International 4300 Fuse Box Diagram: Troubleshooting Guide
The 2005 International 4300 fuse box diagram allows drivers to locate the main electrical panel, usually situated on the passenger side dashboard. By identifying specific fuses for the ECU or OBD-II port, you can troubleshoot issues causing a check engine light and restore power to critical sensors for accurate diagnostic code reading.
📌 Key Takeaways
- The diagram identifies power routing for essential engine and cabin electronics
- The ECU fuse is the most critical component for engine operation and starting
- Always disconnect the battery before replacing high-amperage circuit breakers
- Use the diagram to verify fuse ratings before installation to prevent electrical fires
- Reference this diagram whenever the OBD-II port fails to communicate with scanners
Finding an accurate 2005 international 4300 fuse box diagram is the first and most crucial step in resolving electrical issues on this heavy-duty workhorse. Whether you are dealing with a dead instrument cluster, flickering headlights, or a complete lack of power to the diagnostic port, the fuse box serves as the primary map for your truck’s nervous system. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the electrical distribution system, explaining where these components are located, how to interpret the labels, and what specific circuits control vital systems like the engine management and lighting. By understanding this diagram, you will learn how to efficiently isolate faults, replace damaged components safely, and restore your vehicle to peak operating condition.
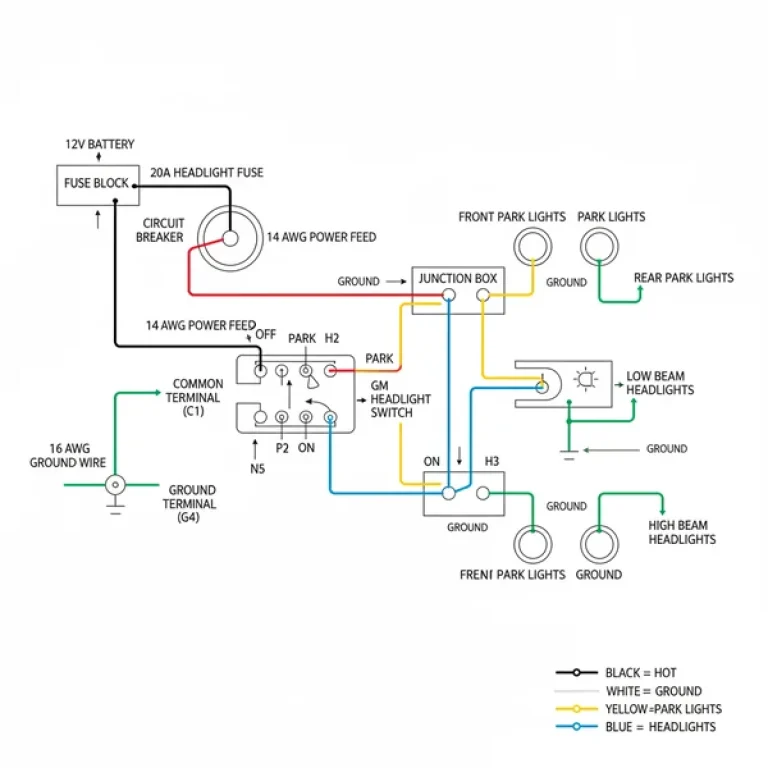
The electrical system of the 2005 International 4300 is split into several distribution points, primarily focused on the in-cab fuse panel and the under-hood power distribution center. The in-cab panel is typically located on the passenger side of the dashboard, concealed behind a removable plastic cover. This panel contains the fuses and relays for interior comfort features, lighting, and low-amperage control circuits. Each slot is numbered and corresponds to a specific legend printed on the inside of the access door. The layout is designed logically, grouping lighting circuits together and separating high-draw motor circuits to prevent cascading failures.
In addition to the cabin panel, there is often a “Mega-Fuse” block or a primary power distribution center located near the battery box or on the driver-side firewall. This secondary location handles high-amperage power delivery to the ECU (Engine Control Unit), the starter solenoid, and the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) blower motors. The diagram for this section uses larger-format fuses and high-capacity relays. Understanding the color-coding is essential: standard blade fuses follow the industry-standard colors (blue for 15A, yellow for 20A, green for 30A), while the larger J-Case fuses provide protection for heavy-duty components. Many diagrams also highlight the link to the OBD-II port, which is critical for technicians trying to pull a diagnostic code when the check engine light is illuminated.
The 2005 International 4300 utilizes a multiplexing system for certain lighting and body controls. This means that while a fuse might look intact, the Body Controller (BC) may have “soft-tripped” a circuit, requiring a battery reset or a specialized scanner to clear the fault.
Reading and interpreting the 2005 international 4300 fuse box diagram requires a systematic approach to ensure you don’t accidentally disable a critical safety system. Follow these steps to navigate the electrical diagnostic process:
1. Locate the Access Points: Begin by finding the primary fuse panel inside the cab. It is located on the lower dash panel on the passenger side. Pull the latch or remove the thumb screws to reveal the panel. Locate the secondary power distribution center under the hood, usually mounted on the firewall or near the driver-side wheel well.
2. Clean and Inspect the Legend: Dust and grime can make the printed diagram difficult to read. Use a damp cloth to clean the inside of the fuse box cover. Match the physical orientation of the fuses in the box to the diagram on the cover. Note that the diagram is usually a mirror image of the layout or oriented based on the way the cover sits when installed.
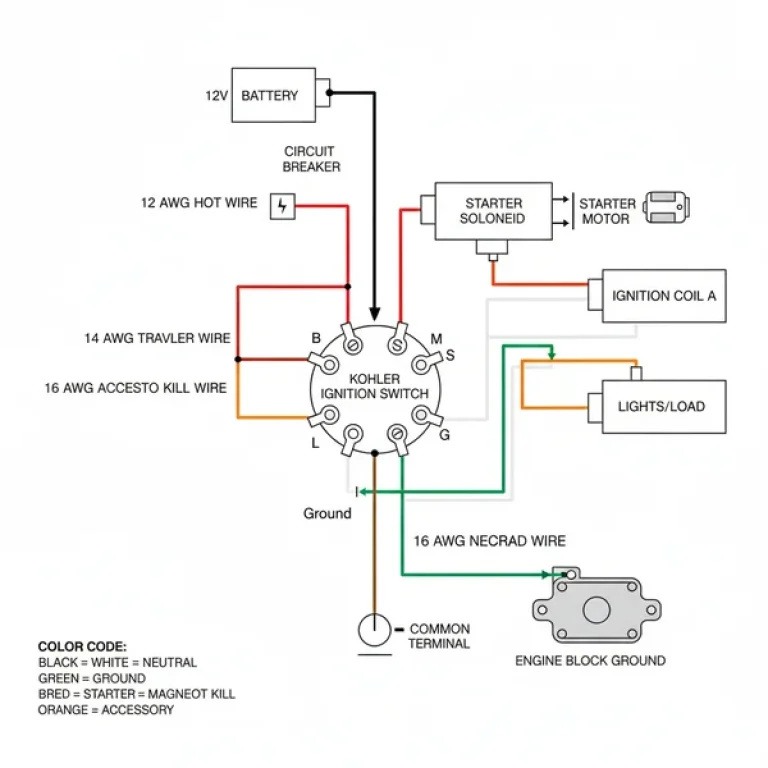
3. Identify the Symptom-Related Fuse: If your check engine light is on but your scanner won’t connect, look specifically for the fuse labeled “OBD-II,” “Diagnostic,” or “Cigar Lighter,” as these often share a power source. If the engine won’t crank, focus on the “ECU Power,” “Ignition,” and “Starter Relay” positions.
4. Use the Right Tools: Never pull a fuse with your fingers if you can avoid it. Use a dedicated fuse puller tool to prevent cracking the plastic housing. You will also need a digital multimeter or a 12V test light to check for continuity without removing every single fuse.
5. Verify the Amperage: Before replacing a blown fuse, check the diagram for the correct amperage rating. Installing a 30A fuse where a 10A fuse is required can lead to melted wires or even an electrical fire.
6. Check for Grounding and Connection: If the fuse is intact but the component still doesn’t work, use your multimeter to check the ground side of the circuit. On the International 4300, ground wires are often white and can become corroded near the frame rails.
7. Inspect the Relays: Relays are the square boxes in the panel. Unlike fuses, you cannot tell if they are bad just by looking at them. The diagram will show which relay controls the accessory belt driven components like the A/C compressor. You can often swap a known good relay (like the horn relay) with a suspect one (like the A/C relay) to test functionality.
8. Final Torque and Seal: If you are working on the under-hood distribution block, ensure all nuts and bolts holding the main power cables are tightened to the correct torque spec (typically 80-100 inch-pounds for smaller terminals). Ensure the weather seal on the cover is intact to prevent moisture from causing future shorts.
Never bypass a blown fuse with a piece of wire or a “jumper.” Fuses are designed to be the weakest link in the circuit; bypassing them shifts the heat load to the wiring harness, which can result in thousands of dollars in damage or a vehicle fire.
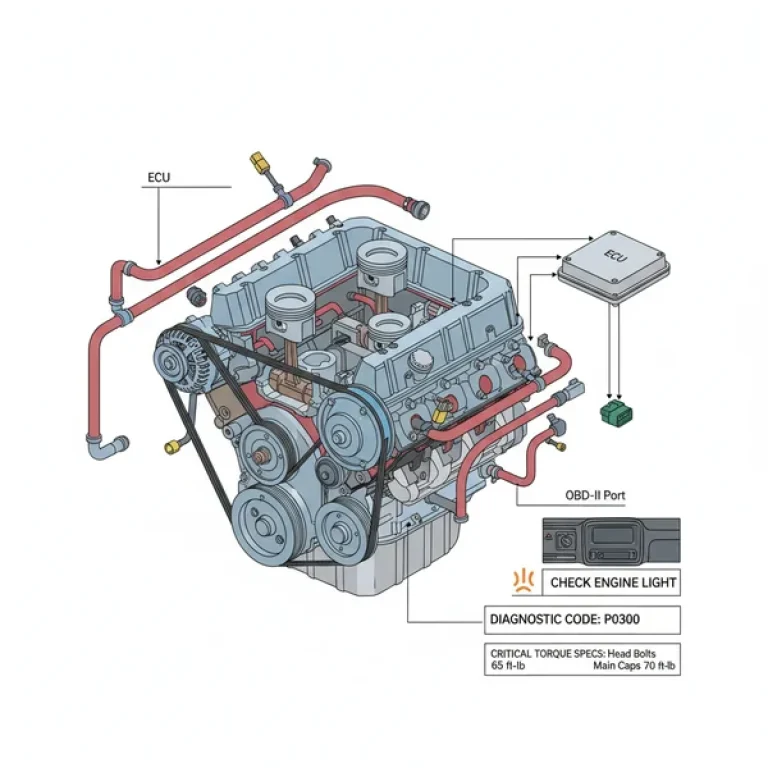
When troubleshooting a 2005 International 4300, you will likely encounter a few frequent issues that the fuse diagram can help resolve. One common problem is the “no-start, no-communication” issue. This usually occurs when the ECU fuse is blown or the relay has failed due to heat. Without power to the ECU, the truck cannot manage fuel injection or timing, and a diagnostic scanner will fail to pull any diagnostic code.
Another frequent complaint involves the exterior lighting. If all your trailer lights or marker lights go out at once, it is rarely a bulb issue; it is usually a blown “Tail/Marker” fuse or a faulty relay in the body controller interface. Look for signs of “pushed-back” pins in the fuse box, where the metal terminal behind the fuse has been pushed out of its plastic seat, resulting in an intermittent connection. If you see signs of melting or discoloration around a fuse slot, this indicates a high-resistance short-circuit that requires professional attention.
Keep a spare “Diagnostic Port” fuse in your glovebox. Many roadside inspectors use the OBD-II port to check for emissions compliance, and if your port lacks power due to a blown cigar lighter fuse, you could face an unnecessary fine or delay.
To maintain the electrical health of your 4300, follow these best practices. First, always perform a visual inspection of the accessory belt and alternator connections during every oil change. A slipping belt can cause erratic voltage, which may lead to “ghost” fuse failures where fuses blow for no apparent reason due to voltage spikes. Additionally, while the 4300’s engine relies on a gear-driven system rather than a timing chain, the electrical sensors monitoring engine timing are highly sensitive to voltage drops.
Maintaining proper coolant flow is also surprisingly relevant to your electrical system. The engine temperature sensors and cooling fan relays are integrated into the ECU’s logic. If the cooling system fails and the engine begins to overheat, the ECU may intentionally trip certain circuits or limit power to protect the hardware. Ensure that the wires leading to the fan clutch and temperature sensors are routed away from hot exhaust manifolds to prevent the insulation from melting and shorting against the engine block.
- ✓ Use Dielectric Grease: Apply a small amount of dielectric grease to the pins of external relays to prevent moisture intrusion and corrosion.
- ✓ Label Custom Add-ons: If you add strobe lights or GPS units, label where you tapped into the fuse box to make future troubleshooting easier.
- ✓ Check Battery Grounds: A loose ground at the frame can mimic a blown fuse by cutting off the return path for the electricity.
- ✓ Carry a Test Light: A simple 12V test light is the fastest way to check both sides of a fuse while it is still plugged into the box.
By keeping a printed copy of the 2005 international 4300 fuse box diagram in your truck, you empower yourself to handle most common electrical issues on the road. This proactive approach not only saves time and money on service calls but also ensures that your vehicle remains safe and compliant with all road regulations. Remember that the fuse box is the first line of defense; respect the amperage ratings, keep the connections clean, and always investigate the root cause of a blown fuse to prevent it from happening again.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the International 4300 Fuse Box Diagram: Troubleshooting Guide
Identify the fuse panel location, typically behind the passenger side dashboard panel or near the battery box.
Locate the specific circuit on the diagram map that corresponds to the component experiencing an electrical failure.
Understand the amperage requirements and fuse types indicated on the diagram to prevent damaging the electrical system.
Connect a diagnostic code scanner to the OBD-II port to see if electrical issues are triggering dashboard warnings.
Verify that the new fuse is properly seated and ensure the mounting bracket meets the manufacturer’s torque spec.
Complete the installation by testing the circuit and confirming that the check engine light has been cleared successfully.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is International 4300 fuse box diagram?
This diagram is a visual schematic used to identify the location, amperage, and function of every fuse and relay in your truck. It is essential for pinpointing electrical failures in the ECU or lighting systems, allowing you to quickly find which fuse corresponds to specific interior or exterior components.
How do you read International 4300 fuse box diagram?
To read the diagram correctly, match the numbered slot on the physical fuse panel with the legend provided in the schematic. The diagram identifies the circuit name, fuse type, and required amperage. This helps ensure you do not use an incorrect fuse that could lead to electrical fires.
What are the parts of International 4300 fuse box?
The system consists of several parts including standard blade fuses, high-voltage relays, and circuit breakers. It also houses the connections for the OBD-II diagnostic port and power distribution for the ECU. Understanding these parts helps you differentiate between a simple blown fuse and a more complex relay failure.
Why is the ECU fuse important?
The ECU fuse is critical because it provides power to the truck’s central engine control module. If this fuse blows, the engine may stall or fail to start entirely. Checking this fuse is a vital first step when troubleshooting a check engine light or communication errors during diagnostics.
What is the difference between the dash and engine fuse boxes?
The dashboard fuse box typically handles interior electronics like lights and gauges, while the engine compartment or battery box fuses handle heavy-duty power distribution. The dashboard panel is usually more accessible for routine maintenance, whereas the exterior boxes protect high-current components from environmental factors and heavy electrical loads.
How do I use International 4300 fuse box diagram?
Use the diagram to find the power supply fuse for the diagnostic systems. If the OBD-II port isn’t working, check the designated fuse. Once power is restored, you can retrieve a diagnostic code to identify why the light is on, ensuring the sensor circuits are receiving proper voltage.