Toyota Tundra 5.7 Engine Diagram: Component Identification
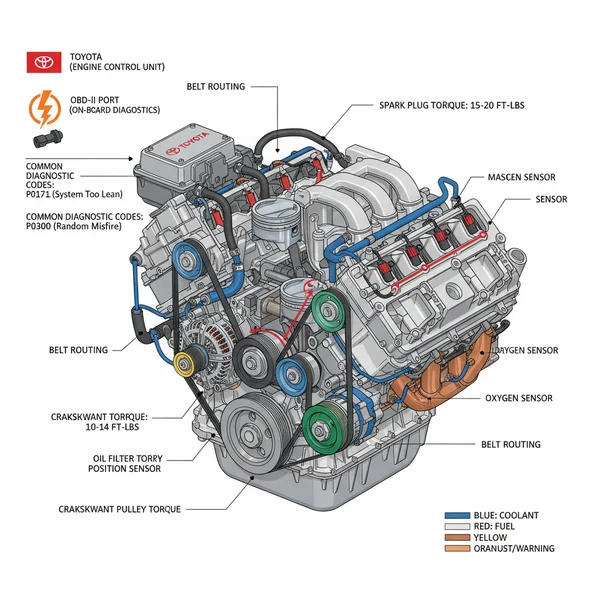
A Toyota Tundra 5.7 engine diagram illustrates the layout of the i-FORCE V8, highlighting the intake manifold, fuel injectors, and sensor locations. It is essential for locating the ECU and using an OBD-II scanner to interpret a check engine light or diagnostic code, ensuring repairs follow the correct torque spec for safety.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Visualizes the i-FORCE 5.7L V8 component arrangement
- Identifying the ECU and sensor locations for diagnostic work
- Always adhere to the specific torque spec for internal bolts
- Use the diagram to trace wiring when a check engine light appears
- Essential tool during routine maintenance or complex engine repairs
The 3UR-FE engine, famously known as the powerhouse behind one of the most reliable full-size trucks on the market, is a complex piece of engineering that requires a precise understanding to maintain. Navigating the engine bay can be daunting for even seasoned DIY mechanics without a clear roadmap. Obtaining an accurate toyota tundra 5.7 engine diagram is the first step in demystifying the intricate web of sensors, belts, and hoses that provide the truck with its legendary towing capacity. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the primary components of the 5.7L V8, explaining how the various systems interact and providing you with the technical knowledge needed to diagnose issues, perform routine maintenance, and interpret complex diagnostic data.
Understanding the 3UR-FE Engine Layout
The 5.7-liter V8 engine is a double overhead cam (DOHC) 32-valve design that utilizes a sophisticated Dual VVT-i (Variable Valve Timing with intelligence) system. When viewing a toyota tundra 5.7 engine diagram, you will notice the engine is dominated by a large, composite intake manifold that sits centrally between the two cylinder banks. This manifold is designed to optimize airflow for high-torque output. Flanking the intake are the two aluminum cylinder heads, which house the timing chain assemblies and the spark plug wells.
At the front of the engine, the accessory belt (serpentine belt) follows a specific routing path to power the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Unlike some smaller engines, the 5.7 Tundra uses a robust timing chain rather than a rubber belt, which is designed to last the lifetime of the vehicle under normal conditions. The cooling system is also a prominent feature in any diagram, showing the coolant flow from the radiator through the front-mounted water pump and into the engine block and heads. Understanding this flow is critical for preventing the overheating issues that can occur if the thermostat or water pump fails.
How to Read and Interpret the Engine Diagram

Interpreting a technical engine diagram requires a systematic approach. You are not just looking for parts; you are looking for the relationships between mechanical components and electronic controls. Follow these steps to master the use of your toyota tundra 5.7 engine diagram for any repair or inspection task.
Always verify the specific revision of your diagram. While the 5.7L 3UR-FE remained consistent for many years, minor changes in sensor locations or wiring harness routing can occur between different production runs.
1. Identify the Orientation: Start by determining the front of the engine, which is always the side with the accessory belt and cooling fan. The cylinder numbering on this engine begins with Cylinder 1 on the front of the passenger side (Bank 1) and Cylinder 2 on the front of the driver side (Bank 2).
2. Trace the Accessory Belt Path: Use the diagram to identify the seven pulleys involved in the belt system. If you are replacing the belt, note the position of the automatic tensioner, which is located on the lower passenger side of the front timing cover.
3. Locate the Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The ECU serves as the brain of the engine. In the Tundra, it is typically located in the engine bay, protected by a plastic housing. The diagram will show the massive wiring harnesses that lead from the ECU to the various sensors on the block and intake.
4. Connect the OBD-II System: When a check engine light appears, you will use the OBD-II port located under the dashboard to pull a diagnostic code. The engine diagram helps you cross-reference that code with a physical sensor on the engine, such as the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor or Oxygen sensors.
5. Map the Coolant Flow: Trace the hoses on the diagram. Cold coolant enters the lower part of the block, is circulated by the water pump, and exits through the upper radiator hose after passing through the thermostat.
6. Identify Torque Spec Requirements: A high-quality diagram or service manual will list specific torque values for critical bolts. For example, the intake manifold bolts and spark plugs have very specific requirements to prevent vacuum leaks or stripped threads.
7. Check the Oil System: Identify the location of the cartridge-style oil filter housing, which is found on the bottom of the engine near the front. This is a common point of confusion for those used to traditional spin-on filters.
8. Inspect the Air Injection System: The 5.7 engine features a secondary air injection system. The diagram will show the pumps and valves located near the back of the engine or inside the fender wells, which are often the cause of specific emissions-related codes.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting

Even with its reputation for durability, the 5.7L engine has a few common “weak spots” that owners should be aware of. One frequent issue is the cam tower leak, where oil seeps from the seal between the camshaft housing and the cylinder head. A diagram can help you pinpoint exactly where these towers sit relative to the valve covers.
Another common concern involves the secondary air injection pumps. If your check engine light is on and your scanner reveals a P0418 or P0419 diagnostic code, the diagram will help you locate the pumps and the switching valves. Failure of these components often puts the truck into “limp mode,” significantly reducing power to protect the engine.
The starter on the 5.7L Tundra is located underneath the intake manifold. Replacing it requires removing the entire intake assembly, a task that should only be attempted with a clear diagram and proper gasket replacements on hand.
If you notice a drop in coolant levels without a visible leak on the ground, use your diagram to check the “valley” of the engine under the intake manifold. The coolant crossover pipe can sometimes develop a slow leak in this hidden area. Monitoring your coolant flow and checking for crusty pink residue (Toyota’s signature coolant color) can save the engine from catastrophic overheating.
Pro Tips and Best Practices for Maintenance
Maintaining a 5.7L engine requires more than just oil changes; it requires an eye for detail and the use of quality components. To keep your Tundra running smoothly, follow these professional recommendations:
- ✓ Use Genuine Filters: The 3UR-FE is sensitive to oil flow. Always use OEM Toyota cartridge filters to ensure the internal bypass valves operate at the correct pressure.
- ✓ Monitor the Serpentine Belt: The accessory belt is the lifeline for the alternator and water pump. Inspect it every 30,000 miles for cracks or glazing.
- ✓ Adhere to Torque Specs: When replacing spark plugs, use a torque wrench to meet the 15-18 ft-lb requirement. Over-tightening can damage the aluminum threads in the cylinder head.
- ✓ Clean the MAF Sensor: A dirty Mass Air Flow sensor can cause poor fuel economy and rough idling. It is easily found on the air intake tube via your engine diagram.
When troubleshooting an electrical issue, always check the ground points indicated on your wiring diagram. A corroded ground wire can trigger a “ghost” check engine light or multiple unrelated diagnostic codes.
For high-mileage engines, pay close attention to the timing chain tensioners. While the chain itself is very durable, the plastic guides can wear over time. Listening for a “rattle” upon cold starts can help you catch a tensioner issue before it leads to timing jumps. Additionally, ensure you are using the correct 0W-20 synthetic oil, as the VVT-i system relies on specific oil viscosity to adjust the cam timing accurately.
Understanding your toyota tundra 5.7 engine diagram transforms you from a passive owner into an informed steward of your vehicle. By recognizing the placement of the ECU, the path of the accessory belt, and the logic of the coolant flow, you gain the confidence to handle repairs that would otherwise cost thousands at a dealership. Whether you are clearing a diagnostic code or performing a weekend tune-up, the diagram is your most valuable tool in the garage. Keep it accessible, study the connections, and your Tundra will reward you with many more years of heavy-duty performance.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the Toyota Tundra 5.7 Engine Diagram: Component Identification
Identify the main engine orientation, noting the location of the front pulleys and the rear transmission interface.
Locate the ECU and major sensor groupings shown on the schematic to understand the control system layout.
Understand how the intake and exhaust systems are routed to facilitate air flow through the V8 cylinders.
Connect the visual representation to the physical engine bay by matching landmarks like the air box and battery.
Verify that every bolt you tighten matches the manufacturer-recommended torque spec to prevent mechanical failure or leaks.
Complete the diagnostic process by using an OBD-II scanner to clear any remaining check engine light after repairs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Toyota Tundra 5.7 engine diagram?
This visual schematic provides a detailed map of the 5.7L V8 i-FORCE engine used in Toyota Tundras. It illustrates the placement of mechanical parts like the alternator and water pump, alongside electrical components like the ECU, helping owners and mechanics navigate the engine bay during complex repairs.
How do you read Toyota Tundra 5.7 engine diagram?
Begin by identifying the front of the engine, typically where the drive belts and cooling fan are located. Use the provided legend to match numbered callouts with specific parts. Follow the path of the wiring harnesses and vacuum lines to understand how different systems, like fuel and air, interact.
What are the parts of Toyota Tundra 5.7 engine?
The 5.7L engine consists of a cast aluminum block, dual overhead cams, and 32 valves. Critical components shown in a diagram include the intake manifold, fuel rails, ignition coils, and various sensors that send data to the ECU via the OBD-II system for real-time engine monitoring and performance adjustments.
Why is the ECU important?
The ECU, or Engine Control Unit, acts as the brain of your Toyota Tundra. It processes data from sensors to manage fuel injection and ignition timing. If a fault occurs, the ECU triggers a check engine light and stores a diagnostic code accessible via an OBD-II port for fast troubleshooting.
What is the difference between an exploded view and a wiring diagram?
An exploded view diagram shows mechanical parts separated to clarify how they assemble, which is helpful for finding a specific torque spec. A wiring diagram focuses on electrical connections between the ECU and sensors, used primarily for electrical troubleshooting when a persistent diagnostic code is present during a scan.
How do I use Toyota Tundra 5.7 engine diagram?
Use the diagram to locate specific components when performing maintenance or troubleshooting. For example, if your check engine light is on, use the diagram to find the sensor associated with the diagnostic code. This ensures you are testing and replacing the correct part before attempting a complex engine repair.