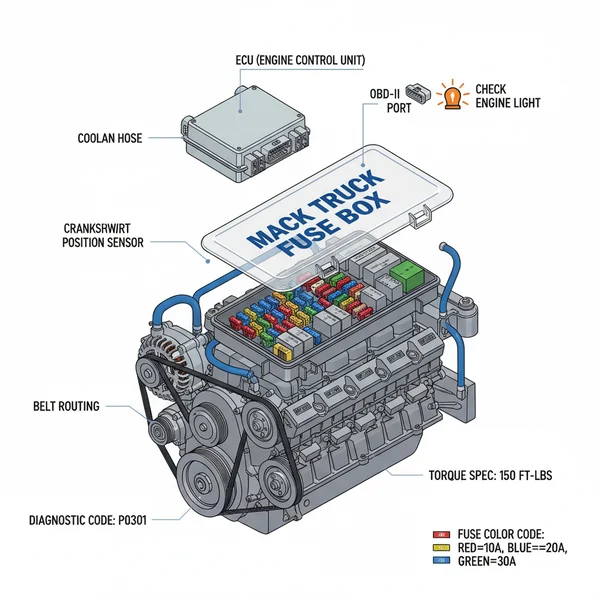
Mack Truck Fuse Box Diagram: Troubleshooting Electrical Issues
A Mack truck fuse box diagram identifies the location and function of every fuse and relay in the vehicle’s electrical system. It is essential for troubleshooting issues like a check engine light, accessing the ECU, or diagnosing power loss to the OBD-II port, ensuring the truck remains operational and safe.
📌 Key Takeaways
- The diagram provides a roadmap for locating specific circuits and power distribution points.
- Identifying the main power relay is critical for preventing total system failure.
- Always disconnect the battery before replacing high-amperage fuses to avoid electrical shock.
- Keep a printed copy of the diagram in the glovebox for roadside emergencies.
- Use the diagram when diagnosing a check engine light or power issues at the OBD-II port.
When your rig’s electrical system starts acting up on the road, having a reliable mack truck fuse box diagram is not just a luxury; it is a critical tool for keeping your vehicle operational. Whether you are dealing with a flickering headlight, a malfunctioning radio, or more serious issues like a non-responsive ECU, knowing exactly where to look saves hours of frustration and expensive downtime. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the fuse layouts found in modern Mack models, helping you interpret complex wiring maps and restore power to critical components quickly and safely. By the end of this article, you will understand how to locate your panels, identify specific circuits, and use diagnostic tools to resolve electrical faults efficiently.
Most Mack trucks, including the Anthem, Granite, and Pinnacle series, utilize a centralized power distribution center. Always refer to the specific legend printed on the inside of your fuse box cover, as configurations can vary based on the engine type and optional sleeper cabin features.
Understanding the Layout of a Mack Truck Fuse Box Diagram
The electrical architecture of a Mack truck is designed for durability and accessibility, typically divided into several key zones. The primary fuse box is often located behind a removable panel on the passenger side of the dashboard or integrated into the kick plate area. A mack truck fuse box diagram acts as a topographical map for this system, using a grid-based coordinate system or numerical labeling to identify every protected circuit.
Visually, the diagram breaks down components into three main categories: high-amp fuses, mini-fuses, and relays. High-amp fuses generally protect the main power feeds to the cab and the ECU (Engine Control Unit), while mini-fuses handle individual accessories like wipers, interior lights, and the OBD-II diagnostic port. Relays are represented by larger squares on the diagram and act as electronically controlled switches for high-draw items like the starter motor or the cooling fans.
Color-coding is a vital aspect of these diagrams. Most manufacturers adhere to standard automotive colors for fuse amperage: red for 10A, blue for 15A, yellow for 20A, and clear or white for 25A. The diagram will also specify the location of spare fuses and the fuse puller tool. In newer models, the diagram might include labels for multiplexed systems, where a single fuse might support a control module that governs several different outputs. Understanding this hierarchy is essential because a single blown fuse in a control circuit can trigger a check engine light or prevent the engine from cranking entirely.
While the physical fuse box contains the hardware, the diagram provides the context. For instance, if you are experiencing a loss of power to your logging device, the diagram will point you toward the “Auxiliary Power” or “Cigar Lighter” circuit. If the truck fails to communicate with a scanning tool, the diagram helps you verify the power supply to the OBD-II pin 16.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use the Fuse Box Diagram and Test Circuits

Navigating the electrical heart of a heavy-duty truck requires a methodical approach. Follow these steps to interpret your mack truck fuse box diagram and resolve electrical issues safely.
Step 1: Locate the Correct Panel
Depending on your specific Mack model, your fuses may be split between the interior cab and an exterior engine compartment box. Start by checking the passenger-side dash panel. You may need a flat-head screwdriver or simply to release a set of thumb tabs to remove the cover. Once removed, look at the back of the cover for the printed legend. If the cover is missing, you must consult the digital version of the diagram in your owner’s manual.
Step 2: Match the Symptom to the Circuit
Before pulling fuses, identify which system is failing. If the engine is running poorly or stalling, look for the ECU or Fuel Pump fuses. If the issue is related to emissions, check the circuits governing the aftertreatment system. Use the diagram to find the corresponding number (e.g., F24) and its physical location on the block.
Never replace a blown fuse with one of a higher amperage rating. Doing so can cause the wiring harness to overheat, potentially leading to an electrical fire. Always use the exact rating specified on the diagram.
Step 3: Perform a Visual and Tool-Based Inspection
Using the fuse puller tool, remove the suspect fuse. Hold it up to a light source to see if the metal link inside is broken. However, visual inspections can be deceiving. The best practice is to use a multimeter or a test light. With the ignition in the “On” position, touch the probes to the two small metal test points on top of the fuse. If you have voltage on one side but not the other, the fuse is blown.
Step 4: Check for Diagnostic Codes
If the fuses are intact but the system is still failing, connect a heavy-duty scanner to the OBD-II port. A blown fuse often leaves a “lost communication” diagnostic code in the system memory. For example, if the ECU fuse is intermittent, you might see codes related to the timing chain synchronization or sensor voltage out of range, simply because the module isn’t receiving steady power.
Step 5: Verify Ground and Torque
Electrical issues aren’t always about the “hot” side. If a fuse keeps blowing, check the ground connections near the fuse box. Ensure that the mounting bolts meet the manufacturer’s torque spec. Loose grounds create resistance, which increases heat and can cause fuses to fail prematurely.
Step 6: Reset and Test
Once the fuse is replaced, clear any active codes using your diagnostic tool to turn off the check engine light. Start the engine and monitor the system performance. If the fuse blows again immediately, there is a direct short-circuit in the wiring that requires further investigation.
Keep a small tube of dielectric grease in your glovebox. Applying a tiny amount to the fuse blades before installation prevents corrosion, especially in exterior fuse boxes where moisture might penetrate.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Electrical Faults

The most frequent issue truck drivers face is a recurring blown fuse. This is rarely a fault of the fuse itself but rather a symptom of an underlying problem. If you find yourself replacing the same fuse every week, the mack truck fuse box diagram can help you trace the circuit to find the culprit. Common areas of failure include:
- ✓ Chafed wiring harnesses rubbing against the frame or engine block.
- ✓ Corroded trailer cord plugs causing shorts in the lighting circuit.
- ✓ Failed relay coils that draw too much current.
If you see a check engine light accompanied by a “low voltage” diagnostic code, the problem might be upstream from the fuse box. Check your accessory belt to ensure the alternator is spinning correctly. A slipping belt can cause erratic voltage spikes that confuse the ECU. Furthermore, check the coolant flow around the engine oil cooler; excessive heat in the engine bay can increase electrical resistance in the wiring, leading to ghost failures that disappear once the truck cools down.
Tips and Best Practices for Mack Truck Electrical Maintenance
Maintaining the integrity of your electrical system is just as important as changing your oil. A well-maintained fuse box ensures that every sensor, from the timing chain position sensor to the exhaust gas temperature probe, communicates accurately with the cab.
First, always use high-quality, OEM-grade fuses. Cheap, off-brand fuses may not blow at the rated amperage, putting your expensive ECU at risk. Second, keep your fuse box dry. If you notice moisture inside the cab-side panel, check the windshield seals or the door weatherstripping for leaks. Moisture is the primary cause of “green crust” corrosion on fuse terminals, which leads to intermittent connectivity issues.
Regularly inspect your accessory belt and tensioner. The alternator provides the raw power that the fuse box distributes; if the belt is worn, the inconsistent power can cause relays to chatter and wear out prematurely. Additionally, ensure that your battery terminals are clean and tightened to the correct torque spec. A loose battery connection can cause a surge that blows multiple fuses simultaneously.
Finally, always keep a printed copy of the mack truck fuse box diagram in your document folder. While many modern trucks have digital displays, if your main screen fails due to a blown fuse, you will need that physical paper copy to find the solution. Following these maintenance steps will reduce the likelihood of being stranded by a simple five-cent piece of plastic and metal. By understanding your truck’s electrical “map,” you empower yourself to handle repairs with confidence and precision.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Mack truck fuse box diagram?
A Mack truck fuse box diagram is a visual map showing the layout and assignment of fuses, relays, and circuit breakers. It identifies which fuse protects specific components like the ECU, headlights, or interior electronics. This guide helps drivers and mechanics quickly pinpoint failed circuits without testing every individual fuse.
How do you read Mack truck fuse box diagram?
To read the diagram, match the numbers or labels on the fuse box cover with the corresponding icons or descriptions on the schematic. Look for amperage ratings and color codes that signify the circuit’s capacity. Understanding these labels allows you to identify which fuse controls the OBD-II or sensors.
What are the parts of Mack truck?
Major parts of the Mack truck electrical system include the Engine Control Unit (ECU), the fuse distribution panel, and the alternator. The fuse box acts as the central hub, housing mini-fuses, maxi-fuses, and relays that protect sensitive electronics and high-draw components like the starter motor or heating elements.
Why is ECU important?
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) is the “brain” of the truck, managing fuel injection, emissions, and engine timing. If the ECU fuse blows, the engine may not start or could throw a diagnostic code. Ensuring the ECU has a stable power supply is vital for optimal truck performance and safety.
What is the difference between OBD-II and ECU?
The ECU is the computer that controls the engine’s performance and monitors sensors. The OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics) is the standardized port used to communicate with the ECU. While the ECU processes data, the OBD-II port allows technicians to retrieve a diagnostic code to identify specific mechanical or electrical faults.
How do I use Mack truck fuse box diagram?
Use the diagram by first locating the fuse box, usually behind the dash or in the engine bay. Reference the chart to find the specific fuse related to your problem, such as a check engine light. This allows for targeted testing and replacement of blown fuses or malfunctioning relays.