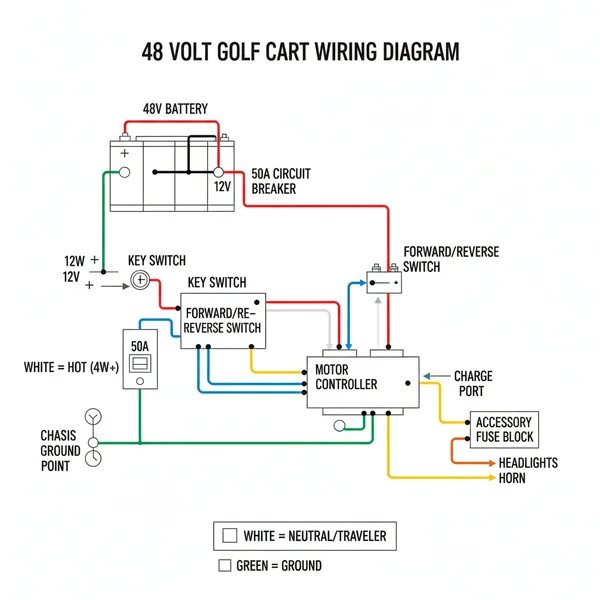
48 Volt Golf Cart Wiring Diagram: Connection Guide
A 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram shows how batteries connect in series to power the motor controller. It tracks current through the hot wire to the solenoid and identifies the ground wire return path. Understanding the common terminal and traveler wire locations ensures accessories like lights function correctly within the circuit.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Illustrates the electrical flow from the battery series to the motor controller
- The solenoid and controller are the most critical components to identify
- Always disconnect the main negative ground wire before performing maintenance
- Use the diagram to trace the traveler wire for accessory or reverse switches
- Consult this diagram when upgrading batteries or troubleshooting power loss
When you are working with a high-performance vehicle like a modern electric cart, having an accurate 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram is more than just a convenience; it is a critical safety requirement. Whether you are performing a total restoration, upgrading your motor, or simply replacing old battery cables, understanding the flow of electricity ensures you don’t accidentally damage expensive components like the controller or the solenoid. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the wiring architecture, explaining how high-voltage energy moves from your battery bank to the motor. By the end of this article, you will have the knowledge needed to identify every major wire, understand the specific gauge requirements for safety, and troubleshoot common electrical failures that plague many cart owners.
The architecture of a 48V system is centered around the battery bank, the solenoid, the motor controller, and the motor itself. Unlike lower-voltage systems, a 48V setup requires precise coordination between these parts to manage the increased energy load. The primary components in the diagram include the battery series strings, which are connected via heavy-duty cables. Depending on your cart’s configuration, you may see six 8-volt batteries, four 12-volt batteries, or eight 6-volt batteries. The diagram visually maps the “series” connection, where the positive terminal of one battery connects to the negative terminal of the next, effectively stacking the voltage until the total reaches 48V.
In a 48V system, the main “Hot Wire” is the positive lead coming from the last battery in the series, while the “Ground Wire” (or common negative) returns to the first battery in the series. Proper labeling of these ends is vital to prevent short circuits.
The diagram also highlights the solenoid, which acts as a heavy-duty relay. It features large studs, often secured with a brass screw or nut, which handle the main power transfer. Small-gauge wires, sometimes referred to as signal or traveler wire sets, connect the solenoid to the key switch and pedal microswitch. These low-current wires “tell” the solenoid when to click shut and allow the 48V current to flow to the controller. The motor controller then acts as a gatekeeper, regulating the voltage sent to the motor based on how far you depress the accelerator. Visualizing this flow helps you distinguish between high-current paths (thick cables) and low-current signal paths (thin wires).
Always disconnect the main negative and main positive cables from the battery bank before touching any wiring. 48 volts can cause severe arching and permanent damage to both you and the cart’s electronics if accidentally shorted.
To successfully implement the layout shown in a 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram, follow these structured steps to ensure a clean and safe installation.
- 1. Prepare Your Workspace and Tools: Gather high-quality copper cables, typically 4-gauge or 6-gauge depending on your motor’s requirements. You will need a digital multimeter to verify voltage, insulated wrenches to prevent shorts, and wire brushes to clean every common terminal. Ensure the cart is on a level surface with the tow/run switch set to “Tow” to de-energize the controller.
- 2. Map the Battery Series: Place your batteries in the trays according to the diagram. Connect the negative terminal of the first battery to the positive of the second, and continue this pattern. In a 48V system, this “daisy chain” is what creates the total potential energy. Use a brass screw or high-quality terminal bolt to ensure a tight, corrosion-resistant connection.
- 3. Install the Main Hot Wire: Run the heavy-gauge red cable from the final positive terminal of the battery bank to one side of the large solenoid post. This is the main power supply. From the other side of the solenoid, a cable will travel to the “B+” terminal on the motor controller.
- 4. Establish the Common Ground: Run the heavy-gauge black ground wire from the “B-” terminal on the controller back to the main negative terminal of the first battery in the series. This completes the high-current loop. For accessory circuits, treat this as the neutral wire equivalent to ensure all 12V converters have a stable return path.
- 5. Wire the Control Circuit: This is where the traveler wire logic comes into play. Connect the small wires from the key switch and the throttle sensor to the small terminals on the solenoid and the logic ports on the controller. These wires carry very little amperage but are essential for signaling the cart to move.
- 6. Connect the Motor Leads: Finally, connect the A1, A2, S1, and S2 (or U, V, W for AC motors) terminals from the controller to the motor. These cables must be of the same heavy gauge as your battery cables, as they carry the full load required to turn the wheels.
- 7. Final Verification: Use your multimeter to check the total voltage at the solenoid. It should read approximately 48V to 51V depending on the charge state. Double-check that no wires are touching the frame or moving parts of the suspension.
Even with a perfect 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram, issues can arise due to vibration, moisture, and heat. One of the most frequent problems is the “clicking” solenoid that doesn’t result in movement. This usually indicates that while the signal traveler wire is working, the high-current hot wire or the solenoid internal contacts have failed. Another common issue is a significant voltage drop under load, which often points to a corroded common terminal or an undersized wire gauge that is creating too much resistance.
Look for melted insulation or “discolored” copper near the battery terminals; this is a clear sign of a loose connection causing heat buildup. If your cart moves slowly or “shudders,” the controller may not be receiving a clean signal from the throttle, or the ground wire return may be compromised. If you detect a smell of ozone or burning plastic, immediately turn the key off and disconnect the batteries. While many wiring issues are simple fixes, if you find that the motor controller itself has internal shorts, it is usually best to seek professional repair to avoid a catastrophic lithium or lead-acid battery fire.
When replacing cables, always upgrade to a 4-gauge wire even if your cart came with 6-gauge. The thicker wire reduces resistance, meaning less heat and more torque for climbing hills or carrying heavy loads.
To keep your 48V system running at peak efficiency, follow a strict maintenance schedule. Every few months, inspect the brass screw terminals on your batteries and solenoid for any signs of green or white oxidation. A simple mixture of baking soda and water can neutralize acid spray, followed by a coat of terminal protector spray to seal out moisture. Consistency is key; a single loose nut on a battery post can lead to a melted terminal and a ruined battery in a matter of minutes.
When purchasing replacement parts, avoid “economy” grade wiring kits. Look for “high-strand-count” copper cables which offer better flexibility and surface area for electron flow. Ensure your lugs are hydraulically crimped rather than just smashed with a hammer; a poor crimp is a leading cause of intermittent power loss. If you are adding accessories like LED lights or a soundbar, never tap into just two batteries to get 16V or 12V. This creates an imbalance in the battery bank. Instead, use a dedicated 48V-to-12V voltage reducer. This device connects to the main hot wire and the common ground, providing a stable 12V output for your accessories while keeping the 48V bank perfectly balanced. By following your 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram precisely and utilizing these best practices, you ensure a longer lifespan for your batteries and a more reliable ride for years to come.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the 48 Volt Golf Cart Wiring Diagram: Connection Guide
Identify the battery layout to determine if your system uses six 8-volt or four 12-volt batteries.
Locate the main positive hot wire that connects the battery bank to the solenoid and controller.
Understand how the traveler wire routes signals between the forward/reverse switch and the motor controller.
Connect the common terminal on the solenoid to ensure power is distributed correctly to the motor.
Verify that the ground wire is securely attached to the main negative terminal to complete the circuit.
Complete the installation by checking all accessory wires, including the neutral wire, for proper seating and insulation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram?
A 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram is a visual map of the electrical system’s power and signal paths. It details the series connections between batteries, the motor, and the controller. By following the diagram, users can safely identify the hot wire and ground wire paths, ensuring the vehicle operates at the correct voltage levels.
How do you read 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram?
Reading this diagram requires identifying the symbols for batteries, switches, and the motor. Look for lines representing the hot wire carrying current and the ground wire completing the circuit. Locate specific components like the common terminal on the key switch or solenoid to understand how power is distributed throughout the entire golf cart system.
What are the parts of 48 volt golf cart?
The main parts include the battery bank (usually six 8V units), the motor, the controller, and the solenoid. Additionally, the wiring harness consists of a hot wire for power, a neutral wire or ground for the return, and a traveler wire for multi-switch functions like the forward and reverse gear selector or light kits.
Why is hot wire important?
The hot wire is essential because it carries the high-voltage electrical load from the battery pack to the motor controller and other active components. Without a properly sized and secured hot wire, the cart will experience voltage drops, power loss, or even electrical fires, making its placement in the wiring diagram a critical safety concern.
What is the difference between 36V and 48V?
The primary difference lies in the battery configuration and power delivery. A 48V system uses higher voltage to provide more torque and better efficiency than a 36V system. While both use a ground wire for safety, the 48V wiring diagram must account for more batteries in series and specialized solenoids that handle the increased electrical pressure.
How do I use 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram?
Use the diagram to troubleshoot electrical failures by tracing paths from the common terminal of the ignition switch to the motor. By identifying the traveler wire in accessory circuits or the neutral wire in the charging system, you can isolate faults, replace damaged components safely, and ensure all connections match the manufacturer’s original specifications.