Toyota Tundra 5.7 Engine Diagram: Component Layout & Specs
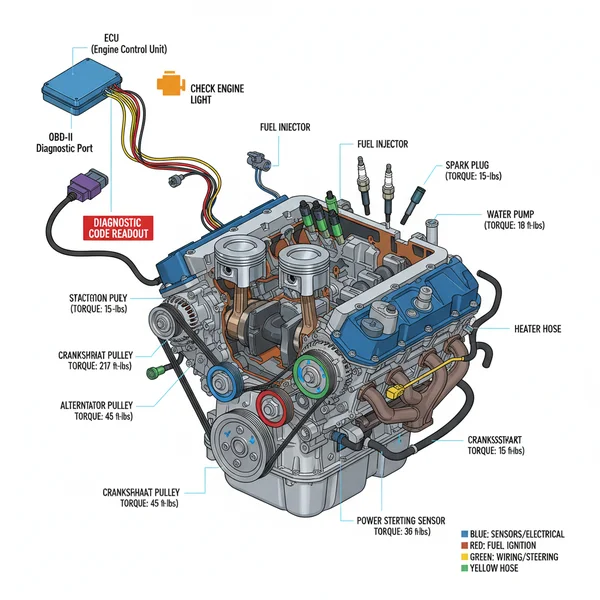
The Toyota Tundra 5.7 engine diagram illustrates the layout of the 3UR-FE V8, highlighting the dual VVT-i system, air intake, and ignition coils. It is essential for locating the ECU and using an OBD-II scanner to resolve a check engine light by identifying a specific diagnostic code for precise mechanical repairs.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Main purpose: Visualize the 3UR-FE V8 layout for maintenance and repair.
- Most important component: The 3UR-FE V8 engine block and its electronic control system.
- Safety: Always disconnect the battery before working near electrical connectors or fuel rails.
- Practical tip: Follow the exact torque spec for intake manifold and spark plug installation.
- When to use: When diagnosing performance issues or performing scheduled mechanical maintenance.
Understanding the internal and external layout of your vehicle is the primary step toward successful DIY maintenance and long-term reliability. Whether you are performing a routine service or diagnosing a complex mechanical fault, a toyota tundra 5.7 engine diagram serves as your essential roadmap. The 3UR-FE V8 engine is a masterpiece of engineering, known for its longevity and power, but its dense component arrangement can be intimidating without a clear visual guide. This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of the engine’s architecture, helping you identify critical sensors, understand fluid paths, and navigate the engine bay with professional-level confidence.
Understanding the 5.7L V8 Engine Layout
The 5.7-liter 3UR-FE engine is a Dual Overhead Cam (DOHC) 32-valve V8 that features an aluminum block and heads. When looking at a toyota tundra 5.7 engine diagram, the first thing you will notice is the massive intake manifold sitting centrally between the two cylinder banks. This “valley” is also where the starter motor is located, a specific design choice that requires the removal of the intake manifold for access.
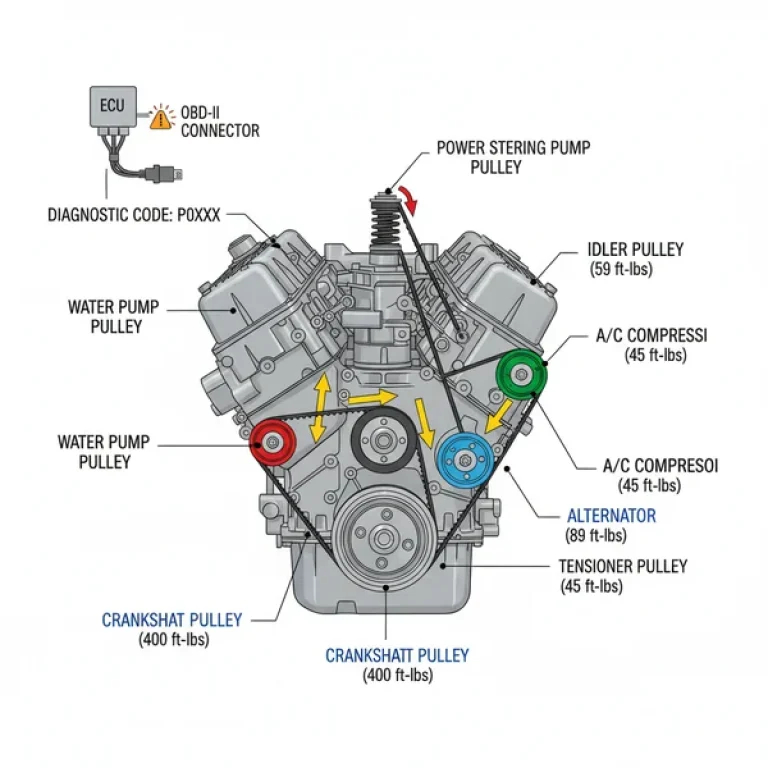
The front of the diagram highlights the accessory belt (serpentine belt) routing. This single belt drives the alternator, water pump, air conditioning compressor, and power steering pump. Unlike older designs, the 3UR-FE utilizes a timing chain rather than a belt, which is housed behind a robust front timing cover. This chain is designed to last the life of the engine, provided oil changes are performed regularly. Furthermore, the diagram illustrates the coolant flow, which moves from the bottom radiator hose, through the water pump, into the engine block and heads, and finally out through the thermostat housing into the upper radiator hose.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A detailed technical illustration of the Toyota 3UR-FE 5.7L V8 engine, showing the serpentine belt routing, intake manifold, spark plug locations, and major sensor positions.]
Step-by-Step Guide to Interpreting the Diagram

Interpreting a technical engine schematic requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to ensure you are reading the diagram correctly and applying it to your Tundra effectively.
Always verify your engine’s specific model code. While the 5.7L 3UR-FE remained consistent for many years, minor revisions to the vacuum lines and electrical connectors may exist based on the vehicle’s emission standards.
- Identify the Front Orientation: Most diagrams are drawn from the perspective of looking at the engine from the front bumper. Locate the cooling fan and the accessory belt pulleys to orient yourself correctly.
- Trace the Accessory Belt Routing: Use the diagram to identify the tensioner pulley. To remove or install the belt, you must rotate this tensioner to release pressure. The diagram will show the exact “S” curve the belt must follow across the seven different pulleys.
- Locate the Cylinder Numbering: On the 5.7L V8, the cylinders are numbered 1-3-5-7 on the passenger side (Bank 1) and 2-4-6-8 on the driver side (Bank 2). This is crucial when a diagnostic code indicates a misfire on a specific cylinder.
- Find the ECU and Sensor Nodes: The ECU (Engine Control Unit) is the brain of the vehicle. The diagram helps you find the wiring harnesses that lead to the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor, Oxygen (O2) sensors, and the throttle body.
- Cross-Reference with the OBD-II System: When the check engine light appears, use the diagram to find the physical location of the component associated with the diagnostic code retrieved from the OBD-II port under the dashboard.
- Apply Proper Torque Specifications: For every bolt you remove based on the diagram—especially for spark plugs or intake bolts—you must reference a torque spec table. Over-tightening into the aluminum head can cause permanent damage.
Never attempt to work on the cooling system while the engine is hot. The coolant flow system is under high pressure and can cause severe burns if the radiator cap or hoses are removed prematurely.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting with the 5.7 Engine

The Toyota 5.7L V8 is legendary for its 300,000-mile capability, but it is not without common points of failure. Using your engine diagram, you can proactively check for these issues:
- ✓ Cam Tower Seeps: Look at the rear of the cylinder heads on your diagram. Oil can sometimes seep from the cam towers, dripping onto the exhaust manifold.
- ✓ Water Pump Failure: The water pump is a known wear item. Use the diagram to locate the weep hole on the pump housing; pink crusty residue here indicates it is time for a replacement.
- ✓ Secondary Air Injection Pump: These pumps are located near the fender wells. If they fail, they will trigger a check engine light and potentially put the truck into a “limp mode.”
- ✓ Starter Motor Location: As mentioned, the starter is under the intake. If your truck fails to crank and the battery is good, the diagram confirms the labor-intensive location of this component.
If you encounter a diagnostic code such as P0300 (Random Misfire) or P0171 (System Too Lean), refer back to your toyota tundra 5.7 engine diagram to inspect the vacuum lines and ignition coils for damage or loose connections before replacing expensive parts.
Tips & Best Practices for Maintenance
To keep your Tundra running smoothly, follow these professional tips derived from years of mechanical experience with the 3UR-FE platform.
When replacing the accessory belt, use a long-reach serpentine belt tool. The space between the fan shroud and the pulleys is tight, and this specialized tool saves significant time and prevents hand injuries.
First, always prioritize the torque spec for spark plugs (typically 13-15 ft-lbs). Because the 5.7 engine uses long-reach iridium plugs, installing them incorrectly can lead to combustion leaks or stripped threads in the aluminum head. Second, maintain the coolant flow efficiency by using only Toyota Super Long Life Coolant (SLLC). Mixing generic green coolant with Toyota’s pink fluid can lead to gelling, which clogs the radiator passages.
Third, pay close attention to the timing chain health by using high-quality full synthetic 0W-20 oil. The timing chain tensioners rely on hydraulic oil pressure; dirty or incorrect viscosity oil can cause the chain to rattle or wear prematurely. Finally, keep a digital copy of the toyota tundra 5.7 engine diagram on your phone. Having this reference available while standing over the engine bay is far more efficient than running back and forth to a computer or manual.
By mastering the layout of your engine and understanding how each component interacts, you ensure that your Toyota Tundra remains the reliable workhorse it was built to be. Whether you are clearing a check engine light or performing a weekend tune-up, the right diagram is your most valuable tool in the garage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Toyota Tundra 5.7 engine diagram?
A Toyota Tundra 5.7 engine diagram is a visual schematic of the 3UR-FE V8 powerplant. It maps out critical internal and external components, including the fuel system, ignition coils, and cooling lines. This reference helps owners and mechanics identify specific parts for repair, maintenance, or electrical troubleshooting tasks.
How do you read a Toyota Tundra 5.7 engine diagram?
To read the diagram, start by identifying the orientation, typically looking from the front bumper toward the firewall. Follow the labeled lines to specific sensors or mechanical parts. Pay close attention to the legend, which explains symbols for electrical grounds, vacuum hoses, and various harness connections to the ECU.
What are the parts of the Toyota Tundra 5.7 engine?
The 5.7L V8 consists of the engine block, aluminum cylinder heads, dual overhead cams, and the VVT-i system. External parts include the alternator, starter, water pump, and air intake assembly. Key electronic components involve the ECU, oxygen sensors, and various modules that communicate via the onboard diagnostic system.
Why is the ECU important in this diagram?
The ECU is the brain of the Tundra, managing fuel injection timing, spark advance, and emissions. In a diagram, it shows how the unit receives signals from sensors to optimize performance. Understanding its wiring helps diagnose complex issues when a generic diagnostic code doesn’t provide the full story.
What is the difference between mechanical and electrical diagrams?
Mechanical diagrams focus on physical placement and hardware assembly, highlighting parts like the timing chain or pulleys. Electrical diagrams illustrate the wiring harness, showing how components connect to the power source and ECU. Both are necessary for a complete repair, especially when tracking down a stubborn check engine light.
How do I use a Toyota Tundra 5.7 engine diagram?
Use the diagram to locate components when performing tasks like replacing spark plugs or checking for vacuum leaks. Match the visual representation to the actual engine bay to ensure you are working on the correct part. It is also vital for verifying the correct torque spec for various bolts.