Freightliner Cascadia Fuse Box Diagram: Troubleshooting Guide
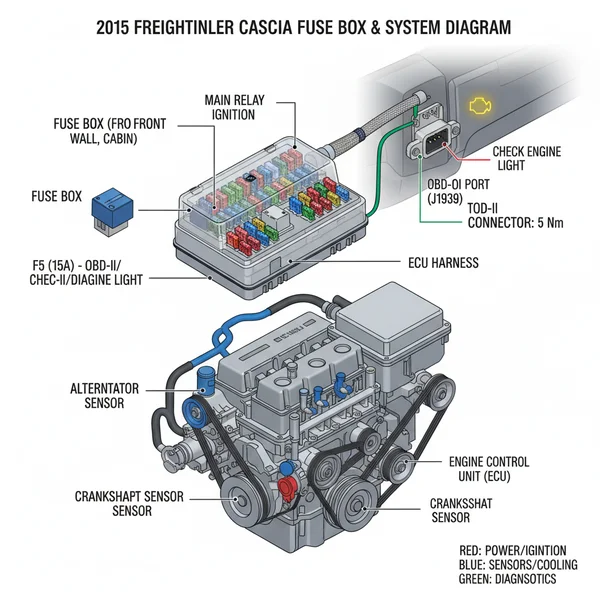
The Freightliner Cascadia fuse box, or Power Distribution Center (PDC), is primarily located in the dashboard on the passenger side. This diagram identifies circuits for the ECU and lights. Using it helps resolve a check engine light and diagnostic code issues by ensuring power reaches the OBD-II diagnostic systems and communication modules.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides exact locations for all interior and exterior fuses
- The ECU fuse is the most critical component for engine starts
- Disconnect battery power before replacing high-amperage fuses
- Essential for powering the OBD-II port during diagnostics
- Helps identify the source of ghost check engine lights
Navigating the electrical architecture of a Class 8 truck requires precision, and the 2015 Freightliner Cascadia fuse box diagram is the essential roadmap for any owner-operator or fleet technician. Whether you are dealing with a sudden loss of lighting, a malfunctioning sensor, or a communication error with the ECU, understanding where your fuses and relays are located is the first step in effective troubleshooting. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the Power Distribution Center (PDC) and the Signal Detect and Actuation Modules (SAM), helping you minimize downtime. You will learn how to locate specific circuits, interpret the diagram legend, and use these components to clear diagnostic codes or address a stubborn check engine light.
The 2015 Freightliner Cascadia utilizes a sophisticated modular electrical system, primarily managed by the SAM Cab and SAM Chassis modules. Unlike older trucks with a single centralized fuse panel, the Cascadia splits its electrical load to improve efficiency and simplify the wiring harness. The primary fuse boxes are categorized into two main locations: the interior SAM Cab (located behind the passenger-side dashboard panel) and the exterior SAM Chassis (located on the driver-side firewall or under the hood area). The 2015 freightliner cascadia fuse box diagram typically uses an alpha-numeric grid system (e.g., F1, R2) to help users identify specific fuses and relays.
Most Cascadia models also feature a high-current “Mega-Fuse” block located near the battery box. These fuses protect major systems like the alternator and the starter motor. Always check these first if the truck has no power at all.
The diagram itself consists of several clusters. The SAM Cab module contains fuses for the instrument cluster, HVAC, interior lighting, and the OBD-II diagnostic port. The SAM Chassis module focuses on exterior elements, such as headlights, turn signals, and the ABS system. Each fuse is color-coded by amperage: red for 10A, blue for 15A, yellow for 20A, and clear/white for 25A. If you are looking at the physical board, you will see integrated relays alongside these fuses, which act as remote switches for high-draw components like the engine cooling fan or the fuel heater.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: 2015 Freightliner Cascadia Fuse Box Map – SAM Cab and SAM Chassis Layout]
Never replace a fuse with one of a higher amperage rating. Doing so can cause the wiring harness to overheat, potentially leading to an electrical fire or permanent damage to the ECU.
To effectively use the 2015 freightliner cascadia fuse box diagram, follow these structured steps to diagnose and repair electrical faults safely:
- ✓ 1. Locate the SAM Cab: Open the passenger door and remove the dash panel cover located directly in front of the passenger seat. You will see a large module with dozens of fuses and several multi-pin connectors.
- ✓ 2. Locate the SAM Chassis: Open the hood and look at the driver-side firewall. The chassis fuse box is protected by a weather-sealed plastic cover. Ensure the seals are intact to prevent moisture intrusion.
- ✓ 3. Identify the Faulty Circuit: Refer to the diagram printed on the inside of the fuse box cover or your digital manual. If your check engine light is on, look specifically for fuses labeled “Engine Control,” “EMS,” or “ECU Power.”
- ✓ 4. Connect an OBD-II Scanner: Before pulling fuses, plug a diagnostic tool into the OBD-II port. This may provide a specific diagnostic code that points you toward a particular circuit, such as a fuel injector or an oxygen sensor.
- ✓ 5. Test with a Multimeter: Set your multimeter to the DC Voltage setting. Touch the probes to the small metal test points on top of the fuse. If you have voltage on one side but not the other, the fuse is blown.
- ✓ 6. Inspect High-Current Circuits: For issues like the engine not cranking, inspect the battery power distribution block. Check the torque spec on the terminal nuts; loose connections can mimic a blown fuse and cause intermittent power loss.
- ✓ 7. Reset the System: After replacing a fuse, turn the ignition to the “On” position for 30 seconds before cranking. This allows the ECU to cycle and clear temporary faults related to the circuit interruption.
When working with these components, keep in mind that the 2015 Cascadia is heavily reliant on CAN-bus communication. This means that a problem in one area, like a corroded accessory belt pulley sensor or a faulty coolant flow sensor, can send ripple effects throughout the electrical system. Always ensure your batteries are at full charge, as low voltage can trigger “ghost” diagnostic codes that suggest fuse issues when none exist.
One of the most frequent problems users encounter with the 2015 Freightliner Cascadia is the “No Communication” error with the ECU. This is often caused by a blown fuse in the SAM Cab or the battery-mounted power distribution box. If your check engine light is illuminated but your scanner cannot pull a diagnostic code, the fuse powering the OBD-II port or the data link itself is likely the culprit.
Another common issue involves moisture in the SAM Chassis. Because this module is located in the engine bay, it is susceptible to road salt and water. If you notice erratic behavior in your exterior lights or trailer power, inspect the fuse box for green corrosion on the pins. This corrosion can bridge circuits, causing fuses to blow repeatedly. If a fuse blows immediately after replacement, do not keep replacing it. This indicates a hard short to ground, often found in the wiring harness near moving parts like the accessory belt or areas with high vibration.
Keep a small packet of dielectric grease in your tool kit. Applying a thin layer to the pins of new fuses and relays helps prevent oxidation and ensures a solid electrical connection, especially in the SAM Chassis module.
Maintaining the electrical health of your 2015 Freightliner Cascadia goes beyond just swapping fuses. Regular inspections of the entire power system are recommended. Every 50,000 miles, check the tension and condition of your accessory belt. A slipping belt can cause the alternator to output inconsistent voltage, which stresses the fuses and can lead to premature failure of sensitive electronics. Additionally, monitor your coolant flow and temperature sensors. These sensors are vital for the ECU to manage engine timing; a blown fuse in these circuits can force the truck into “limp mode” to prevent engine damage.
While the Cascadia uses a gear-driven timing system rather than a timing chain, the electronic synchronization of the camshaft and crankshaft is still handled by sensors that rely on the SAM modules. Ensuring these circuits are clean and properly fused is critical for engine performance. For cost-saving, always carry a dedicated “trucker’s fuse kit” that includes the specific Mini-ATC and Maxi fuses used by Freightliner. Purchasing these in bulk is significantly cheaper than buying them at a truck stop during an emergency. If you find yourself frequently replacing fuses for the same circuit, invest in a professional circuit tracer to find the wire rub-through before it leads to a more expensive ECU failure. By following the 2015 freightliner cascadia fuse box diagram and maintaining a proactive approach to electrical health, you can ensure your truck remains reliable for the long haul.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the Freightliner Cascadia Fuse Box Diagram: Troubleshooting Guide
Identify the symptom and the corresponding circuit using the diagram’s legend.
Locate the passenger-side dashboard panel or the engine compartment PDC depending on the circuit.
Understand how the amperage ratings correlate to the specific colors of the fuses provided.
Connect a diagnostic scanner to the OBD-II port if a check engine light is present.
Verify that the fuse for the ECU is intact and seated properly within the terminal.
Complete the repair by replacing any blown fuses and clearing any stored diagnostic code.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Freightliner Cascadia fuse box diagram?
A Freightliner Cascadia fuse box diagram is a visual map showing the location, function, and amperage of electrical fuses and relays within the vehicle. It helps technicians identify which circuit is responsible for specific components, allowing for efficient troubleshooting of electrical failures like a persistent check engine light or sensor issues.
How do you read a Freightliner Cascadia fuse box diagram?
To read the diagram, match the numbered slots on the physical fuse panel with the corresponding numbers on the chart. Each entry lists the fuse’s purpose, such as the ECU or cabin lighting, and its required amperage. This ensures you replace blown fuses with the correct rating to prevent wiring damage.
What are the parts of the Freightliner Cascadia electrical system?
The system includes the Power Distribution Center (PDC), which houses fuses and relays, the engine control unit (ECU) for management, and various wiring harnesses. It also features the OBD-II port for diagnostics. Understanding these parts allows you to trace power flow from the main battery source to individual electronic components.
Why is the ECU fuse important?
The ECU fuse is critical because it provides power to the vehicle’s computer system. If this fuse blows, the engine may fail to start or produce a diagnostic code related to communication loss. Ensuring this fuse is functional is the first step when the truck experiences significant engine management power-loss issues.
What is the difference between a fuse and a relay?
A fuse is a safety device that breaks the circuit if the current becomes too high, protecting wiring from melting. A relay is an electromagnetic switch that allows a low-current signal to control a high-current circuit. Both are essential components found within the Freightliner Cascadia main fuse box assembly for protection.
How do I use this fuse box diagram?
Use the diagram to locate the specific fuse associated with your symptom, such as a dead OBD-II port. Once identified, pull the fuse to check for a broken internal filament. If you must remove the housing, ensure you follow the manufacturer’s torque spec when reattaching any main terminal bolts.