Volvo Penta Cooling System Diagram: Maintenance & Repair
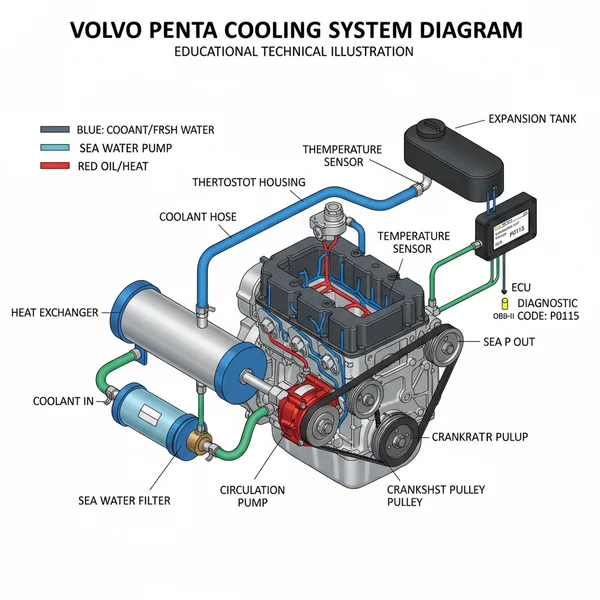
A Volvo Penta cooling system diagram illustrates the flow of coolant through the engine, heat exchanger, and raw water pump. It helps technicians identify paths for fresh and raw water circuits, ensuring proper heat dissipation. Using this visual map is essential for diagnosing overheating issues and maintaining peak marine engine performance.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides a visual map of the closed-loop and raw water circuits
- Identify the heat exchanger as the central cooling hub
- Ensure all hose clamps meet the specified torque spec to prevent leaks
- Use the diagram to trace air pockets or blockages
- Refer to this during routine impeller changes or winterization
Whether you are performing routine maintenance or diagnosing an unexpected overheat, understanding the volvo penta cooling system diagram is the most critical step for any boat owner or marine technician. These engines rely on a complex, dual-circuit system to maintain optimal operating temperatures while operating in harsh saltwater or freshwater environments. Having the correct schematic allows you to trace the specific path of both raw water and internal coolant, ensuring that every heat exchanger, hose, and pump is functioning correctly. In this guide, you will learn how to interpret the cooling flow, identify key components like the heat exchanger and thermostat, and use diagnostic tools to keep your engine running at peak performance.
Most Volvo Penta engines utilize a “closed cooling” system. This means the engine block is filled with a mixture of antifreeze and distilled water (freshwater circuit), which is cooled by an external source of raw water (lake or ocean water) via a heat exchanger.
Understanding the Cooling System Components
The volvo penta cooling system diagram typically illustrates two distinct but interactive loops. The first loop is the raw water circuit. This begins at the sea strainer or drive intake, where water is drawn in by the raw water pump. This pump is usually driven by the accessory belt at the front of the engine. The raw water passes through the oil cooler and into the heat exchanger before being injected into the exhaust risers to be discharged overboard. Because this water is often corrosive, the diagram highlights specific sacrificial anodes designed to protect the metal components from galvanic corrosion.
The second loop is the freshwater or “closed” circuit. This circuit remains inside the engine and functions similarly to an automotive cooling system. It includes the circulation pump, the engine block water jackets, the cylinder head, and the internal side of the heat exchanger. The coolant flow in this circuit is regulated by a thermostat. When the engine is cold, the thermostat remains closed, recirculating coolant within the block to reach operating temperature quickly. Once the threshold is met, the thermostat opens, allowing the hot coolant to flow into the heat exchanger where it transfers its heat to the raw water.
In modern fuel-injected models, the ECU (Engine Control Unit) monitors this entire process through various sensors. If the temperature exceeds safe parameters, the ECU may trigger a check engine light or even reduce engine power to prevent catastrophic failure. Variations in the diagram often depend on whether the engine is a gasoline V6/V8 or a D-series diesel. Diesel models often include additional cooling for the turbocharger and intercooler, which will be represented by additional branches in the plumbing schematic.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER – Interactive Volvo Penta Cooling Flow Schematic showing Raw Water vs. Freshwater Loops]
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Read and Use the Diagram

Interpreting a volvo penta cooling system diagram requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to use the diagram for successful maintenance or repair.
1. Identify the Intake Source
Locate the starting point of the raw water flow on your diagram. On sterndrive models, this is typically at the lower unit of the outdrive. On inboard models, it begins at a thru-hull fitting and sea strainer. Tracing from this point allows you to check for obstructions like seaweed or plastic bags that often clog the initial intake.
2. Locate the Raw Water Pump and Accessory Belt
Check the diagram to see how the raw water pump is mounted. It is usually found on the lower front of the engine. Ensure the accessory belt is properly tensioned and not frayed, as a slipping belt will lead to immediate cooling loss. If you are replacing the impeller, the diagram will show the orientation of the pump housing and the specific bolt pattern.
3. Trace the Heat Exchanger Path
The heat exchanger is the “radiator” of the marine engine. Use the diagram to identify the inlet and outlet ports for both the raw water and the internal coolant. If you notice a temperature spike, you should inspect the “stack” (the internal tube bundle) inside the exchanger for scale buildup or debris that the diagram shows can accumulate at the narrow entry points.
4. Verify the Thermostat Location
The thermostat is generally housed at the top of the engine where the manifold meets the cooling hoses. Refer to the diagram to see which hoses lead to the bypass circuit. When installing a new thermostat, always refer to the manufacturer’s torque spec for the housing bolts to avoid cracking the casting or causing a vacuum leak.
5. Monitor the ECU and Sensors
Modern systems use an ECU to process data from the coolant temperature sensor. If your dashboard displays a diagnostic code or the check engine light illuminates, the diagram can help you locate the specific sensor responsible for that data. While marine engines don’t use a standard OBD-II port like a car, they use an NMEA 2000 or a proprietary Vodia connection that functions identically for reading error codes.
6. Check the Circulation Pump and Timing Chain Area
Behind the accessory belt and pulleys lies the circulation pump. While the timing chain is shielded behind a cover, the cooling diagram shows how the water pump interacts with the front of the block. Ensure there is no weeping from the “tell-tale” hole on the pump, as this indicates a failing internal seal.
7. Inspect the Exhaust Manifolds and Risers
Finally, trace the flow to where the water exits. The diagram will show how water is mixed with exhaust gases in the risers. This is a high-wear area. If the diagram shows a blockage here, back-pressure can build up, potentially pushing water back into the cylinders through the exhaust valves.
Never open the pressure cap on the expansion tank while the engine is hot. Marine cooling systems operate under significant pressure, and escaping steam can cause severe burns.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting

The most frequent issue encountered is a “dry run” impeller failure. If the raw water intake is blocked, the rubber impeller inside the pump will disintegrate within seconds. The volvo penta cooling system diagram helps you trace where those broken rubber bits may have traveled, often lodging in the oil cooler or the heat exchanger inlet.
Another common problem is the “Check Engine” alarm triggered by a faulty sensor. By using the diagram, you can perform a visual inspection of the wiring harness leading to the ECU. If you have a diagnostic code reader, you can pinpoint whether the issue is a genuine overheat or a sensor failure. For example, a “Code 22” on some systems indicates a coolant pressure circuit fault.
If you notice a drop in coolant levels without a visible leak, the diagram can point you toward the heat exchanger’s internal seals. If the internal tubes leak, the engine coolant can be pushed out through the raw water exhaust, leaving no puddle in the bilge but causing the engine to run dangerously hot.
Tips & Best Practices for Cooling System Maintenance
To ensure the longevity of your Volvo Penta engine, follow these professional maintenance strategies:
- ✓ Annual Impeller Replacement: Even if it looks fine, rubber hardens over time. Replace the raw water impeller every season to prevent mid-water failures.
- ✓ Flush After Every Saltwater Use: Salt crystalizes and narrows the passages shown in your cooling diagram. A freshwater flush is the best defense against “narrowing” of the heat exchanger tubes.
- ✓ Monitor Zinc Anodes: Locate the zinc plugs on your heat exchanger diagram and check them every 90 days. These sacrificial metals should be replaced when they are 50% eroded.
- ✓ Check Belt Tension: A loose accessory belt will not spin the water pumps at the required RPM, leading to “creeping” temperatures at high speeds.
When reassembling cooling components, always use marine-grade thread sealant on hose barbs and follow the specific torque spec for every bolt. Over-tightening can easily crack aluminum housings found on modern Volvo Penta engines.
Maintaining your marine engine doesn’t have to be a mystery. By keeping a printed copy of the volvo penta cooling system diagram on your boat, you are equipped to handle everything from a simple hose replacement to a complex diagnostic routine. Regular inspection of the coolant flow, combined with attention to ECU warnings and physical component wear, will ensure that your time on the water is spent enjoying the view rather than staring at a temperature gauge. Consistent care of the heat exchanger, pumps, and belts is the most cost-effective way to extend the life of your engine and prevent the dreaded check engine light from ruining your day.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Volvo Penta cooling system diagram?
It is a schematic representation showing the routing of water and coolant through a marine engine. It details how raw water is pulled in to cool the internal engine coolant via a heat exchanger. This visual tool is indispensable for identifying hose connections, pump locations, and thermostat housings for repair.
How do you read Volvo Penta cooling system diagram?
Start by identifying the intake point where raw water enters the system. Follow the arrows indicating flow direction through the water pump, heat exchanger, and exhaust manifold. Use the legend to distinguish between freshwater and seawater paths, ensuring you recognize how each circuit interacts to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
What are the parts of Volvo Penta cooling system?
The system typically consists of a raw water pump, a freshwater circulation pump, a heat exchanger, and a thermostat. It also includes an expansion tank, various hoses, and sensors that communicate with the ECU to monitor thermal health and trigger a check engine light if temperatures exceed safe operating limits.
Why is the heat exchanger important?
The heat exchanger acts as the radiator for marine engines, transferring heat from the internal engine coolant to the external raw water without the two fluids mixing. If it becomes clogged or corroded, the engine will overheat, potentially causing the ECU to store a specific diagnostic code for the operator.
What is the difference between open and closed cooling?
Open cooling systems pull raw water directly through the engine block, while closed systems use a heat exchanger and internal coolant. Closed systems are preferred for saltwater environments because they protect the engine’s internal components from corrosion. The diagram helps visualize how these two systems differ in complexity and flow.
How do I use Volvo Penta cooling system diagram?
Utilize the diagram during troubleshooting to verify that every hose is connected to the correct port. It serves as a reference when replacing the impeller or flushing the system. By cross-referencing the layout, you can effectively pinpoint leaks or blockages that lead to an illuminated check engine light.