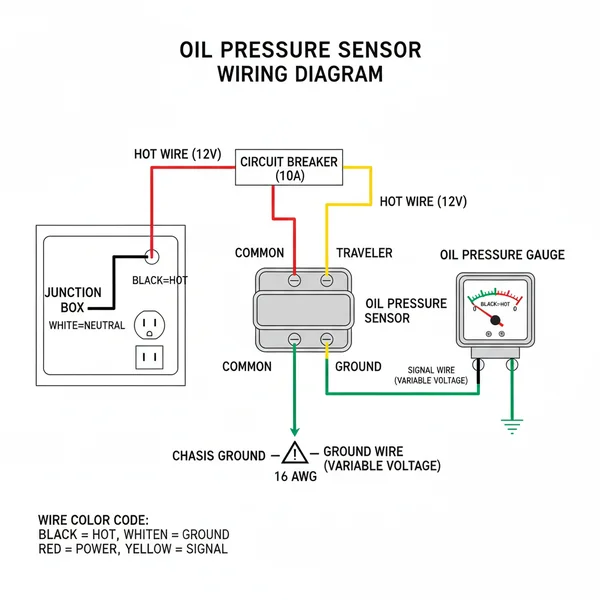
Oil Pressure Sensor Wiring Diagram: Installation Guide
An oil pressure sensor wiring diagram illustrates the connection between the engine block sensor and the instrument cluster. It identifies the signal path, ground requirements, and power source needed to convert mechanical pressure into electrical signals, ensuring your vehicle’s computer or gauge accurately monitors vital lubrication levels during engine operation.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Visualizes the electrical circuit between the engine sensor and the dashboard display.
- The variable resistor sensor unit is the most critical component to identify.
- Ensure the sensor threads are properly sealed to prevent high-pressure oil leaks.
- Check for clean, corrosion-free ground connections for accurate gauge readings.
- Use this diagram when troubleshooting flickering oil lights or inaccurate pressure gauges.
Understanding an oil pressure sensor wiring diagram is a fundamental skill for any automotive enthusiast, mechanic, or DIYer looking to maintain engine longevity. Whether you are troubleshooting a flickering warning light or installing a high-precision aftermarket gauge, the ability to trace electrical paths from the engine block to the dashboard is crucial. A proper wiring diagram does more than just show connections; it illustrates how the system converts mechanical pressure into an electrical signal that you can interpret. In this comprehensive guide, you will learn the anatomy of these circuits, how to identify specific terminals, and the steps required to ensure your engine monitoring system is both accurate and reliable.
An oil pressure sensor (or sending unit) typically functions by varying internal resistance based on the pressure exerted by the engine oil. This change in resistance alters the voltage sent to the gauge, which the needle or digital display then interprets as PSI or BAR.
Decoding the Oil Pressure Sensor Wiring Diagram
The standard wiring diagram for an oil pressure system is divided into three primary segments: the power source, the sending unit, and the display gauge. At the heart of the diagram is the gauge, which acts as the translator for the entire circuit. Most diagrams feature a hot wire that connects to a switched ignition source, ensuring the system only draws power when the vehicle is running. This prevents battery drain while the car is parked. The connection point on the back of the gauge is frequently a brass screw or a threaded stud, which provides a high-conductivity interface for the ring terminals.
In a typical 1-wire or 2-wire setup, you will see a signal path—sometimes referred to in technical circles as a traveler wire—that bridges the gap between the sensor on the engine block and the dashboard. If the system utilizes a 3-wire sensor, the diagram will also include a 5V or 12V reference line. The common terminal in these diagrams serves as the shared reference point for the electrical return. Furthermore, the ground wire is often represented by a chassis symbol, indicating that the sensor body or a dedicated wire must complete the circuit back to the negative battery terminal to allow current flow. Color-coding is standard in these diagrams: red or orange for the hot wire, black for the ground, and often blue or green for the signal wire.
[ IGNITION SWITCH (+) ]----------( HOT WIRE )----------[ GAUGE (+ PIN) ]
|
[ BRASS SCREW ]
|
[ SENSOR / SENDING UNIT ]<-------( TRAVELER/SIGNAL )-----------'
|
[ GROUND WIRE (-) ]----------[ CHASSIS GROUND ]
Visual representation of a standard 2-wire oil pressure monitoring circuit.
Step-by-Step Installation and Interpretation Guide

To successfully implement the layout shown in an oil pressure sensor wiring diagram, you must follow a methodical approach. Reading the diagram is the first step, but physical execution requires precision to avoid electrical shorts or inaccurate readings.
- ✓ Step 1: Identify Your Components - Before touching any wires, locate the oil pressure sending unit on your engine block. It is usually found near the oil filter or on the main oil gallery. Compare the physical terminals on your sensor and gauge to those illustrated in your specific diagram.
- ✓ Step 2: Prepare the Wiring Harness - Select the appropriate gauge wire (typically 18-AWG for signal and power) to handle the low current of the sensor system. Strip the ends and crimp on high-quality ring or spade terminals.
- ✓ Step 3: Connect the Hot Wire - Route a wire from a switched 12V source in your fuse box to the positive terminal on the gauge. Use a fuse tap to ensure the circuit is protected. This "hot" connection is what provides the initial voltage required for the gauge to operate.
- ✓ Step 4: Establish the Signal Path - Attach the signal wire to the brass screw marked "S" or "Send" on the gauge. Run this wire through the firewall using a rubber grommet and attach it to the terminal on the oil pressure sensor. This is the "traveler" that carries the variable resistance signal.
- ✓ Step 5: Ground the System - If your gauge has an internal light, you may need to connect a neutral wire or return wire to a solid metal part of the dashboard frame. Ensure the sensor itself is properly grounded; if you use too much thread sealant, it may insulate the sensor from the engine block, breaking the ground wire path.
- ✓ Step 6: Final Voltage Test - With the ignition on (engine off), use a multimeter to check the voltage at the gauge. You should see a steady reading consistent with your battery output.
Never connect the signal terminal of the sensor directly to a 12V power source without the gauge in-line. Doing so can instantly burn out the internal resistor of the sending unit, rendering it useless.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting

When the physical reality doesn't match the oil pressure sensor wiring diagram, problems arise. The most frequent issue is a "pegged" gauge, where the needle shoots to the maximum position the moment the ignition is turned on. This usually indicates a "ground out" on the signal wire or a completely failed sensor. Conversely, a needle that stays at zero despite the engine running often points to a break in the signal wire or a loss of power to the hot wire terminal.
The diagram helps you troubleshoot by identifying the common terminal points where connections are most likely to vibrate loose. Use a multimeter to check the resistance (ohms) of the sensor. If the sensor reads "infinite" resistance, the internal coil is broken. If the voltage at the gauge is fluctuating wildly, check the ground wire connection. A poor ground is the leading cause of "bouncing" needles or inaccurate readings. If the gauge lights up but the needle doesn't move, verify that the signal wire is attached to the correct brass screw and not swapped with the light circuit's neutral wire.
Tips & Best Practices for Wiring Success
To ensure your wiring job lasts for years, focus on the quality of your connections and the protection of your wires. Engine bays are harsh environments filled with heat, vibration, and moisture. Always use automotive-grade TXL or GXL wire, which features insulation designed to withstand high temperatures without melting.
When installing the sensor into the engine block, use a small amount of conductive thread sealant rather than standard white Teflon tape. Standard tape can act as an insulator, preventing the sensor from making a clean electrical connection with the block, which serves as the primary ground.
Another best practice is to utilize corrugated loom or expandable sleeving to protect the traveler wire as it passes near the exhaust manifold or moving suspension parts. When making connections at the gauge, use heat-shrink tubing over your crimp connectors. This prevents the hot wire from accidentally touching the common terminal or the mounting bracket, which would cause a short circuit. If you are working on a budget, sourcing a mechanical gauge may seem cheaper, but an electronic gauge using a proper oil pressure sensor wiring diagram is much safer, as it keeps pressurized hot oil out of the passenger cabin. Investing in a high-quality sending unit with a matching gauge ensures the resistance curves are synchronized, providing you with the most accurate data possible for your engine's health.
By following these guidelines and carefully studying your oil pressure sensor wiring diagram, you can confidently maintain or upgrade your vehicle's monitoring system. Proper wiring ensures that you are alerted to oil pressure drops before they become catastrophic, giving you peace of mind every time you turn the key.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is oil pressure sensor wiring diagram?
An oil pressure sensor wiring diagram is a schematic showing how the sensor connects to the engine control unit or dashboard gauge. It details the electrical path for power, signal, and grounding, allowing technicians to verify circuit integrity and ensure the system correctly reports engine oil pressure levels.
How do you read oil pressure sensor wiring diagram?
Start by identifying the power source, often a hot wire from the ignition. Follow the signal line from the sensor's common terminal to the gauge or PCM. Check for symbols representing the ground wire and any connectors, ensuring you understand the electrical flow from the sensor to the display.
What are the parts of oil pressure sensor?
The system typically consists of the sensor unit with a diaphragm and variable resistor, a wiring harness, and a gauge or ECU. It utilizes a hot wire for power and a ground wire to complete the circuit, translating physical pressure changes into measurable voltage or resistance values for monitoring.
Why is ground wire important?
The ground wire is critical because the oil pressure sensor operates by varying resistance to ground. If the ground connection is poor or corroded, the circuit will fail or provide inaccurate readings, potentially causing false warnings or failing to alert the driver of actual dangerously low oil pressure conditions.
What is the difference between a sensor and a switch?
An oil pressure sensor provides a variable signal for a continuous gauge reading, while a switch acts like a traveler wire for a simple warning light. The switch only triggers when pressure falls below a set point, whereas the sensor allows for real-time monitoring of exact engine lubrication levels.
How do I use oil pressure sensor wiring diagram?
Use the diagram to perform a continuity test between the sensor and the gauge. Identify the signal wire to check for breaks and verify that the hot wire provides sufficient voltage. This tool is essential for pinpointing whether a malfunction is located within the sensor unit or the wiring.