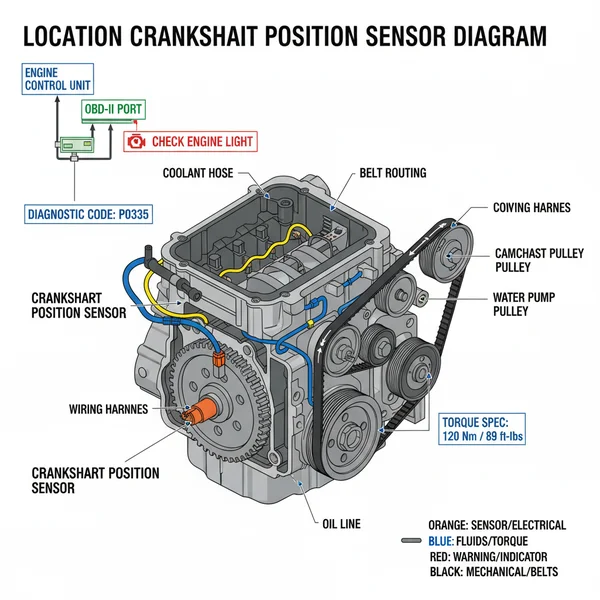
A location crankshaft position sensor diagram identifies where this vital component sits relative to the flywheel or crankshaft pulley. It provides the visual context needed to resolve a check engine light by locating the sensor that sends timing data to the ECU. Use it to find the mounting bolt and verify the wiring harness.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides the exact mounting coordinates on the engine block or bell housing
- Helps identify the sensor responsible for sending RPM data to the ECU
- Critical for resolving no-start conditions or stalling issues
- Illustrates the electrical connector path for testing circuit integrity
- Essential when a diagnostic code points to a timing synchronization error
Locating a faulty sensor can be the difference between a quick fix and a frustrating day in the garage. This guide provides a comprehensive location crankshaft position sensor diagram overview to help you identify, test, and replace this critical engine component. Whether you are dealing with a sudden stall or a stubborn no-start condition, understanding where this sensor sits and how it interacts with your engine’s internal geometry is essential. In the following sections, you will learn about the different mounting styles used by various manufacturers, the specific tools required for access, and how to interpret the electrical signals that the sensor sends to your vehicle’s computer. By following this technical breakdown, you will gain the confidence to perform your own diagnostics and repairs, saving time and money while ensuring your engine runs at peak efficiency.
The crankshaft position sensor (CKP) is the “heartbeat” monitor of your engine. It tracks the exact position and rotational speed of the crankshaft, allowing the computer to time fuel injection and spark plug firing perfectly.
Understanding the Location Crankshaft Position Sensor Diagram
When looking at a location crankshaft position sensor diagram, the most important element to identify is the relationship between the sensor and the reluctor wheel (also known as a tone ring). The diagram typically illustrates the sensor mounted in one of three primary locations. The most common location is at the front of the engine, usually positioned just behind or beside the harmonic balancer. In this configuration, the sensor “reads” teeth on the back of the pulley or a dedicated wheel attached to the crankshaft snout. This area is often crowded by the accessory belt and various pulleys, making the diagram essential for visual navigation.
Another common variation shown in diagrams is the rear-mounted sensor. In these designs, the sensor is located at the back of the engine block, near the junction where the engine meets the transmission. Here, the sensor monitors the teeth on the flywheel or flexplate. Diagrams for these models often require a “bottom-up” perspective, as the sensor is usually accessed from underneath the vehicle. Finally, some high-performance or modern overhead cam engines may place the sensor deep within the timing chain housing, where it can monitor the crankshaft’s internal counterweights directly.
The diagram will also highlight the electrical connector and the mounting bolt. Most crankshaft sensors are held in place by a single 10mm or 8mm bolt. The diagram should clearly label the air gap—the tiny space between the sensor tip and the reluctor teeth. If this gap is inconsistent or obstructed by debris, the ECU (Engine Control Unit) will receive “dirty” data, leading to misfires or total engine failure.

Step-by-Step Guide to Locating and Replacing the Sensor

Interpreting a location crankshaft position sensor diagram and translating that to physical work on your vehicle requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to ensure a safe and successful replacement.
Step 1: Perform an Initial Diagnostic Scan
Before picking up a wrench, use an OBD-II scanner to pull any stored fault codes. If you see a diagnostic code like P0335 (Crankshaft Position Sensor “A” Circuit) or P0336 (Range/Performance), your suspicions are confirmed. The scanner provides the electronic proof that matches the physical symptoms you are experiencing.
Step 2: Ensure Vehicle Safety
Park the vehicle on a level surface and engage the parking brake. Since many sensors are located near the bottom of the block, you will likely need to lift the front of the car using a floor jack and secure it with jack stands. Never work under a car supported only by a jack. Disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent any electrical shorts or accidental engine cranking while your hands are near the accessory belt.
Step 3: Clear the Path to the Sensor
Referencing your diagram, identify any components blocking your view. You may need to remove the plastic splash shield under the engine or, in some cases, the accessory belt itself if the sensor is tucked behind the tensioner. If the sensor is rear-mounted, you might need to move heat shields or wiring harnesses out of the way.
Step 4: Inspect for Fluid Leaks
Before removing the old sensor, check the area for signs of coolant flow leaks or oil spray. A leaking water pump or front main seal can coat the sensor in fluids, causing the internal electronics to overheat or short out. If you find a leak, it must be repaired, or the new sensor will likely fail shortly after installation.
Step 5: Disconnect and Remove
Carefully depress the locking tab on the electrical connector and pull it away from the sensor. Be gentle, as these plastic clips become brittle over time due to engine heat. Use a socket and extension to remove the mounting bolt. If the sensor is stuck, gently wiggle it back and forth or use a pair of pliers to rotate it slightly to break the O-ring seal.
Step 6: Install the New Component
Compare the old sensor to the new one to ensure they are identical in length and connector shape. Lubricate the O-ring on the new sensor with a drop of clean engine oil to help it slide into the hole without tearing. Insert the sensor and hand-thread the bolt to avoid cross-threading.
Step 7: Final Tightening and Testing
Consult your service manual for the specific torque spec. Usually, these bolts require very little force (often between 7 and 10 foot-pounds). Over-tightening can crack the sensor’s plastic housing. Reconnect the wiring harness, lower the vehicle, and reconnect the battery.
Always wait for the engine to cool completely before attempting this repair. The crankshaft sensor is often located near the exhaust manifold or the engine block where heat is retained longest.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting

The most frequent problem users encounter is a “crank, no-start” condition. Because the ECU relies on the crankshaft sensor to know when to trigger the ignition, a dead sensor means no spark. If your check engine light is on, the computer has likely already detected an irrational signal. However, sensors can also fail “softly,” where they only malfunction when they get hot. This results in the engine stalling after 20 minutes of driving and refusing to start until it cools down.
Using the location crankshaft position sensor diagram helps you troubleshoot by identifying nearby interference. For example, if the diagram shows the sensor wire running near high-voltage spark plug wires, electromagnetic interference (EMI) could be the culprit. Additionally, check the harness for fraying. Since these sensors are low to the ground, road debris can sometimes snag the wiring, leading to intermittent signals that are difficult to diagnose without a visual inspection.
- ✓ P0335: No signal detected by the ECU.
- ✓ P0336: Signal is present but “noisy” or out of sync.
- ✓ Tachometer Drop: If the needle hits zero while cranking, the sensor is likely dead.
Tips and Best Practices for Maintenance
To ensure longevity after following a location crankshaft position sensor diagram for replacement, always choose high-quality OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) sensors. While aftermarket options are cheaper, the CKP is a precision instrument; slight variations in magnetic strength can cause timing drift, which reduces fuel economy and power.
Another pro tip is to inspect the reluctor wheel through the sensor hole using a flashlight before installing the new part. If any of the teeth are chipped or if there is metal debris stuck to the wheel, the new sensor will provide inaccurate readings. Cleaning the mounting surface with a lint-free rag is also vital to ensure the sensor sits perfectly flush, maintaining the correct air gap.
Some vehicles require a “Crankshaft Variation Relearn” procedure after replacement. This involves using a high-end scan tool to tell the ECU to recalibrate itself to the new sensor’s specific signal pattern.
Regular maintenance of your cooling system can also indirectly protect your sensor. Since coolant flow issues can lead to localized hotspots on the engine block, an overheating engine can melt the internal windings of a crankshaft sensor. By keeping your engine temperature within normal parameters and checking the integrity of your timing chain or belt, you ensure that the mechanical components the sensor monitors stay in perfect alignment. Following these steps and utilizing a proper diagram ensures your vehicle remains reliable for miles to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a location crankshaft position sensor diagram?
A location crankshaft position sensor diagram is a visual map showing where the sensor is mounted on an engine. It typically highlights the sensor’s proximity to the crankshaft balancer or transmission bell housing. This tool is essential for mechanics trying to troubleshoot a specific diagnostic code related to engine timing.
How do you read a location crankshaft position sensor diagram?
To read this diagram, identify the engine block and transmission meeting point first. Look for a small cylindrical sensor plugged into the block or housing. The diagram will often show the electrical connector orientation and the single retaining bolt, which usually requires a specific torque spec during the reinstallation process.
What are the parts of a location crankshaft position sensor diagram?
The primary parts include the sensor body, the magnetic pickup tip, the mounting flange, and the electrical pigtail or connector. It also illustrates the reluctor ring or tone wheel on the crankshaft that the sensor monitors to send rotation data directly to the vehicle’s onboard ECU system for timing.
Why is the ECU important in this diagram?
The ECU is the brain of the vehicle that interprets the pulses from the crankshaft position sensor. Without this data, the ECU cannot manage fuel injection or ignition timing correctly. If the sensor fails, the ECU triggers a check engine light and records a diagnostic code in the OBD-II system.
What is the difference between a crank and cam sensor?
While a location crankshaft position sensor diagram shows the sensor at the bottom of the engine near the crank, a camshaft sensor is located at the top near the cylinder head. Both send data to the ECU, but the crankshaft sensor is the primary reference for engine speed and position.
How do I use a location crankshaft position sensor diagram?
Use the diagram to identify the physical location before starting a repair. It helps you navigate around components like the starter or exhaust manifold that might block your view. Once located, use an OBD-II scanner to confirm the failure and follow the diagram to ensure proper wire harness routing.