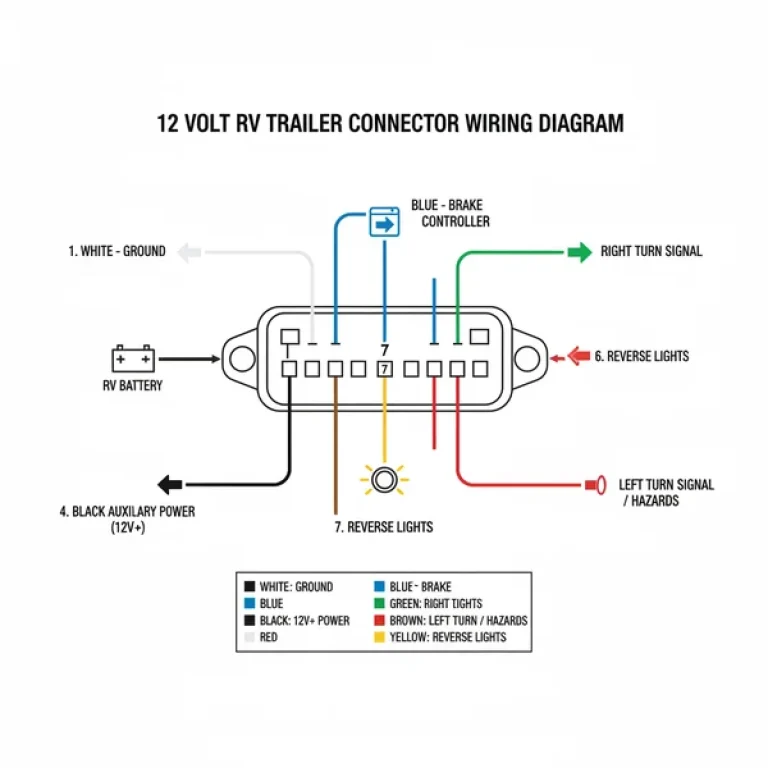
Wiring Diagram RV Battery Hook Up Picture: Installation Guide
An RV battery wiring diagram illustrates how to connect deep-cycle batteries in series or parallel to power your coach. It identifies the positive hot wire, negative ground wire, and neutral wire connections. Proper identification of the common terminal ensures efficient charging and power distribution through your vehicle’s electrical system and inverter components.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Visualize the safe configuration of RV battery banks for reliable off-grid power.
- Identify the main battery terminals and fuse locations to prevent short circuits.
- Always connect the ground wire last to ensure maximum safety during the installation process.
- Use high-gauge cabling to handle heavy electrical loads from the inverter and converter.
- Refer to this diagram when replacing old batteries or adding solar charging capabilities.
Understanding how to properly configure your house power starts with a clear wiring diagram RV battery hook up picture. Whether you are upgrading to a lithium-ion system, adding a second battery for extended boondocking, or simply replacing old lead-acid cells, the way you bridge your power source determines the efficiency and safety of your entire coach. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down the complexities of DC electrical systems, explore the differences between series and parallel configurations, and provide the technical specifications needed to ensure your lights, pumps, and appliances stay powered. You will learn about wire thickness, terminal connections, and how to integrate your battery bank into the larger RV electrical grid without risking a short circuit or fire.
Deconstructing the RV Battery Wiring Diagram
A wiring diagram RV battery hook up picture serves as a roadmap for the flow of direct current (DC) electricity. At its most basic level, the diagram illustrates how multiple batteries are interconnected to create a single cohesive power bank. There are two primary ways to arrange these batteries: parallel and series. In a parallel setup, the positive terminals are connected to positive, and negative to negative. This maintains the same voltage—usually 12 volts—while doubling the amp-hour capacity. In a series setup, the positive terminal of one battery connects to the negative of the next, doubling the voltage (converting two 6-volt batteries into a 12-volt system) while keeping the capacity the same.
The diagram also highlights the common terminal points where the house loads connect. In a professional setup, the main positive cable (often referred to as the hot wire in generalized terms, though technically the positive DC lead) and the main ground wire should be pulled from opposite corners of the battery bank. This ensures an even draw across all cells, preventing one battery from wearing out faster than the others. Labels in a standard diagram will also indicate the specific gauge of the wire required. High-draw components like an inverter require a significantly thicker gauge than small LED lighting circuits to prevent resistance-based heat buildup.
When looking at a wiring diagram, always identify the “Common Terminal” on your battery selector switch. This is the point where power is distributed to the RV’s fuse panel. Incorrectly landing a wire on the wrong terminal can bypass your master shut-off, leading to phantom parasitic draws that can kill your batteries during storage.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A detailed technical illustration showing four 6V batteries wired in series-parallel to create a 12V bank. The diagram features red lines for positive leads, black lines for negative leads, and a clear indication of the chassis ground point. Labels include ‘Positive Bus Bar’, ‘Negative Bus Bar’, ‘2/0 AWG Gauge Wire’, and ‘Main Disconnect Switch’.]
Step-by-Step Installation and Implementation

To successfully implement a wiring diagram RV battery hook up picture, you must approach the task with precision and the right set of tools. Safety is paramount when dealing with high-capacity batteries, as even a 12-volt system can produce enough current to melt a wrench if shorted.
Required Tools and Materials:
- ✓ Insulated socket set and wrenches
- ✓ High-quality wire crimping tool
- ✓ Digital multimeter to verify voltage
- ✓ Heat shrink tubing and a heat gun
- ✓ Proper gauge battery cables (2/0 AWG is common for large banks)
- ✓ Wire brush or terminal cleaner
Installation Steps:
1. Preparation and Safety: Disconnect the RV from shore power and turn off any onboard generators. Ensure the battery disconnect switch is in the “OFF” position. Wear safety goggles to protect against potential acid splashes or sparks.
2. Position the Batteries: Place your batteries in the designated battery box or compartment. Ensure they are secured with straps to prevent movement during travel. Arrange them so the terminals are easily accessible according to your wiring diagram.
3. Connect the Bridge Wires: Following your diagram, connect the jumpers between the batteries. If you are doing a parallel hookup, connect positive to positive and negative to negative. Ensure the lugs are seated flat against the battery terminal for maximum contact.
4. Establish the Ground Wire: Attach the main negative cable to the negative terminal of the last battery in the bank. The other end must be securely fastened to the RV’s metal chassis. This ground wire completes the circuit for all DC components in the vehicle.
5. Connect the Hot Wire (Positive Lead): Connect the main positive cable to the positive terminal on the opposite end of the bank. This cable should lead directly to a high-amp fuse or circuit breaker before reaching the main disconnect switch or the common terminal of your power distribution center.
6. Integrate the Inverter (If Applicable): If your RV uses an inverter to create AC power, it will have its own set of heavy cables. Ensure these are connected directly to the battery bank terminals rather than through thin-gauge distribution blocks to handle the high current.
7. Final Verification: Use a multimeter to check the voltage across the main positive and negative leads. For a 12-volt system, you should see a reading between 12.6V and 13.2V (or higher if using lithium). Check all connections for tightness; a loose nut is a leading cause of electrical fires.
Never mix battery types or ages within the same bank. Adding a new battery to a bank of old ones will result in the older batteries “pulling down” the new one, significantly shortening its lifespan. Always replace the entire bank at once for optimal performance.
Troubleshooting Common Wiring Issues

Even with a perfect wiring diagram RV battery hook up picture, issues can arise during the installation or after a few months of vibration on the road. One frequent problem is a significant voltage drop. If your multimeter shows 12.8V at the battery but only 11.5V at your lights, you likely have a resistance issue caused by a thin gauge wire or a corroded connection.
Another common issue involves the confusion between AC and DC components. While a battery system is DC, it eventually feeds into an inverter that provides AC power to your outlets. In these AC circuits, you will encounter the traveler wire (for 3-way switches), the neutral wire, and the brass screw terminals on outlets. Beginners often mistakenly try to ground DC components to the neutral wire of an AC circuit, which is extremely dangerous. Always keep your DC chassis ground and AC neutral separate.
If you notice a “rotten egg” smell near your batteries, they are likely overcharging and gassing. Check the voltage output from your converter/charger. If the voltage exceeds 14.4V for an extended period on a lead-acid battery, the charger may be failing, or the battery bank configuration may be incorrect, forcing too much current into too few cells.
Tips and Best Practices for Long-Term Reliability
Maintaining your battery hookup is just as important as the initial installation. To get the most out of your system, follow these professional best practices:
Apply a thin layer of dielectric grease or terminal protector spray to all exposed copper and terminal connections. This prevents the white, powdery corrosion that naturally builds up in moist environments, ensuring your voltage remains stable year-round.
First, prioritize cable quality. Always use “Marine Grade” tinned copper wire. Unlike standard automotive wire, tinned copper resists the internal corrosion that occurs in the humid environments RVs often inhabit. When selecting your gauge, always round up. If a calculator suggests 4 AWG, use 2 AWG to minimize heat and maximize efficiency.
Second, consider the placement of your fuses. A fuse should be placed as close to the battery positive terminal as possible (within 18 inches). This “hot wire” protection ensures that if the main cable rubs against the chassis and shorts out, the fuse blows before the cable turns into a heating element that could ignite the coach.
Finally, monitor your state of charge properly. A simple voltmeter is better than nothing, but a true shunt-based battery monitor is a superior investment. These devices measure the actual flow of current into and out of the battery, giving you an accurate “fuel gauge” for your electricity. This prevents you from accidentally discharging your batteries below the recommended 50% depth of discharge (for lead-acid) or 10% (for lithium), significantly extending the life of your expensive battery bank.
In conclusion, having a clear wiring diagram RV battery hook up picture is the foundation of a reliable mobile power system. By understanding the relationship between voltage, gauge, and proper grounding, you can create a robust electrical setup that supports all your travel adventures. Always double-check your connections, respect the power of high-capacity batteries, and don’t hesitate to consult a professional if the complexity of your specific RV model exceeds your comfort level. Properly wired batteries aren’t just about convenience; they are about the safety and longevity of your home on wheels.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is wiring diagram rv battery hook up picture?
This diagram is a visual blueprint that shows how RV batteries connect to the vehicle’s electrical system. It details the paths for the hot wire and neutral wire while illustrating how to link multiple batteries in series or parallel configurations to achieve the desired voltage and amp-hour capacity for camping.
How do you read wiring diagram rv battery hook up picture?
To read the diagram, follow the lines from the battery terminals to the distribution panel. Look for symbols representing the ground wire and common terminal connections. Solid lines usually indicate primary power cables, while dashed lines might represent auxiliary circuits like a traveler wire used in specialized switching setups.
What are the parts of wiring diagram rv battery hook up picture?
The main parts include the battery bank, main fuse, disconnect switch, and inverter. The diagram also highlights the common terminal for grounding, the hot wire for power delivery, and the neutral wire for return paths. It may also show how a traveler wire integrates with multi-way lighting or charging switches.
Why is ground wire important?
The ground wire is critical because it provides a safe return path for electrical current to the chassis. In an RV, this prevents electrical shocks and protects sensitive electronics from power surges. Without a proper ground, the neutral wire and hot wire could create a dangerous short circuit scenario.
What is the difference between series and parallel?
A series connection links batteries end-to-end to increase voltage, keeping amperage the same. A parallel connection links all positive terminals and all negative terminals to increase capacity while maintaining the same voltage. The wiring diagram clarifies where the hot wire connects to ensure the desired output for your RV.
How do I use wiring diagram rv battery hook up picture?
Use the diagram as a step-by-step reference during physical installation. Match the physical terminals on your batteries to the diagram’s common terminal and power points. This ensures you correctly route the hot wire through fuses and disconnects before it reaches your RV’s internal power center or inverter.