Rear Door Leer Truck Cap Parts Diagram: Repair & ID Guide
A rear door Leer truck cap parts diagram illustrates the full structural layout of the glass, frame, and locking system. It helps you identify every component, such as gas struts, latches, and seals, ensuring you select the correct configuration for your specific model when performing repairs or replacements.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides a visual map for accurate part identification
- The locking mechanism is the most critical component to verify
- Check seal integrity regularly to prevent water leakage
- Use the diagram to cross-reference part numbers before ordering
- Essential for DIY repairs and professional restoration projects
Maintaining your truck topper requires a clear understanding of its hardware, and finding a reliable rear door leer truck cap parts diagram is the first step toward successful repair or upgrade. Whether you are dealing with a shattered glass panel, failing gas struts, or a stubborn locking mechanism, having a visual reference of the door’s internal structure ensures you order the correct components and perform the work safely. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the typical rear door configuration, helping you navigate the various mounting systems and latching hardware found on most modern caps. By the end of this article, you will be able to identify every critical element of your rear door assembly and understand how they function together as a unified system.
Understanding the Rear Door Component Layout
The rear door of a truck cap is more than just a piece of glass; it is a complex assembly designed to withstand wind resistance, vibration, and environmental exposure. When viewing a standard rear door leer truck cap parts diagram, the most prominent feature is the tempered safety glass, which serves as the primary structural component of the door. This glass is usually framed by an aluminum or fiberglass perimeter, depending on the specific model series of the cap. The frame provides the necessary rigidity for the hinges and the locking handle to mount securely without stressing the glass itself.
The system layout is typically organized into three main functional groups: the support system, the latching system, and the sealing system. The support system consists of the gas struts (also known as lift assists or shocks) and the top hinge rail. These components work in tandem to hold the door open and ensure it pivots smoothly along the top edge of the canopy. The latching system includes the exterior handle, internal cables or rods, and the rotary latches that catch onto the strike plates on the truck bed. Finally, the sealing system involves the bottom bulb seal and side weatherstripping, which are essential for keeping moisture and dust out of your cargo area. Understanding this configuration is vital because a failure in one component, such as a sagging gas strut, can place undue stress on other parts like the hinges or the glass frame.
Most Leer rear doors use specialized rotary latches. Unlike traditional residential locks, these latches rotate around a striker pin, providing a more secure, automotive-grade closure that prevents the door from bouncing while the truck is in motion.
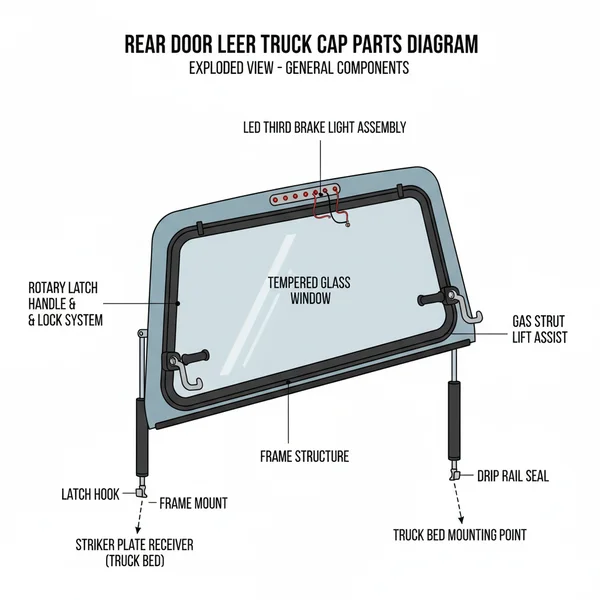
(Imagine a visual breakdown: At the top, the Hinge Rail attaches to the cap body. Two Gas Struts connect the side frames to the interior of the cap. The Center Handle connects via Latch Cables to Rotary Latches at the bottom corners. A Bottom Seal runs the entire width of the glass.)
Step-by-Step Guide to Interpreting and Servicing the Door

Reading a parts diagram is the easy part; applying that knowledge to a physical repair requires a methodical approach. To properly service your rear door, follow these steps to ensure you maintain the structural integrity of the unit.
- ✓ 1. Identify your specific model series (e.g., 100R, 100XR, or 100XL) to ensure the diagram matches your door style.
- ✓ 2. Locate the serial number on the inside roof of the cap for precise part matching.
- ✓ 3. Prepare tools: A 10mm socket set, a flat-head screwdriver for strut clips, and a hex key set.
- ✓ 4. Use the diagram to trace the path of the latching cables from the handle to the corners.
- ✓ 5. Check the tension of the actuator rods to ensure both sides release simultaneously.
When you are ready to perform a repair, such as replacing the gas struts or the lock handle, safety is paramount. The rear door glass is heavy and awkward. Always have a second person available to hold the glass in the open position while you remove the support hardware.
Never attempt to remove both gas struts at the same time without someone holding the door. Without the struts, the door can fall with enough force to shatter the tempered glass or cause personal injury.
To begin a hardware replacement, start by referencing the mounting points on your diagram. If you are replacing a lock handle, you will need to remove the interior cover plate to access the mounting screws. Once the handle is free, the linkage rods or cables must be detached. This is a critical moment to observe the orientation of the clips; the diagram will show how these components should be positioned. When installing new parts, reverse the removal process, ensuring that all fasteners are snug but not over-tightened, as excessive pressure can crack the fiberglass or stress the glass.
For those replacing the bottom seal, ensure the surface of the glass or frame is cleaned with isopropyl alcohol before applying the new adhesive-backed seal. Proper alignment of the seal according to the diagram ensures that the door closes with a water-tight fit against the truck’s tailgate.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Techniques
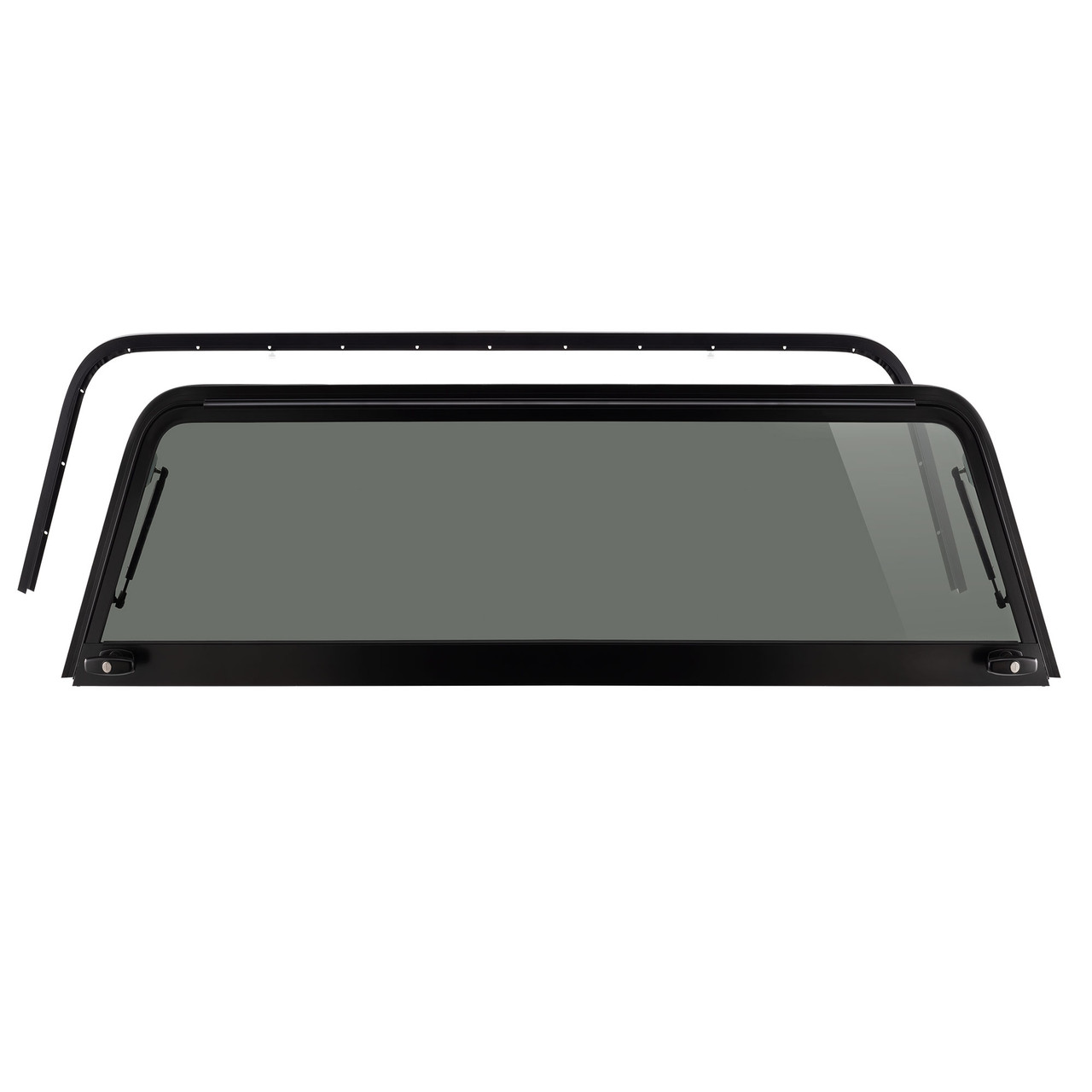

Even with a high-quality rear door leer truck cap parts diagram, real-world wear and tear can lead to frustrating issues. One of the most frequent problems is “strut fatigue,” where the gas-charged shocks lose their pressure over time. You will notice this when the door fails to stay open or feels significantly heavier to lift. If the struts are failing, the diagram will help you identify the specific pound-rating required for replacement—typically between 30 to 50 pounds of force depending on the glass size.
Another common issue is latch misalignment. If you find yourself having to slam the door or pull it to one side to get it to lock, your rotary latches likely need adjustment. Use the diagram to locate the adjustment nuts on the latch cables. By shortening or lengthening these cables, you can synchronize the timing of the latches so they catch the striker pins at exactly the same moment.
Warning signs of failing components include:
1. Grinding noises when turning the handle (indicates debris in the lock cylinder).
2. Water pooling on the tailgate (indicates a compressed or torn bulb seal).
3. The door sitting crooked in the frame (indicates a loose or bent hinge rail).
If you notice a hairline crack in the glass or if the frame has become separated from the glass panel, it is usually time to seek professional help. Tempered glass cannot be repaired once it begins to fail structurally, and professional installation ensures the door remains safe at highway speeds.
Tips and Best Practices for Maintenance
To extend the life of your truck cap hardware and avoid frequent part replacements, a proactive maintenance routine is essential. The components shown in your rear door leer truck cap parts diagram are subject to road salt, grime, and extreme temperature fluctuations, all of which can accelerate degradation.
Lubricate your lock cylinders and rotary latches every six months using a dry graphite spray. Avoid using oil-based lubricants like WD-40, as they attract dust and grit, which can eventually jam the internal tumblers of the lock.
Maintenance Recommendations:
1. Clean the gas strut rods: Wipe the silver shafts of the gas struts with a clean, soft cloth to remove dust. This prevents the seals from being scored and leaking gas.
2. Inspect the hinge rail: Periodically check the screws along the top hinge rail. Vibration from driving can loosen these over time, leading to a rattling door.
3. Treat the rubber seals: Use a silicone-based protectant on the bottom bulb seal and side weatherstripping to keep the rubber pliable and prevent it from cracking in the sun.
4. Check the striker pins: Ensure the pins mounted to the truck bed or cap frame are tight. A loose striker pin is the leading cause of “ghost opening,” where the door pops open while driving.
When it comes to replacement parts, always prioritize OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) components. While universal latches or struts may seem like a cost-saving measure, they often lack the exact specifications required for the unique configuration of a Leer door. Using the correct parts ensures that the geometry of the door remains within factory tolerances, preserving the resale value of your truck cap and ensuring the safety of your cargo. By keeping a copy of your rear door leer truck cap parts diagram handy and following these best practices, you can enjoy a functional, secure, and weather-tight truck topper for many years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is rear door leer truck cap parts diagram?
This diagram is a visual schematic representing the internal and external assembly of a Leer topper’s rear entrance. It details the precise structure of the door frame, glass, and hardware, allowing owners to visualize the entire system for maintenance, part identification, and structural troubleshooting during repair sessions.
How do you read rear door leer truck cap parts diagram?
To read the diagram, start by identifying the main frame lines and work inward toward smaller hardware. Each component is usually numbered, corresponding to a parts list. Pay close attention to the spatial layout, which indicates how different elements like the latches and gas struts interact within the configuration.
What are the parts of rear door leer truck cap?
The primary parts include the tempered glass door, the aluminum or fiberglass frame, gas shock struts for lifting, and the handle assembly. Additionally, the system features weatherstripping seals, rotary latches, strikers, and mounting hinges that ensure the door remains secure and watertight during vehicle operation.
Why is the locking component important?
The locking component is vital for cargo security and structural stability. This system ensures the rear door remains closed while driving, preventing vibrations from damaging the glass. A correctly functioning lock also compresses the weather seals, maintaining the interior environment and protecting your belongings from external weather conditions.
What is the difference between a rotary latch and a standard latch?
A rotary latch offers a more secure, automotive-style closure by rotating around a striker bolt, providing superior hold and noise reduction. Standard latches often use a simpler sliding or pivoting mechanism. The choice depends on your specific Leer model’s configuration and the level of security required.
How do I use rear door leer truck cap parts diagram?
Use the diagram to identify broken or worn-out parts before purchasing replacements. Match the visual layout of your door to the schematic to ensure compatibility. It also serves as a guide for disassembly and reassembly, showing exactly where each fastener and component fits within the overall structure.