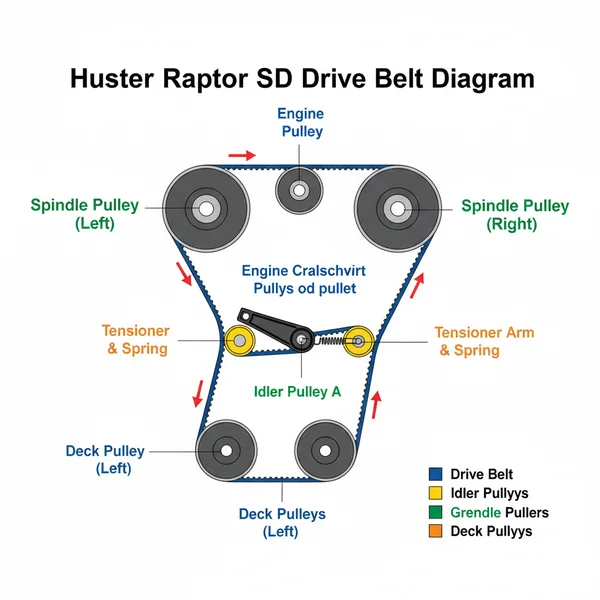
The Hustler Raptor SD drive belt diagram illustrates the path from the engine pulley to the transmission pumps. This specific layout ensures power is transferred efficiently through the drive system. Understanding this configuration is vital for correctly installing the belt around idler pulleys and tensioners to maintain optimal mower performance and steering.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Main purpose of this diagram is to ensure correct belt routing for mower propulsion
- The engine pulley is the most important component to identify first
- Always engage the parking brake and remove the spark plug wire for safety
- Check pulley alignment to prevent premature belt wear and vibration
- Use this diagram during belt replacement or when adjusting the tensioner
Maintaining your zero-turn mower requires a blend of mechanical patience and technical knowledge, and having a clear hustler raptor sd drive belt diagram is the most critical tool in your arsenal when things go wrong. Whether you are performing routine seasonal maintenance or reacting to a sudden belt snap in the middle of a job, understanding the drive system is vital. This specific system, responsible for the propulsion of your machine, is far more complex than the deck belt used for cutting grass. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down the entire drive belt configuration, explore the intricate layout of the hydrostatic system, and provide a detailed roadmap for belt replacement. By the end of this article, you will have the expertise needed to navigate the internal structure of your Hustler Raptor SD and ensure your mower remains in peak operating condition.
The Architecture of the Hustler Raptor SD Drive System
The drive belt system on a Hustler Raptor SD is the mechanical bridge between the engine’s power and the hydrostatic transmissions that turn the wheels. Unlike the mower deck belt, which is easily visible, the drive belt is tucked deep within the chassis, wrapped around the engine’s crankshaft pulley and the two independent hydro-gear pumps. Understanding the hustler raptor sd drive belt diagram requires an appreciation of this specific layout. The belt must navigate a series of pulleys while maintaining constant tension to prevent slippage during zero-turn maneuvers.
[DIAGRAM VISUALIZATION]
2. Left Hydro Pump Pulley: Located on the left side of the frame.
3. Right Hydro Pump Pulley: Located on the right side of the frame.
4. Tensioner Idler Pulley: The movable component that maintains pressure.
5. Stationary Idler Pulley: Provides the necessary routing angle.
The configuration typically follows a specific path: the belt leaves the engine pulley, wraps around the first hydro pump pulley, travels across to the second hydro pump pulley, and is kept taut by a spring-loaded idler arm. This structure ensures that both pumps receive equal torque, allowing for the precise, synchronized movement that Hustler mowers are known for. It is important to note that depending on the specific frame size of your Raptor SD (such as 48″, 54″, or 60″), the exact distance between these components might vary slightly, but the fundamental routing logic remains consistent across the SD line. The diagram serves as a visual map to ensure the belt is seated correctly in the grooves of the “V” pulleys while resting against the flat surface of the idler pulleys.
The Hustler Raptor SD drive belt is a heavy-duty, multi-layered V-belt. Using a generic belt rather than an OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) part can lead to premature failure because the system configuration relies on specific friction coefficients and heat resistance that standard belts may not provide.
Interpreting the Routing Layout

When looking at the hustler raptor sd drive belt diagram, you will notice that the belt has two distinct sides: a narrow “V” side and a wider “flat” side. The “V” side is designed to wedge into the grooves of the drive pulleys (Engine and Hydro Pumps) to maximize grip and power transfer. Conversely, the “flat” side of the belt typically runs against the idler pulleys, which are designed to push against the back of the belt to provide tension. If you install the belt with the wrong side facing a pulley, it will cause immediate smoking, rapid wear, and potential damage to the pulley bearings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Drive Belt Replacement

Replacing the drive belt is a more labor-intensive task than replacing a deck belt because of its location under the seat and behind the engine. However, by following the hustler raptor sd drive belt diagram and these structured steps, you can complete the job with basic hand tools.
Required Tools and Materials:
- ✓ 1/2-inch and 9/16-inch sockets and ratchets
- ✓ A long pry bar or a dedicated belt tensioner tool
- ✓ Replacement Hustler OEM Drive Belt
- ✓ Work gloves and eye protection
Always disconnect the spark plug wires and engage the parking brake before working on the drive system. Ensure the engine and exhaust components are completely cool to the touch to avoid severe burns.
Step 1: Access the Drive System
Park the mower on a level surface and lower the deck to its lowest setting. To get the best view of the drive belt structure, you will need to flip the seat forward. In some cases, removing the floor pan or the rear engine guard may provide additional clearance, though most of the work on the Raptor SD is performed from the top and rear.
Step 2: Relieve the Tension
Locate the idler arm, which is usually held under pressure by a heavy-duty extension spring. Using a pry bar or a socket on the idler pulley bolt, carefully rotate the arm to compress the spring. This will create slack in the belt.
Step 3: Remove the Old Belt
Starting at the engine pulley (at the very back of the machine), slip the belt off the pulley. You will then need to feed the belt around the cooling fans located on top of the left and right hydrostatic transmissions. This is the most tedious part of the process, as you must be careful not to damage the plastic fan blades.
Step 4: Clean the Pulley System
Before installing the new belt, use compressed air or a rag to clean debris from the pulley grooves. Buildup of grass clippings and dirt can cause the new belt to track incorrectly or wear prematurely. Check that all idler pulleys spin freely and do not have “play” or grinding noises in their bearings.
While the belt is off, inspect the tensioner spring. If the spring appears stretched or has visible gaps between the coils while at rest, replace it. A weak spring is the leading cause of drive belt “slapping” and vibration.
Step 5: Route the New Belt
Referencing your hustler raptor sd drive belt diagram, begin routing the new belt. The best method is to start at the hydro pumps and work your way back to the engine. Ensure the belt is properly seated between the fan blades and the pulleys on both the left and right transmissions.
Step 6: Final Alignment and Tensioning
Once the belt is looped around the engine pulley and both pump pulleys, use your pry bar again to move the idler arm and slip the belt over the idler pulley. Double-check the entire path. Ensure the belt isn’t twisted and that it isn’t caught on any belt keepers (small metal tabs designed to keep the belt from jumping off).
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
Even with a perfect hustler raptor sd drive belt diagram, users often face specific challenges during the maintenance process. Recognizing these symptoms early can save the drive system from total failure.
1. Belt Slippage and Power Loss: If your mower feels sluggish when climbing hills or if one wheel seems to have more power than the other, the drive belt may be slipping. This is often caused by a stretched belt or oil leaking from a hydro pump onto the pulley surface.
2. Squealing Noises: A high-pitched squeal when you engage the drive levers usually indicates a glazed belt or a failing idler pulley bearing. If the diagram shows the belt is routed correctly but the noise persists, check the tensioner arm for smooth movement.
3. Frequent Belt “Jumping”: If the belt repeatedly jumps off the pulleys, the configuration of the belt keepers might be incorrect. Ensure that the metal pins surrounding the engine pulley are close enough to prevent the belt from escaping when slack, but not touching the belt during operation.
Tips & Best Practices for Longevity
To maximize the life of your drive system, you should look beyond just the hustler raptor sd drive belt diagram and adopt a proactive maintenance mindset. The drive system operates in a harsh environment filled with heat, dust, and vibration.
Regular Inspections: Every 50 hours of operation, perform a visual check of the belt. Look for “chunking” (where pieces of the V-rib are missing) or fraying on the edges. If you see the internal cords of the belt, it is at imminent risk of snapping.
Keep it Cool: The hydrostatic pumps generate significant heat. Ensure that the cooling fans on top of the pumps are clean and that no grass is packed around the drive belt area. Excess heat is the number one enemy of rubber belt compounds, causing them to become brittle and crack.
Buy Quality Components: While aftermarket belts are often cheaper, the Hustler Raptor SD uses a very specific belt length and thickness. A belt that is even 1/4 inch too long will not be properly tensioned by the idler arm, leading to excessive vibration and wear on the pump input shafts.
Monitor the Hydrostatic Fluid: While not directly part of the belt diagram, the health of your transmissions affects the belt. If a pump starts to seize, it will put immense strain on the drive belt, often causing it to burn through in a matter of seconds. Ensure your hydro fluid is at the correct level and changed according to the manufacturer’s intervals.
In conclusion, mastering the hustler raptor sd drive belt diagram is about more than just knowing where the rubber loops; it is about understanding the synergy between the engine and the hydrostatic drive system. By following the correct routing, maintaining proper tension, and using high-quality components, you ensure that your Hustler Raptor SD continues to provide the precision and power you expect. Regular maintenance of this critical system will extend the life of your mower and provide a much smoother, more reliable mowing experience for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Hustler Raptor SD drive belt diagram?
This diagram is a visual representation of the drive system’s belt routing. It identifies each component, such as the engine pulley, hydrostatic transmission pulleys, and idler pulleys. By showing the exact structure of the belt path, it helps owners ensure the belt is installed correctly for proper mower propulsion.
How do you read a Hustler Raptor SD drive belt diagram?
Start by identifying the engine pulley as the power source. Follow the line representing the belt as it wraps around the transmission pulleys and idler arms. Pay attention to which side of the belt (flat or V-side) touches each specific pulley component within the system layout for accuracy.
What are the parts of a Hustler Raptor SD drive system?
The system includes the engine drive pulley, two hydrostatic transmission pulleys, a tensioner arm, and several idler pulleys. This configuration works together to transfer rotational force from the engine to the wheels. Each component must be in good condition to ensure the mower maneuvers and drives correctly during operation.
Why is the tensioner component important?
The tensioner is a critical component because it maintains the necessary pressure on the belt. Without proper tension, the belt would slip, leading to loss of power or total drive failure. This part of the structure automatically adjusts for minor belt stretching to keep the drive system operating efficiently.
What is the difference between the drive belt and the deck belt?
The drive belt is responsible for moving the mower forward and backward by powering the transmissions. In contrast, the deck belt is part of the blade system configuration, transferring power to the cutting blades. Both follow different routing paths and utilize different pulleys to perform their unique mechanical functions.
How do I use a Hustler Raptor SD drive belt diagram?
Use the diagram as a blueprint during maintenance or replacement. Begin by locating the fixed pulleys and then map out the belt’s path through the tensioning system. Verify that the belt is seated in every groove shown in the layout to prevent it from jumping off during use.