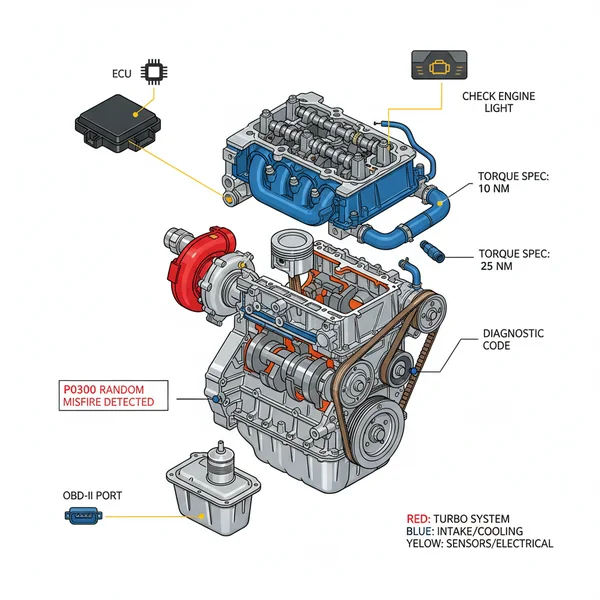
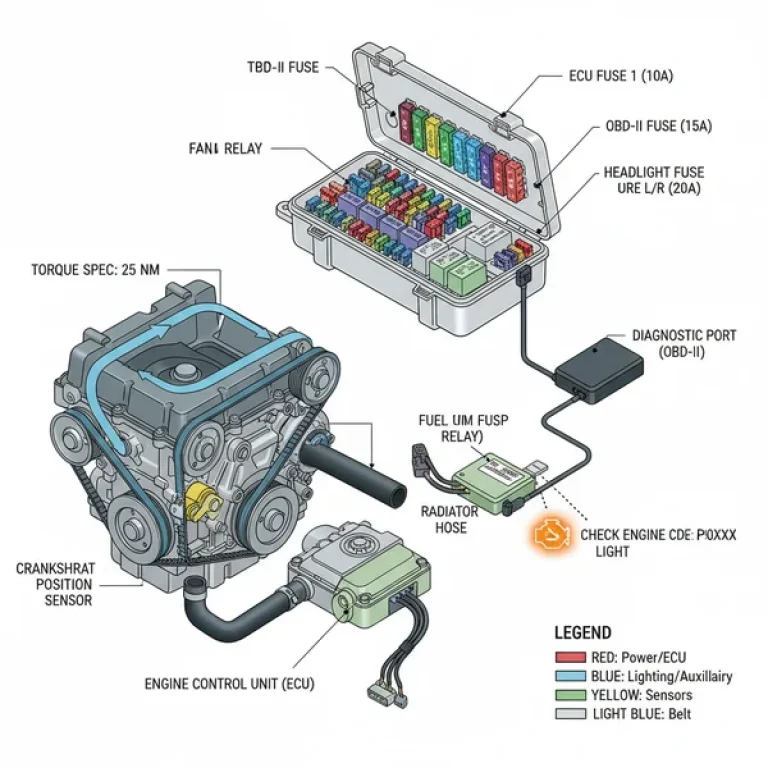
Honda 1.5 Turbo Engine Diagram: Component Identification
A Honda 1.5 Turbo engine diagram illustrates the layout of internal components, vacuum lines, and electrical sensors. It helps owners locate parts like the turbocharger and ECU. By referencing these visuals, you can accurately troubleshoot a check engine light or ensure every bolt meets the proper torque spec during repairs.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Visualizing the layout of the L15B7 and L15BE series turbocharging systems.
- Identifying the ECU and its role in monitoring engine performance.
- Ensuring critical fasteners are tightened to the factory torque spec.
- Connecting an OBD-II scanner to read any stored diagnostic code.
- Using the diagram to locate sensors causing a check engine light.
Navigating the complexities of a modern Earth Dreams powerplant requires more than just a basic understanding of internal combustion; it demands a precise visual reference. Whether you are performing a routine spark plug replacement on a Civic or diagnosing a boost leak on a CR-V, having a reliable honda 1.5 turbo engine diagram is the cornerstone of a successful repair. This guide is designed to bridge the gap between amateur curiosity and professional execution. By providing a clear breakdown of the engine’s architecture, we help you identify critical sensors, fluid paths, and mechanical linkages. In the following sections, you will learn how to interpret the layout of this sophisticated direct-injection system, understand the vital role of electronic controls, and gain the confidence to maintain your vehicle’s peak performance through accurate visual mapping.
Understanding the L-Series Turbocharged Layout
The Honda 1.5L Turbo engine, often referred to by its engine codes such as the L15B7 or L15BE, is a marvel of downsized displacement and forced induction. When looking at a comprehensive diagram of this engine, the first thing you will notice is the “front-facing” turbocharger configuration. Unlike older naturally aspirated designs where the exhaust manifold sits tucked against the firewall, the 1.5T positions the turbocharger and integrated exhaust manifold at the front of the engine bay, close to the radiator. This allows for shorter piping to the intercooler, which reduces turbo lag and improves throttle response.
The diagram typically highlights several key subsystems. First is the air induction path, which tracks air from the intake box through the turbocharger, down to the front-mounted intercooler, and finally into the intake manifold. Second is the high-pressure fuel system. Because this is a direct-injection engine, the diagram will show a mechanical fuel pump driven by the camshaft, feeding fuel directly into the combustion chamber rather than the intake ports. Furthermore, the honda 1.5 turbo engine diagram will illustrate the intricate coolant flow paths that manage heat for both the engine block and the turbo’s center housing rotating assembly (CHRA). This dual-cooling approach is vital for preventing oil coking after the engine is shut down.
Most diagrams use color-coding to differentiate systems: Blue for the cooling system, Red for high-heat exhaust/turbo zones, and Yellow or Orange for electrical/sensor pathways. Always verify your specific engine code (found on a metal plate near the transmission bellhousing) before ordering parts based on a diagram.
graph TD
A[Air Intake] --> B[Turbocharger]
B --> C[Intercooler]
C --> D[Throttle Body]
D --> E[Intake Manifold]
E --> F[Combustion Chamber]
G[Mechanical Fuel Pump] --> F
H[ECU] --> I[Wastegate Actuator]
H --> J[Direct Injectors]
K[Coolant Pump] --> L[Turbo Cooling]
K --> M[Engine Block]
N[Timing Chain] --> O[Camshafts]
How to Read and Apply the Engine Diagram

Interpreting a honda 1.5 turbo engine diagram is a skill that saves hours of frustration. To use these visual tools effectively, follow this structured approach to navigate your engine bay like a professional technician.
Step 1: Establish Your Orientation
Before touching a wrench, identify the “front” of the engine. In a transverse-mounted Honda 1.5T, the “front” of the engine (where the accessory belt is located) is usually on the passenger side of the vehicle. The “rear” of the engine is where it connects to the transmission on the driver’s side. Your diagram will usually specify if the view is “Front Elevation,” “Top Down,” or “Exploded View.”
Step 2: Locate the ECU and Electrical Hubs
The ECU (Engine Control Unit) acts as the brain of the operation. On the diagram, trace the wiring harnesses leading away from the ECU to various sensors like the MAF (Mass Air Flow) and MAP (Manifold Absolute Pressure). This is crucial when you are dealing with a check engine light. Understanding where these sensors live allows you to quickly inspect for loose connections or frayed wires before replacing expensive components.
Step 3: Identify the OBD-II Linkage
While the OBD-II port is located inside the cabin (usually under the driver-side dashboard), its logical connection in the diagram leads directly to the ECU. When you pull a diagnostic code, use the diagram to find the physical component associated with that code. For example, if you receive a code for “Turbocharger Boost Sensor A Circuit,” the diagram will show you exactly which sensor on the charge pipe needs your attention.
Step 4: Trace the Drive System
Locate the accessory belt (serpentine belt) routing. This engine uses a single belt to drive the alternator and A/C compressor. The diagram will show the specific path the belt must take around the tensioner and idler pulleys. This is one of the most common “DIY” mistakes; without the diagram, it is very easy to loop the belt incorrectly, leading to reversed pulley rotation or belt failure.
Unlike older Honda engines that used a rubber timing belt, the 1.5 Turbo utilizes a timing chain. The timing chain is an internal component and is not visible without removing the side timing cover. Never attempt to adjust the timing chain without the specific factory service manual and proper timing alignment tools.
Step 5: Reference Torque Specifications
A good diagram or its accompanying data sheet will provide the torque spec for critical fasteners. For the 1.5T, pay special attention to the spark plug torque (typically around 13 lb-ft) and the oil drain plug (30 lb-ft). Because this engine uses an aluminum block, over-tightening bolts can easily strip threads, leading to incredibly costly repairs. Always use a calibrated torque wrench for any internal or high-pressure fuel system components.
Step 6: Analyze the Cooling Circuit
The coolant flow in a turbocharged engine is more complex than in a standard engine. The diagram will show the primary loop for the radiator and the secondary loop for the turbocharger. When bleeding the system after a flush, knowing the highest point in the diagram (usually the bleeder valve or the expansion tank) ensures you remove all air pockets that could cause localized overheating near the cylinder head.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting

Even with Honda’s reputation for reliability, the 1.5 Turbo engine has specific areas that require monitoring. Using your diagram, you can pinpoint where these issues typically arise. One common problem is “oil dilution,” where fuel makes its way past the piston rings into the oil pan. By referencing the high-pressure fuel pump and injector locations on your honda 1.5 turbo engine diagram, you can understand how the direct injection process works and why short trips in cold weather contribute to this issue.
Another frequent concern is the “limp mode” triggered by a check engine light. This often relates to the electronic wastegate actuator on the turbo. The diagram helps you locate this actuator to check for physical binding or electrical corrosion. If you encounter a diagnostic code such as P0299 (Underboost), use the diagram to inspect every junction in the intercooler piping for a loose clamp or a cracked rubber boot. Identifying a small air leak visually is much cheaper than replacing a turbocharger prematurely.
If you’re troubleshooting a rough idle, focus on the “Intake Side” of your diagram. Check the PCV (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) valve and the MAP sensor. Carbon buildup on the intake valves is a common trait of direct-injection engines; periodic cleaning can prevent the diagnostic codes associated with misfires.
Maintenance Tips and Best Practices
To keep your 1.5 Turbo running for hundreds of thousands of miles, follow these maintenance best practices derived from professional mechanical standards. The complexity of the ECU and sensitive turbo components means that preventative care is much more cost-effective than reactive repairs.
- ✓ Use High-Quality Full Synthetic Oil: The turbocharger spins at over 150,000 RPM. Only 0W-20 full synthetic oil (specifically API SN PLUS or SP rated) should be used to prevent low-speed pre-ignition (LSPI) and protect the timing chain from premature wear.
- ✓ Monitor the Accessory Belt: Inspect the belt for cracks every 30,000 miles. A snapped accessory belt on this engine will result in immediate loss of cooling and charging, potentially overheating the engine in minutes.
- ✓ Keep the Air Filter Clean: A clogged filter makes the turbo work harder to pull air, increasing heat and reducing efficiency. It’s the cheapest way to ensure your honda 1.5 turbo engine diagram remains a reference for maintenance rather than a roadmap for repair.
- ✓ Check OBD-II Regularly: Even if there is no check engine light, scanning for “pending codes” can give you an early warning of sensor degradation or fuel trim issues.
Finally, always respect the torque spec for every bolt you touch. The L-series engine uses many “one-time use” stretch bolts, particularly in the suspension and internal engine components. If your diagram indicates a bolt is “torque-to-yield,” do not reuse it. Investing in a high-quality set of tools and a digital OBD-II scanner will pay for itself within the first two DIY oil changes and inspections. By combining the visual clarity of a honda 1.5 turbo engine diagram with disciplined maintenance habits, you ensure that your Honda remains the reliable, efficient, and spirited vehicle it was engineered to be.
In conclusion, the Honda 1.5 Turbo engine is a sophisticated piece of machinery that rewards those who take the time to understand its layout. From tracing the coolant flow to ensuring the accessory belt is properly seated, the diagram is your most valuable tool in the garage. Stay proactive, follow the manufacturer’s specifications, and use the visual data provided to keep your engine running at its peak potential for years to come.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the Honda 1.5 Turbo Engine Diagram: Component Identification
Identify the main engine architecture by locating the turbocharger and intake assembly.
Locate the ECU and the primary sensor clusters within the engine compartment.
Understand how the air and fuel systems interact based on the flow lines.
Connect an OBD-II scanner to the vehicle to retrieve any active diagnostic code.
Verify that every component is properly seated and the check engine light is cleared.
Complete the assembly by tightening all bolts to the manufacturer’s specified torque spec.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Honda 1.5 Turbo engine diagram?
A Honda 1.5 Turbo engine diagram is a visual map showing the placement of mechanical and electrical parts. It displays how the turbocharger, intake manifold, and sensors interact. This tool is essential for DIY mechanics to locate specific components like the ECU or vacuum hoses when performing routine repairs.
How do you read a Honda 1.5 Turbo engine diagram?
Begin by identifying the front of the engine, usually where the drive belts are located. Follow the flow of air from the intake to the turbocharger and into the cylinders. Use the legend to decode symbols for electrical connectors, fluid lines, and sensors monitored by the vehicle’s ECU system.
What are the parts of a Honda 1.5 Turbo engine?
Major parts include the direct-injection fuel system, variable valve timing, a single-scroll turbocharger, and an intercooler. Electronic components like the ECU manage these systems. Support parts include the wastegate actuator, blow-off valve, and various sensors that interface with the OBD-II port to provide real-time engine data for mechanics.
Why is the ECU component important?
The ECU acts as the brain of the engine, constantly adjusting fuel trim, ignition timing, and boost pressure. It receives data from numerous sensors to optimize efficiency. If it detects a fault, it triggers a check engine light and stores a diagnostic code for the technician to retrieve and analyze.
What is the difference between an engine diagram and a wiring schematic?
An engine diagram focuses on the physical location and spatial relationship of mechanical parts within the engine bay. A wiring schematic details the electrical paths between the ECU and various sensors. Both are necessary for diagnosing electrical issues that lead to a triggered check engine light or poor vehicle performance.
How do I use a Honda 1.5 Turbo engine diagram?
Use the diagram to identify the specific location of a part mentioned in a diagnostic code. Once located, you can inspect the component for damage or loose connections. Always refer to the diagram to find the correct torque spec for fasteners when reassembling engine components after a repair.