Holley Sniper EFI Wiring Diagram: Installation Guide
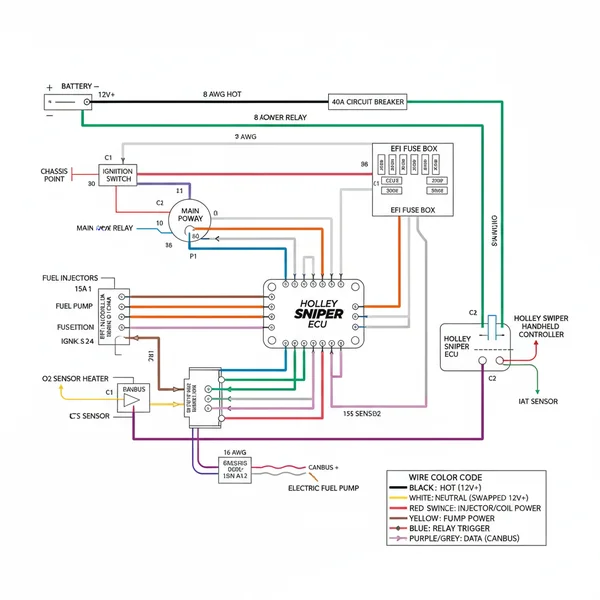
The Holley Sniper EFI wiring diagram illustrates the essential connections for the ECU, fuel pump, and sensors. It details how the main power harness links directly to the battery, the switched ignition source triggers the system, and how various inputs like the O2 sensor and coolant temp sensor integrate for precise fuel management.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides a visual map for connecting the ECU to engine components
- Identifying the main 7-pin and 10-pin connectors is critical
- Direct battery connection is required to prevent electrical interference
- Always use high-quality crimps and heat shrink on all connections
- Use this diagram during initial setup or when diagnosing sensor errors
Upgrading your vehicle from a traditional carburetor to a modern fuel injection system is one of the most significant performance improvements you can make. However, the success of this conversion hinges entirely on the quality of your electrical connections. Having a clear and accurate holley sniper efi wiring diagram is essential for any DIY enthusiast looking to ensure their engine starts reliably and runs at peak efficiency. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the intricate web of connections, from high-current power leads to sensitive signal wires. You will learn the specific functions of each color-coded wire, how to avoid common electrical interference issues, and the best practices for securing your harness for long-term durability.
The Holley Sniper EFI system is designed to be “plug-and-play,” but that does not mean the installation is foolproof. The system relies on a complex series of inputs and outputs to manage fuel delivery and ignition timing in real-time. The primary holley sniper efi wiring diagram consists of several distinct harnesses: the main power harness, the 7-pin main connector, the 10-pin I/O connector, and the integrated oxygen sensor lead. Unlike a simple household light switch that might utilize a traveler wire or a common terminal, the Sniper system uses a DC-direct architecture where every connection must be high-integrity to prevent voltage fluctuations.
The most critical wires in the entire system are the thick 10-gauge red and black power leads. These MUST be connected directly to the battery terminals, not to a starter solenoid or a remote distribution block, to ensure the ECU receives “clean” power without noise from the alternator or starter.
The main 7-pin connector is the heart of the installation. It includes the pink wire, which acts as the “wake-up” signal for the ECU, and the blue wire, which controls the fuel pump. It is important to note that the blue wire provides a 12V positive signal but is limited in its current capacity. If your fuel pump requires more than 7 amps, you must use a relay. In a house, you might connect a hot wire to a brass screw on a receptacle, but in the automotive world, we use weather-pack connectors and crimped terminals to withstand vibration and heat. The ground wire strategy is equally vital; the Sniper requires a shared ground reference for all sensors to prevent “ground loops,” which can cause erratic sensor readings and poor engine performance.
[BATTERY (+)] <---- (10 Gauge Red) ---- [ECU MAIN POWER] [BATTERY (-)] <---- (10 Gauge Black) ---- [ECU MAIN GROUND] [IGNITION SWITCH] <---- (Pink Wire) ---- [7-PIN CONNECTOR] [FUEL PUMP RELAY] <---- (Blue Wire) ---- [7-PIN CONNECTOR] [COIL (-) or DIST] <---- (Yellow/Purple) ---- [RPM SIGNAL] [O2 SENSOR] <---- (Dedicated Lead) ---- [EXHAUST BUNG] [COOLANT TEMP] <---- (Dedicated Lead) ---- [ENGINE BLOCK]
Implementing the holley sniper efi wiring diagram requires a methodical approach. Follow these steps to ensure a professional-grade installation:
- ✓ Step 1: Direct Battery Connection. Route the thick 10-gauge red and black wires from the main harness directly to the battery. Even if you have a rear-mounted battery, do not shortcut this by grounding to the chassis. The chassis often acts like a neutral wire in a house, carrying return currents from various accessories that can introduce electrical noise into the ECU.
- ✓ Step 2: Switched 12V Source. Locate the pink wire on the 7-pin harness. This wire must be connected to a source that has 12V while the key is in both the "ON" and "CRANK" positions. Many factory ignition switches drop power to the accessories during cranking; if the pink wire loses voltage during the start cycle, the ECU will reboot, and the car will never start.
- ✓ Step 3: RPM Signal Input. This is the most common point of failure. If you are using a standard coil ignition, connect the Yellow wire to the negative side of the coil. If you are using a capacitive discharge ignition (like an MSD box), the Yellow wire MUST NOT touch the coil; instead, it must connect to the "Tach Output" on the ignition box.
- ✓ Step 4: Fuel Pump Wiring. The blue wire triggers the fuel pump. While it can power some small pumps directly, it is best practice to use this wire to trigger a relay. Connect the blue wire to terminal 86 of a standard automotive relay, terminal 85 to ground, terminal 30 to a fused battery source, and terminal 87 to the pump.
- ✓ Step 5: Sensor Installation. Install the Oxygen (O2) sensor in the exhaust manifold or header, ensuring it is angled upward to prevent moisture buildup. Connect the Coolant Temperature Sensor (CTS) to the intake manifold. Ensure these wires are routed away from high-heat sources like exhaust pipes.
- ✓ Step 6: EMI Suppression. Route the main ECU harness as far away as possible from spark plug wires, the alternator, and the ignition coil. These components emit Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) that can disrupt the signal "traveling" through your data wires.
Never use a "test light" on EFI wiring, as the current draw from the bulb can damage sensitive ECU circuits. Always use a high-impedance digital multimeter to check for voltage and continuity.
Even with a perfect holley sniper efi wiring diagram, issues can arise during the initial setup. The most frequent problem users encounter is the "No RPM Signal" error. If the ECU doesn't see the engine turning over, it will not fire the injectors. This is usually due to the Yellow wire being connected incorrectly or picking up interference. If you see erratic RPM jumps on your handheld display while cranking, you likely have EMI noise.
Another common issue is low voltage during cranking. If your battery is weak or your 10-gauge power leads are poorly crimped, the voltage can drop below 9V, causing the ECU to shut down. Unlike a household circuit where a loose brass screw might just cause a flickering light, a loose connection in an EFI system can lead to lean-out conditions that damage your engine. If you experience "RFI resets," where the handheld screen goes blank or returns to the home menu while the engine is running, check your spark plug wires. You must use RFI-suppression (spiral core) wires; solid core wires are strictly prohibited with EFI systems.
When splicing wires, avoid using "T-taps" or "Scotchlok" connectors. These are notorious for creating high-resistance points. Instead, use a Western Union solder joint and cover it with adhesive-lined heat shrink tubing for a waterproof, vibration-resistant connection.
To achieve a professional installation that lasts for years, focus on the details of your wire management. Use high-quality nylon braided loom rather than the cheap plastic convoluted tubing. This not only looks better but provides superior heat protection. When routing wires through the firewall, always use a rubber grommet to prevent the metal edge from cutting through the insulation and causing a short circuit.
Maintenance of your EFI system is relatively simple but shouldn't be ignored. Periodically check the battery terminals for corrosion, as even a small amount of oxidation can increase resistance and lower the voltage reaching the ECU. If you ever need to perform welding on the vehicle, disconnect both the positive and negative leads of the EFI system from the battery to prevent high-frequency current from frying the ECU.
By following the holley sniper efi wiring diagram and adhering to these technical guidelines, you transform your vehicle's reliability. Whether you are navigating the complexities of a common terminal on a relay or ensuring your ground wire is perfectly seated, the time spent on clean wiring will pay dividends in throttle response, fuel economy, and overall drivability. Modernizing your engine with a Holley Sniper system is a rewarding project that bridges the gap between classic iron and 21st-century technology.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the Holley Sniper Efi Wiring Diagram: Installation Guide
Identify the main power harness and ensure the ground wire is long enough to reach the battery.
Locate the common terminal on the ignition switch to find a clean 12V switched power source.
Understand how the hot wire connects directly to the battery positive to provide constant voltage.
Connect the O2 sensor and coolant temperature sensor to their designated ports on the main harness.
Verify that the neutral wire or signal ground is not shared with high-noise components like the alternator.
Complete the installation by securing all loose wires with loom and checking for continuity across the circuit.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Holley Sniper EFI wiring diagram?
A Holley Sniper EFI wiring diagram is a schematic that outlines the electrical connections required to convert a carbureted engine to electronic fuel injection. It shows how the throttle body unit communicates with the fuel pump, ignition system, and various sensors to ensure the engine receives the correct air-fuel mixture.
How do you read a Holley Sniper EFI wiring diagram?
To read the diagram, start by identifying the main harness connectors. Follow the color-coded lines to their respective terminations, such as the battery, ignition coil, or fuel pump. Pay close attention to the symbols for grounds and switched power sources to ensure the system initializes correctly when the key is turned.
What are the parts of the Holley Sniper EFI wiring?
The main parts include the 7-pin power harness, the 10-pin input/output connector, and the integrated sensors like the MAP and TPS. It also features a specialized O2 sensor lead and a fuel pump relay wire. These components work together to provide real-time data to the internal engine control unit.
Why is the ground wire important?
The ground wire is vital because the Sniper EFI system is highly sensitive to electrical noise. A poor ground can cause erratic idling, sensor failure, or even ECU damage. Connecting both the main and signal grounds directly to the negative battery terminal ensures a stable reference voltage and prevents interference.
What is the difference between a hot wire and a traveler wire?
In this context, the hot wire provides constant or switched 12V power to the system. While a traveler wire is typically found in 3-way lighting circuits, in automotive wiring, it may refer to signal wires passing data between the ECU and external modules like a CD ignition box or handheld controller.
How do I use a Holley Sniper EFI wiring diagram?
Use the diagram as a blueprint during the physical installation of the harness. Lay the wires across the engine bay according to the schematic, ensuring no leads touch hot exhaust or moving parts. Refer to it again during the initial setup on the handheld screen to verify pin locations.