Mercedes Benz Engine Parts Diagram: Repair Guide
A Mercedes Benz engine parts diagram illustrates the complex relationship between mechanical hardware and electronic controls like the ECU. By studying this layout, you can easily locate sensors, interpret a diagnostic code from an OBD-II scanner, and ensure every bolt meets the exact torque spec during your next DIY repair.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Identify core mechanical and electronic engine components easily
- The ECU is the central control unit for engine performance
- Always use a specific torque spec when tightening engine bolts
- Diagrams simplify diagnosing complex sensor and hardware failures
- Use the diagram whenever performing major service or part replacements
Understanding the intricate engineering of a German-engineered powerplant requires more than just mechanical intuition; it demands a clear visual reference. Whether you are a dedicated DIY enthusiast or a first-time owner looking to save on repair costs, a high-quality mercedes benz engine parts diagram serves as your essential roadmap. This guide provides a detailed breakdown of the internal and external components that make these vehicles legendary for their performance. You will learn how to identify critical sensors, understand complex fluid systems, and navigate the electronic control architecture that keeps your luxury vehicle running smoothly and efficiently.
Understanding the Mercedes Benz Engine Parts Diagram
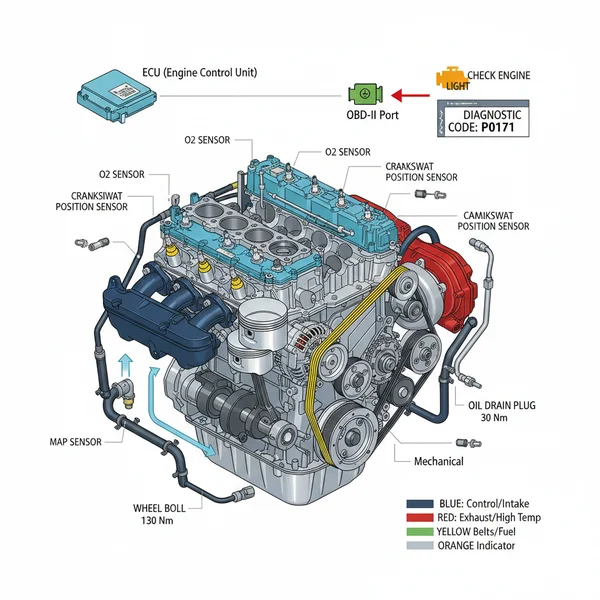
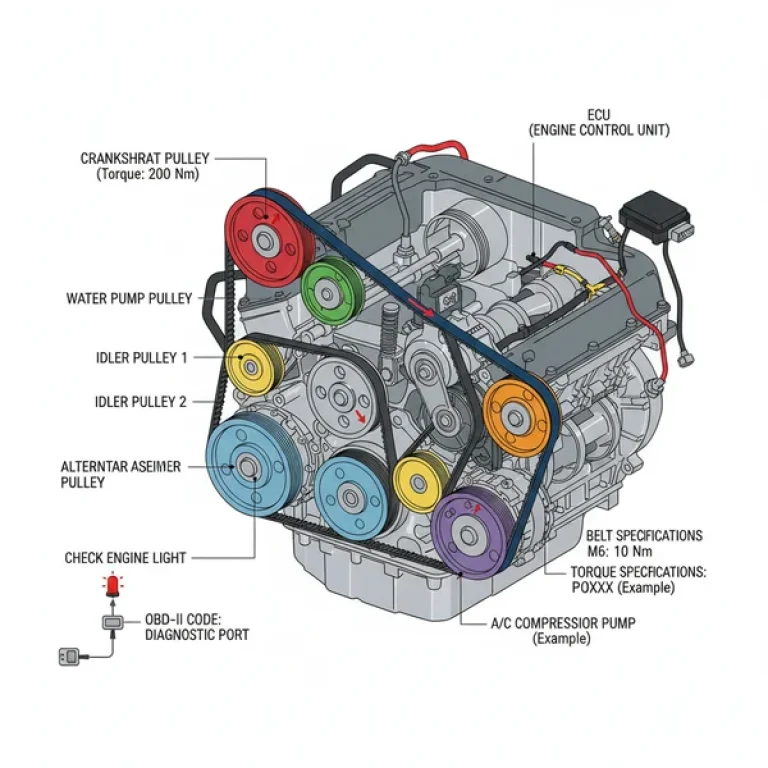
A Mercedes Benz engine parts diagram is significantly more complex than those of standard domestic vehicles due to the high level of integration between mechanical components and electronic sensors. When you first view the diagram, you will notice it is typically divided into several sub-systems: the cylinder block and head, the fuel injection system, the cooling circuit, and the electrical harness. The diagram serves as a blueprint, showing not just where a part is located, but how it interacts with neighboring components. For instance, you will see how the accessory belt routes around the alternator, water pump, and AC compressor, ensuring that the tensioner is correctly positioned to prevent slippage.
Most Mercedes diagrams use a proprietary numbering system. The first three digits usually indicate the engine series (e.g., M272, M274, or OM642), which is vital for ordering the correct replacement components from an authorized catalog.
At the heart of the schematic is the ECU (Electronic Control Unit), which is often depicted at the top or side of the engine bay. The diagram will trace wiring from this “brain” to various actuators and sensors. You will also find detailed views of the timing chain assembly, which is a critical area for Mercedes engines. Unlike vehicles with rubber belts, the Mercedes chain is designed for longevity, but the diagram will show the guide rails and hydraulic tensioners that require periodic inspection. Another focal point in these diagrams is the coolant flow path. Mercedes engines use a pressurized, multi-stage cooling system designed to reach operating temperature quickly, and the diagram illustrates how the thermostat manages flow between the block and the radiator.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A detailed 3D exploded view of a Mercedes-Benz M274 engine, showing the turbocharger, intake manifold, cylinder head, ECU placement, and the routing of the accessory belt. Key components are numbered with a corresponding legend.]
Visual breakdowns often use color-coding to differentiate between fluid types: blue or green for coolant flow, red for transmission fluid (if the cooler is integrated), and black or brown for engine oil. Understanding these variations is crucial because a 2.0L inline-4 turbo engine will have a vastly different component layout than a 4.0L V8 Biturbo, even if they share the same sensor types. Always ensure your diagram matches your specific VIN (Vehicle Identification Number) to account for mid-generation updates or regional specification differences.
Step-by-Step: How to Use and Interpret the Diagram

Interpreting a professional-grade mercedes benz engine parts diagram can be daunting at first glance. However, by following a structured approach, you can use these visuals to perform everything from basic maintenance to complex repairs. Before you begin, ensure you have a clean workspace and the necessary diagnostic tools, such as an OBD-II scanner, to cross-reference physical parts with digital error logs.
- ✓ Step 1: Identify Your Engine Code – Look for the engine ID etched into the block or on a sticker in the engine bay. Common codes like M271 or M276 will help you find the exact diagram for your vehicle’s configuration.
- ✓ Step 2: Locate the ECU and Main Sensors – Find the ECU on the diagram to understand the electrical “hub.” From here, trace the lines to the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor and Oxygen (O2) sensors.
- ✓ Step 3: Analyze the Accessory Belt Routing – If you are replacing a belt, look at the diagram’s belt path. Take note of which pulleys are grooved and which are smooth to ensure the accessory belt is seated perfectly.
- ✓ Step 4: Trace the Cooling System – Follow the coolant flow from the expansion tank through the water pump and into the engine block. This helps in identifying the specific hose or gasket that may be causing a leak.
- ✓ Step 5: Reference the Torque Specs – Most high-quality diagrams include a table of torque spec values. This is non-negotiable for Mercedes engines, as over-tightening a bolt into an aluminum block can cause catastrophic failure.
- ✓ Step 6: Match OBD-II Codes to Components – If your check engine light is on, use your OBD-II scanner to pull a diagnostic code. Find the component associated with that code on the diagram to locate it physically under the hood.
Mercedes-Benz engines often use “stretch bolts” (Torque-to-Yield). These are designed to be used only once. Always consult your diagram and manual to see if a bolt must be replaced after being loosened.
When working with these diagrams, you will need a specialized toolset. Mercedes frequently uses Torx and E-Torx (External Torx) fasteners. Having a complete set of these, along with a high-accuracy torque wrench, is essential. Before removing any part shown on the diagram, disconnect the battery—especially if you are working near the ECU or fuel rail—to prevent electrical surges or fire hazards. Use the diagram to identify “one-way” clips and plastic connectors that are notorious for becoming brittle over time; the diagram often shows the specific release mechanism for these delicate parts.
Troubleshooting Common Mercedes Engine Issues

One of the most frequent reasons owners consult a mercedes benz engine parts diagram is to address a persistent check engine light. When the ECU detects a parameter outside of the normal operating range, it triggers a diagnostic code. By using the diagram, you can pinpoint the exact sensor or actuator responsible. For example, a code P0011 indicates an issue with the camshaft timing. By looking at the diagram, you can find the Camshaft Adjustment Magnets on the front of the cylinder head, which are a common failure point in several Mercedes models.
Another common issue involves the timing chain and its associated tensioners. If you hear a rattling sound upon a cold start, the diagram will help you locate the inspection plug for the chain tensioner. Similarly, if you notice an overheating condition, the diagram is invaluable for tracing coolant flow to see if the thermostat or a specific bypass valve is stuck. Often, a leak isn’t a cracked block but a simple O-ring on a plastic coolant pipe, clearly identified in an exploded view diagram. Using the diagram to visualize the system allows you to rule out expensive parts in favor of simple, low-cost seals.
If you encounter a “limp mode” condition with no obvious mechanical failure, use the diagram to find the ground points for the engine wiring harness. Corrosion at these points often sends false signals to the ECU.
Best Practices for Engine Maintenance and Longevity
To keep your Mercedes Benz performing at its peak, preventative maintenance must be your top priority. The engineering tolerances in these engines are incredibly tight, meaning that using the correct torque spec for every spark plug, oil filter housing, and valve cover bolt is mandatory. Referencing your parts diagram ensures that you are not just replacing parts, but maintaining the structural integrity of the entire assembly. For instance, when servicing the accessory belt, it is best practice to replace the idler pulleys and tensioner at the same time, as shown in the diagram’s “drive group.”
Quality components are the cornerstone of Mercedes maintenance. While aftermarket parts are available, “OEM” (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts are recommended for anything connected to the ECU or the internal timing of the engine. Sensors like the Crankshaft Position Sensor or the MAF sensor are highly sensitive; using non-genuine parts can lead to erratic engine behavior and recurring check engine light issues. Additionally, always use the specific synthetic oil grade recommended for your engine type to ensure the timing chain remains properly lubricated, as these chains rely heavily on oil pressure and quality to function without stretching.
Finally, keep a digital or printed copy of the mercedes benz engine parts diagram in your vehicle or garage. Being able to quickly identify a part during a roadside emergency can be the difference between a simple fix and an expensive tow. Regularly inspect the areas highlighted in your diagram for signs of wear, such as oil “sweating” near the turbocharger or cracks in the plastic cooling reservoirs. By combining the visual data from a comprehensive diagram with a proactive maintenance schedule, you can ensure that your Mercedes Benz remains a reliable and powerful machine for hundreds of thousands of miles.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Mercedes Benz engine parts diagram?
A Mercedes Benz engine parts diagram is a technical illustration that identifies the physical location and part numbers of engine components. It covers everything from the cylinder head to electrical sensors, allowing owners to visualize how the system functions while facilitating accurate part ordering and maintenance for the vehicle.
How do you read a Mercedes Benz engine parts diagram?
To read a Mercedes Benz engine parts diagram, start by identifying the main engine block and then trace individual systems like fuel or cooling. Use the numbered legend to correlate parts with their specific names and OEM numbers, ensuring you understand the assembly sequence before starting any repairs.
What are the parts of a Mercedes Benz engine?
The main parts of a Mercedes engine include the cylinder head, pistons, camshafts, and intake manifold. Essential electronic components include the ECU, fuel injectors, and various sensors that communicate through the OBD-II system to monitor engine health and ensure emissions standards are met during various vehicle operating conditions.
Why is the ECU important in this diagram?
The ECU is critical because it acts as the brain of your Mercedes engine. It processes data from sensors to manage fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions. If the ECU detects an irregularity, it triggers the check engine light, alerting the driver to a potential mechanical or electronic failure.
What is the difference between mechanical parts and sensors?
The difference between a mechanical part and a sensor is their function; mechanical parts like valves provide the physical power, while sensors monitor conditions. For example, a crankshaft sensor tracks position, sending data to the ECU, which then uses that information to adjust timing and optimize the engine’s performance.
How do I use a Mercedes Benz engine parts diagram?
Use this diagram by referencing it alongside a diagnostic code retrieved from an OBD-II scanner. Once you identify the faulty component on the diagram, follow the layout to access the part, perform the repair, and then use the diagram to find the correct torque spec for safe reassembly.