewer connections than a double-acting pump (power down). Furthermore, some diagrams may include a dedicated charging line from the tow vehicle (the 7-way plug), which uses a smaller gauge wire to provide a “trickle charge” to the trailer battery while driving. Understanding these distinctions is the first step in successful installation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Wiring Your Hydraulic Dump Trailer

Following a hydraulic dump trailer wiring diagram requires a methodical approach. Before you begin, gather the necessary tools and materials: a high-quality wire crimper, a multimeter to test voltage, heat-shrink tubing, and the correct gauge of wire. For the main power leads, anything less than 2 AWG or 4 AWG can lead to significant power loss and heat buildup. For the remote control and solenoid triggers, 14 AWG or 16 AWG is typically sufficient.
Always disconnect the battery terminals before starting any wiring work. A short circuit on a 12V high-amperage system can cause severe burns, fire, or battery explosion.
- Mount the Component Hardware: Secure the battery box, the hydraulic pump, and the solenoid housing to the trailer. Ensure they are protected from moisture and road debris.
- Install the Main Ground: Run a heavy gauge black wire from the negative terminal of the battery to the ground post on the hydraulic motor. If your pump relies on a chassis ground, ensure you scrape away any paint at the contact point to reveal bare metal for a solid connection.
- Connect the Main Power (Hot Wire): Run a red hot wire from the battery’s positive terminal to the common terminal on the solenoid. It is highly recommended to install a 150A to 200A manual reset circuit breaker along this line as close to the battery as possible.
- Wire the Solenoid to the Motor: Connect the output side of the solenoid to the power input on the hydraulic motor using the same heavy-duty wire used in the previous step. This is the path the electricity takes when the solenoid is activated.
- Set Up the Remote Control: Identify the three or four wires coming from your remote. Usually, one wire is the “hot” feed (connected to the battery side of the solenoid), and the others are the traveler wire leads that send signals to the “up” and “down” coils on the solenoid.
- Connect the Control Ground: Ensure the small ground wire (sometimes called the neutral wire in certain control sets) from the solenoid coil is attached to the negative terminal or the trailer frame. Without this, the solenoid’s magnetic field cannot be created.
- Attach Control Terminals: Use the brass screw terminals on the solenoid to secure the traveler wires from the remote. Tighten them firmly but avoid over-torquing, which can strip the threads or crack the solenoid housing.
- Test the System: Reconnect the battery. Use a multimeter to verify you have 12V at the main common terminal. Press the “up” button on the remote and listen for a distinct “click” from the solenoid followed by the motor humming.
When connecting wires to the solenoid, use tinned copper ring terminals and apply a small amount of dielectric grease. This prevents corrosion, which is the leading cause of electrical failure in dump trailers exposed to the elements.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting

Even with a perfect hydraulic dump trailer wiring diagram, issues can arise over time. The most frequent complaint is a “clicking” sound without the motor turning. This usually indicates that the voltage is dropping too low under load, or there is a poor connection at the common terminal. Use your multimeter to check the battery voltage; if it reads below 12.4V at rest, the battery likely needs a charge.
Another common problem is the motor running but the trailer failing to lift. This is often a hydraulic issue, but electrically, it could mean the “down” solenoid is stuck open. If the remote buttons seem reversed, you simply need to swap the traveler wire positions on the solenoid terminals. Watch out for frayed insulation on the hot wire where it passes through the trailer frame; a short here will trip your circuit breaker or, worse, cause a fire. If you see signs of melting plastic or smell ozone, stop operation immediately and inspect all high-current paths.
- ✓ Check for loose brass screw connections on the solenoid.
- ✓ Inspect the ground wire for corrosion at the frame attachment point.
- ✓ Verify the 7-way plug is actually charging the battery while the truck is running.
Tips & Best Practices for Wiring Longevity
To ensure your dump trailer remains functional for years, go beyond the basic hydraulic dump trailer wiring diagram and implement some professional-grade upgrades. First, always use marine-grade, multi-strand copper wire. This type of wire is more flexible and resistant to the constant vibration of road travel. Avoid using solid-core wire, as it will eventually fatigue and snap inside the insulation.
Second, prioritize wire management. Use plastic loom or conduit to protect your hot wire and traveler wire bundles. Secure these to the frame using rubber-lined P-clamps rather than cheap plastic zip ties, which can become brittle and break in cold weather. Ensure that any wire crossing a hinge point has a generous “drip loop” to allow for movement without tension.
Maintenance is also key. Every six months, open the pump box and check the voltage levels. Clean the battery terminals with a wire brush and reapply protective spray. If you notice the brass screw terminals on your solenoid starting to turn green, clean them immediately. Corrosion acts as a resistor, generating heat and reducing the power available to your pump motor. Finally, if you find that your battery dies frequently, consider adding a small solar maintainer to the top of the pump box to keep the charge topped off during periods of inactivity. By following these best practices and keeping a copy of your wiring diagram handy, you can ensure that your hydraulic dump trailer is always ready for the next big haul.
In summary, mastering your hydraulic dump trailer wiring diagram is about understanding the relationship between the 12V power source, the solenoid gatekeeper, and the hydraulic motor. By using the correct gauge of wire, securing your common terminal, and properly routing every traveler wire, you create a system that is both powerful and safe. Proper electrical installation is the foundation of trailer reliability, saving you time and money on future repairs while ensuring peak performance on the job site.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a hydraulic dump trailer wiring diagram?
A hydraulic dump trailer wiring diagram is a visual map showing how electrical components like the battery, solenoid, and remote switch connect to the hydraulic pump. It guides users in identifying the hot wire and ground wire locations to ensure the trailer lifts and lowers safely without short-circuiting the electrical system.
How do you read a hydraulic dump trailer wiring diagram?
To read the diagram, start at the power source and follow the hot wire to the common terminal on the solenoid. Trace lines representing the traveler wire to see how signals move from the remote to the motor. Identify symbols for switches, fuses, and grounds to understand electricity flow.
What are the parts of a hydraulic dump trailer?
The main electrical parts include the 12V battery, a high-amperage solenoid, the hydraulic pump motor, a remote control pendant, and various fuses. The system relies on a thick ground wire for stability and a specific traveler wire to signal the ‘up’ or ‘down’ functions of the hydraulic valves.
Why is the common terminal important?
The common terminal acts as the central junction point for power distribution within the control circuit. It typically links the main power supply to the remote switch, allowing the user to redirect current through the traveler wire to activate the solenoid, which ultimately engages the high-draw hydraulic pump motor safely.
What is the difference between the hot wire and the traveler wire?
The hot wire provides continuous 12V power from the battery to the control system or solenoid. In contrast, the traveler wire only carries current when the remote button is pressed, sending a signal to either lift or lower the trailer. Both are vital for the hydraulic system to function properly.
How do I use a hydraulic dump trailer wiring diagram?
Use the diagram to troubleshoot electrical failures by testing continuity along specific paths. Start by verifying the ground wire connection, then check for power at the hot wire. If the remote fails, use the schematic to locate the traveler wire and common terminal to isolate where the signal is breaking.