Trailer Breakaway System Wiring Diagram: Easy Setup Guide
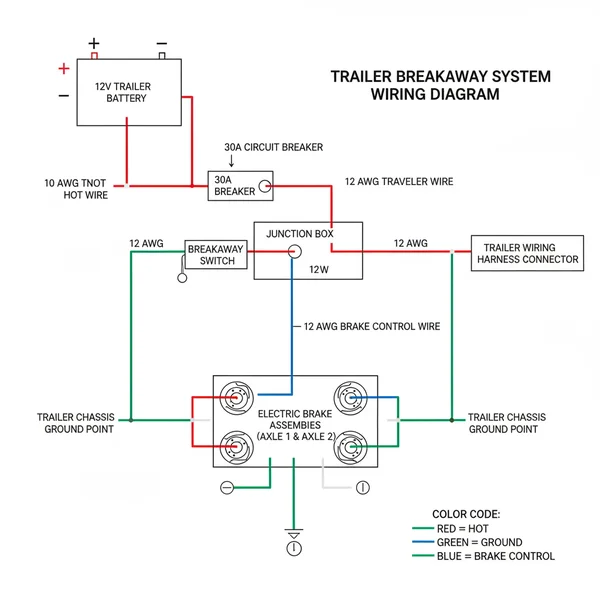
A trailer breakaway system wiring diagram illustrates the connection between the backup battery, breakaway switch, and trailer brakes. It ensures that if the trailer disconnects from the tow vehicle, the hot wire activates the brakes automatically. Correct grounding through the ground wire is essential for completing this emergency safety circuit.
📌 Key Takeaways
- The diagram outlines the emergency brake activation circuit for towing safety.
- The breakaway switch is the most critical component to identify for installation.
- Ensure the dedicated battery is fully charged for reliable emergency braking power.
- Secure all connections with waterproof connectors to prevent long-term wiring corrosion.
- Use this diagram when installing new kits or troubleshooting existing emergency brake systems.
Ensuring your towing setup is equipped with a functional emergency braking mechanism is not just a matter of safety; in most jurisdictions, it is a legal requirement for trailers exceeding a certain weight. If your trailer ever becomes detached from the tow vehicle while in motion, the breakaway system acts as the final line of defense, automatically engaging the electric brakes to bring the trailer to a controlled stop. Understanding a comprehensive trailer breakaway system wiring diagram is the first step toward a successful installation. This guide provides a detailed look at the electrical components, wiring paths, and technical specifications you need to secure your load and protect other drivers on the road. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of how to wire, test, and maintain your breakaway kit.
Understanding the Trailer Breakaway System Wiring Diagram
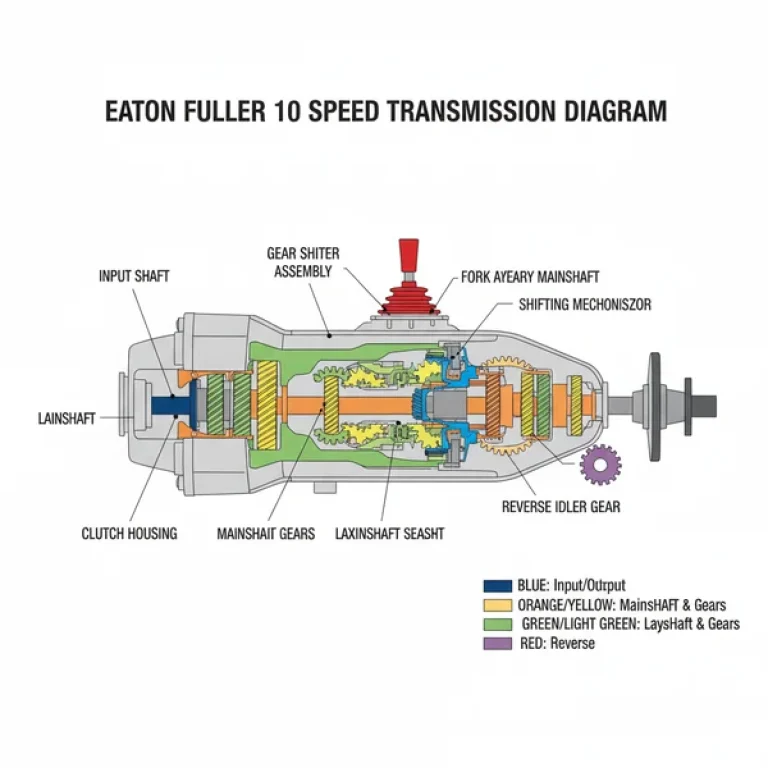
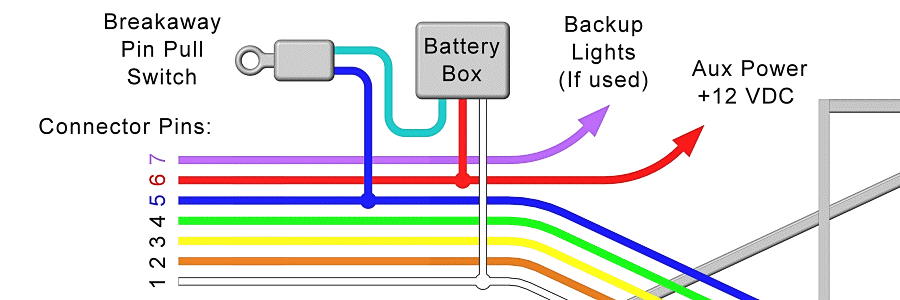
A trailer breakaway system consists of three primary components: a small 12-volt lead-acid or gel cell battery, a plastic or metal breakaway switch with a pull-pin, and the wiring that connects these parts to your trailer’s existing electric brake magnets. The trailer breakaway system wiring diagram illustrates how power flows from the dedicated onboard battery to the brakes only when the pin is physically pulled out of the switch during a separation event.
In a standard diagram, you will notice three distinct circuits. First is the charging circuit, which often utilizes a “hot wire” from the tow vehicle’s 7-way connector to keep the breakaway battery topped off during travel. Second is the ground circuit, which ensures a complete electrical path back to the battery’s negative terminal. Third is the trigger circuit, which involves the switch itself. The switch acts as a gatekeeper; under normal conditions, the internal contacts are held apart by a nylon pin. When the pin is pulled, the contacts close, allowing 12-volt current to bypass the tow vehicle’s brake controller and feed directly into the trailer brake magnets.
Most diagrams will use specific color-coding to simplify the process. A black wire typically represents the positive “hot wire” or 12V power source. A white wire serves as the ground wire, which is often secured to the trailer frame or a common terminal block. The blue wire is the “traveler wire” in the sense that it carries the signal to the brake magnets. It is crucial to note that the gauge of the wire used must be sufficient to handle the amperage draw of all brake magnets simultaneously without significant voltage drop.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A technical wiring schematic showing a 12V battery connected to a breakaway switch. The switch is wired in parallel to the blue trailer brake line. A charging lead connects the battery to the 7-way plug (Pin 4), and all components share a common ground to the trailer frame.]
In DC electrical systems used for trailers, the negative terminal is referred to as the ground. While “neutral wire” is a term usually reserved for AC household wiring, in the context of a trailer, the ground wire provides the return path for the current, performing a similar role to ensure the circuit is complete.
Step-by-Step Installation and Wiring Guide
Following a trailer breakaway system wiring diagram requires a methodical approach to ensure every connection is weatherproof and vibration-resistant. Before you begin, gather the necessary tools and materials.
- ✓ 12V Breakaway Battery and Protective Case
- ✓ Breakaway Switch with Lanyard and Pin
- ✓ 12-Gauge or 14-Gauge Automotive Grade Wire
- ✓ Heat-Shrink Butt Connectors and Ring Terminals
- ✓ Wire Strippers and Crimping Tool
- ✓ Multimeter for Voltage Testing
Step 1: Mount the Battery Case and Switch
Install the battery box on the trailer frame or A-frame tongue, ensuring it is reachable but protected from road debris. Mount the breakaway switch on the side of the trailer tongue. It must be positioned so the cable can reach the tow vehicle’s bumper or hitch frame without being restricted during turns, yet short enough to pull the pin if the hitch fails.
Step 2: Establish the Ground Circuit
Connect the white negative wire from the breakaway battery to the trailer frame. Use a self-tapping screw or a dedicated ground bolt. If you are using a junction box, you may find a common terminal marked for grounds. Ensure the metal surface is sanded clean to provide a solid electrical connection.
Step 3: Connect the Breakaway Switch
The breakaway switch has two wires (usually both black, or one black and one blue). One wire connects to the positive “hot wire” terminal of the breakaway battery. The second wire from the switch connects directly to the trailer’s main brake wire (usually blue). This setup ensures that when the switch is activated, the battery’s full voltage is sent directly to the brakes.
Step 4: Integrate the Charging Circuit
To ensure the battery doesn’t die over time, you must connect the positive terminal of the breakaway battery to the 12V auxiliary power wire (Pin 4) of your trailer’s 7-way plug. This allows the vehicle’s alternator to charge the small battery while you drive. Some systems include a “built-in charger” module; if yours does, connect the charge wire to the common terminal of this module.
Step 5: Inspect and Secure Connections
If your junction box utilizes a terminal strip, ensure each wire is secured under the correct brass screw or terminal clamp. Loose connections are the primary cause of system failure. Use 12-gauge wire for the main power paths to maintain consistent voltage across the entire length of the trailer.
Never use the breakaway system as a parking brake. Leaving the pin pulled for extended periods will cause the brake magnets to overheat and will rapidly drain and potentially damage the breakaway battery.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting

Even with a perfect installation based on a trailer breakaway system wiring diagram, environmental factors like corrosion and vibration can cause issues. The most frequent problem is a dead battery. If the battery cannot hold at least 12 volts, it will not have the power necessary to engage the magnets during an emergency. Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the battery terminals; if it reads below 12.1V, the battery requires charging or replacement.
Another common issue is corrosion inside the breakaway switch. Since these switches are exposed to the elements, moisture can seep into the housing and oxidize the contacts. If you pull the pin and the brakes do not engage, use a jumper wire to bypass the switch. If the brakes engage with a jumper but not the switch, the switch is faulty.
Check for frayed or damaged “traveler wires” leading to the axles. If a wire is pinched against the frame, it may create a short circuit, blowing the fuse on the charging line or preventing the breakaway system from functioning. Finally, ensure the lanyard cable is not tangled; a cable that cannot pull the pin cleanly renders the entire system useless.
Tips & Best Practices for Maintenance
Maintaining your breakaway system is a critical part of trailer ownership. A well-maintained system ensures that the trailer breakaway system wiring diagram you followed translates into real-world safety.
Always test your breakaway system before every trip. With the trailer hitched but the 7-way plug disconnected, pull the breakaway pin and try to pull the trailer forward. If the wheels lock or show significant resistance, the system is working. Remember to reinsert the pin immediately after testing.
For long-term reliability, consider the following recommendations:
1. Battery Care: Small lead-acid batteries have a lifespan of 2 to 3 years. Replace them proactively to avoid failure when you need them most. During the off-season, remove the battery and keep it on a tender in a temperature-controlled environment.
2. Wiring Quality: Use tinned copper marine-grade wire if you frequently tow in salt-heavy environments or near the ocean. This prevents “wicking” where corrosion travels up the wire under the insulation.
3. Connector Protection: Apply dielectric grease to the brass screw terminals in your junction box and the battery terminals. This creates a moisture barrier and prevents oxidation.
4. Wire Routing: Protect your wiring by running it through plastic loom or conduit. Secure it to the frame with UV-rated zip ties or rubber-lined P-clamps to prevent the wire from chafing against sharp metal edges.
5. Component Upgrades: If your kit did not come with a battery meter, consider installing a small LED voltage indicator. This allows for a quick visual confirmation that the charging circuit is working and the battery is healthy without needing a multimeter.
By strictly adhering to a high-quality trailer breakaway system wiring diagram and performing regular maintenance, you ensure that your trailer is equipped with a reliable failsafe. Safety on the road is a combination of proper loading, attentive driving, and mechanical readiness. A properly wired breakaway system is a small investment of time and resources that provides immense peace of mind during every journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is trailer breakaway system wiring diagram?
A trailer breakaway system wiring diagram is a schematic showing how to wire a safety device that triggers trailer brakes during a disconnection. It identifies how the battery connects to the switch and brakes, ensuring the hot wire sends power to the magnets when the pin is pulled from the switch.
How do you read trailer breakaway system wiring diagram?
Reading this diagram involves following the path from the onboard battery to the breakaway switch. You must identify the ground wire connecting to the trailer frame and the hot wire leading to the brakes. Understanding how the switch acts as a bridge during a disconnect is vital for safety.
What are the parts of trailer breakaway system?
The system consists of a dedicated 12V battery, a breakaway switch with a pull-pin, and a wiring harness. The common terminal inside the junction box links these parts. It also includes the trailer’s electric brakes, which are energized by the system if the trailer uncouples from the hitch.
Why is hot wire important?
The hot wire is important because it carries the full current from the breakaway battery to the electric brakes. Unlike a standard traveler wire used in house lighting, this wire must handle high amperage to lock the wheels immediately. If this connection fails, the emergency system will not function.
What is the difference between ground wire and neutral wire?
In a DC trailer system, the ground wire connects to the metal chassis to complete the circuit. While a neutral wire is common in AC household systems to return current, trailers primarily use the frame as a common return. Properly grounding the breakaway system ensures the brakes engage reliably.
How do I use trailer breakaway system wiring diagram?
Use the diagram to map out your installation by locating the battery box and switch mounting point. Identify the common terminal for power distribution and ensure every connection matches the schematic. This ensures that the emergency system remains dormant during normal towing but activates during a hitch failure.