Infiniti G37 Serpentine Belt Diagram: Routing & Install
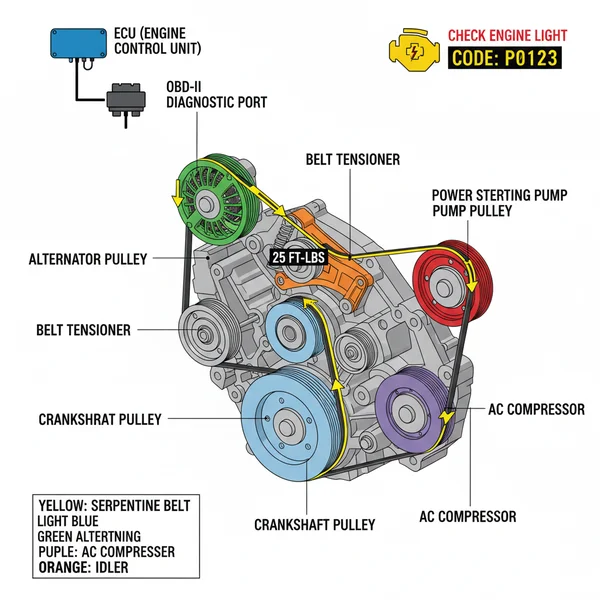
The Infiniti G37 serpentine belt diagram illustrates the precise path the drive belt takes around the alternator, power steering pump, and crankshaft. Following this visual guide ensures proper tension and prevents a check engine light or diagnostic code from appearing due to charging system failures or engine overheating issues.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Visualizes the complex routing path for the VQ37VHR engine
- Identifies the automatic tensioner pulley as the critical adjustment point
- Ensure the belt is seated in all pulley grooves to prevent fraying
- Use the diagram to avoid backwards installation which reverses component rotation
- Consult this when performing routine maintenance or replacing a failed alternator
Maintaining the peak performance of your luxury sports sedan or coupe requires a keen eye on the engine’s peripheral components. If you are hearing a high-pitched squeal upon startup or noticing a heavy feel in your steering, you likely need to inspect your accessory belt system. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed infiniti g37 serpentine belt diagram and a walk-through of the replacement process for the VQ37VHR engine. By understanding the routing and tensioning mechanisms of this system, you can ensure your vehicle remains reliable, avoiding the stress of a snapped belt and the subsequent loss of vital engine functions. In the following sections, you will learn how to identify each pulley, the correct sequence for routing, and the professional tips necessary for a successful DIY installation.
Understanding the Infiniti G37 Serpentine Belt Diagram
The Infiniti G37 utilizes a single, long serpentine belt—often referred to as an accessory belt—to drive several critical engine components. Unlike some older vehicles that use multiple V-belts, the G37’s VQ37VHR engine relies on one continuous loop. This design is efficient but means that if the belt fails, every system it supports fails simultaneously.
When looking at the infiniti g37 serpentine belt diagram from the front of the engine bay, the routing follows a complex “S” pattern around seven distinct points of contact. The diagram essentially maps out the path the belt must take to ensure the ribbed side and the flat side of the belt interface correctly with their respective pulleys.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A technical illustration showing the front of a VQ37VHR engine. The belt starts at the large Crankshaft Pulley (bottom center), goes up to the Power Steering Pump (top left), loops under an Idler Pulley, over the Alternator (top right), down to the A/C Compressor (middle right), and finally around the Tensioner Pulley (middle left) before returning to the Crankshaft.]
The key elements of this diagram include:
- ✓ Crankshaft Pulley: The primary drive source. It provides the rotational force for the entire system.
- ✓ Alternator: Located at the top right, this provides electrical power and charges the battery.
- ✓ Power Steering Pump: Located at the top left, providing the hydraulic pressure needed for easy maneuvering.
- ✓ A/C Compressor: Situated on the lower right side of the engine block.
- ✓ Automatic Tensioner: A spring-loaded arm with a pulley that maintains constant pressure on the belt.
- ✓ Idler Pulleys: These are static pulleys used to guide the belt and provide the necessary “wrap” around the drive pulleys to prevent slipping.
It is important to note that while the accessory belt drives these external components, it does not drive the water pump. On the G37, the water pump is internal and driven by the timing chain. However, the serpentine belt is still indirectly related to coolant flow because it powers the alternator, which in turn powers the electric cooling fans managed by the ECU.
Most G37 models (Sedan, Coupe, and Convertible) share the same routing regardless of being RWD or AWD (x-models). The tensioner is always located on the driver’s side of the engine front.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Replacing the belt using the infiniti g37 serpentine belt diagram is a task that can be completed in about 45 to 60 minutes with basic hand tools. Follow these steps to ensure a safe and proper installation.
Required Tools and Materials
- • 14mm long-handle wrench or a dedicated serpentine belt tool
- • New serpentine belt (OEM Part No: 11720-EY00B or equivalent)
- • Flathead screwdriver (for plastic clips)
- • Work light
Always perform this work on a cold engine. The pulleys and the nearby radiator can cause severe burns if the engine has been running recently.
Step 1: Prepare the Vehicle
Ensure the car is in Park with the emergency brake engaged. While not strictly necessary for the belt itself, many technicians disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent any accidental engine turnover while hands are near the pulleys. Remove the plastic engine cover by unscrewing the two 10mm bolts to gain better visibility of the upper pulleys.
Step 2: Access the Tensioner
Locate the automatic tensioner pulley. It is positioned between the crankshaft and the power steering pump. You will see a 14mm nut in the center of the pulley. This is the point where you will apply leverage to release the belt’s tension.
Step 3: Release Tension and Remove the Old Belt
Place your 14mm wrench or belt tool on the tensioner nut. Rotate the wrench counter-clockwise (pushing toward the passenger side). This will compress the internal spring of the tensioner, creating slack in the belt. While holding the tensioner in this compressed state, use your other hand to slide the belt off the uppermost pulley (usually the power steering pump). Slowly release the tensioner arm. You can now pull the old belt out of the engine bay.
Step 4: Inspect the Pulleys
Before installing the new belt, spin each idler and accessory pulley by hand. They should spin smoothly without any grinding noise or side-to-side play. Check the tensioner for any signs of leaking hydraulic fluid or cracks in the housing.
Step 5: Route the New Belt
Referencing your infiniti g37 serpentine belt diagram, begin threading the new belt from the bottom up. It is often easiest to start by wrapping the belt around the crankshaft pulley, then the A/C compressor, and then through the idler pulleys. Ensure the ribbed side of the belt seats perfectly into the grooves of the pulleys.
Step 6: Final Seating
The final step of routing involves the tensioner. Again, rotate the tensioner counter-clockwise to create space. Slide the belt over the final pulley. Professionals often leave the alternator or power steering pump as the “final” pulley because they are at the top and easiest to reach.
Step 7: Verify Alignment
Before starting the engine, use a flashlight to double-check that the belt is centered on every pulley. If the belt is even one “rib” off-center, it will shred almost immediately upon startup.
If you are working alone, use a zip-tie to loosely hold the belt to a top pulley while you route the bottom sections. This prevents the belt from falling off the crankshaft while you are reaching for the tensioner.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting

A failing serpentine belt on the Infiniti G37 often presents clear warning signs. The most common symptom is a “chirping” or “squealing” sound, especially during cold starts or when the steering wheel is turned to full lock. This indicates that the belt has glazed over (become too smooth) or that the tensioner has weakened.
If a belt snaps while driving, your dashboard will likely light up like a Christmas tree. Since the alternator stops spinning, the battery will no longer charge. This triggers a check engine light and potentially a diagnostic code such as P0562 (System Voltage Low) via the OBD-II port. Without the alternator, the ECU may eventually lose power, causing the engine to stall. Furthermore, the loss of power steering will make the car very difficult to maneuver, posing a significant safety risk.
Visually inspect your belt for “chunking” (where pieces of the ribs are missing) or longitudinal cracks. If you see more than three cracks in a one-inch span, the belt is at the end of its service life and should be replaced immediately.
Tips & Best Practices
To keep your G37 running smoothly, adhere to these maintenance best practices:
- ✓ Standard Inspection: Check the belt every 30,000 miles and replace it every 60,000 to 90,000 miles.
- ✓ Torque Specifications: If you decide to replace the tensioner assembly itself, the mounting torque spec for the VQ37VHR tensioner bolts is approximately 21-25 ft-lbs. Do not over-tighten, as the engine block is aluminum and the threads can strip.
- ✓ Component Quality: Always opt for an EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) belt. These are far more resistant to heat and cracking than older chloroprene belts.
- ✓ The “While You’re In There” Rule: If your G37 has over 100,000 miles, consider replacing the tensioner and idler pulleys at the same time as the belt. Bearings in these pulleys often fail shortly after a new, tighter belt is installed.
By following the infiniti g37 serpentine belt diagram and these professional steps, you can save significant money on labor costs while ensuring your vehicle’s accessory systems—from the alternator to the A/C compressor—function perfectly. Proper maintenance here prevents minor wear from turning into a major roadside breakdown, keeping your Infiniti as reliable as it is powerful.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Infiniti G37 serpentine belt diagram?
An Infiniti G37 serpentine belt diagram is a visual schematic showing how the drive belt wraps around engine accessories like the alternator and AC compressor. It ensures the belt follows the correct path to drive components efficiently without slipping, which is vital for maintaining proper vehicle electrical and cooling performance.
How do you read Infiniti G37 serpentine belt diagram?
Read the diagram by identifying the largest pulley, the crankshaft, as the starting point. Follow the solid line as it loops over and under various pulleys, noting whether the ribbed side or the flat side of the belt contacts each component to ensure the belt is installed correctly.
What are the parts of Infiniti G37 serpentine belt?
The system consists of the multi-ribbed belt, the crankshaft pulley, alternator, power steering pump, AC compressor, and an automatic tensioner. These parts work together to transfer mechanical energy from the engine to essential systems, while the tensioner keeps the belt tight to prevent slipping and noise.
Why is automatic tensioner important?
The automatic tensioner is crucial because it maintains constant pressure on the belt as it stretches over time. A failing tensioner can cause the belt to slip, leading to a battery charging failure or a check engine light if the ECU detects erratic alternator output or engine cooling issues.
What is the difference between serpentine and V-belts?
A serpentine belt is a single, long, multi-ribbed belt that drives all engine accessories, whereas older V-belts are multiple, individual belts that drive separate components. Serpentine belts are more efficient and compact, though their failure results in the loss of all driven accessories simultaneously during a drive.
How do I use Infiniti G37 serpentine belt diagram?
Use the diagram as a reference during installation to confirm the belt’s path before releasing the tensioner. This prevents routing errors that could damage the water pump or power steering. Always cross-reference the diagram if an OBD-II scan reveals codes related to low voltage or high temperatures.