GM Headlight Switch Wiring Diagram: Troubleshooting Guide
A GM headlight switch wiring diagram illustrates the electrical path from the battery to the illumination system. It identifies the hot wire supplying power, the ground wire for circuit completion, and how the common terminal distributes current to high beams, low beams, and parking lights for safe vehicle operation.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Explains the routing of power from the battery to the headlights.
- Identifying the hot wire is crucial for circuit testing.
- Always disconnect the battery to prevent shorts during installation.
- Use a multimeter to verify continuity across the switch terminals.
- Essential for replacing faulty switches or upgrading to LED bulbs.
Restoring a classic vehicle or repairing a modern workhorse often requires a deep dive into the electrical system, and few components are as vital as the light controls. If you are currently staring at a cluster of tangled cables behind your dashboard, a gm headlight switch wiring diagram is the essential roadmap you need to restore visibility and ensure safety. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the circuitry involved in General Motors lighting systems, helping you identify which terminal controls your high beams, parking lights, and interior illumination. By understanding the flow of current from the battery to the lamp filaments, you will gain the confidence to troubleshoot flickering lights, replace worn-out switches, and upgrade your electrical system for better performance and reliability.
Decoding the GM Headlight Switch Wiring Diagram
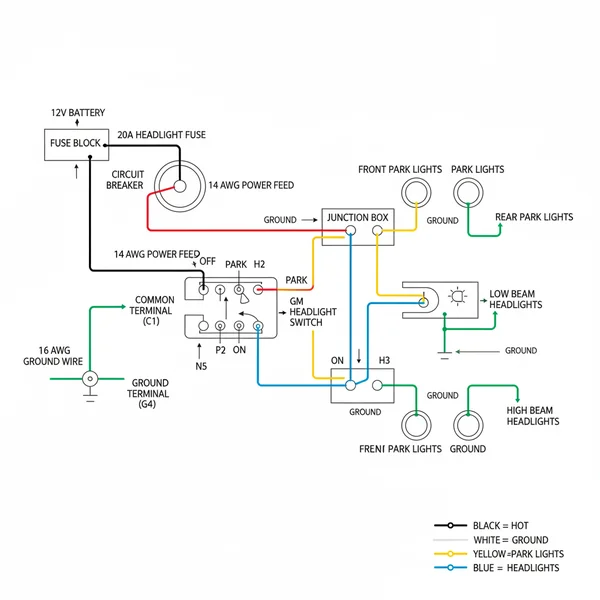
The gm headlight switch wiring diagram is a visual representation of how electricity travels from your vehicle’s power distribution center to the various lighting components. In most GM vehicles, the headlight switch is a multi-function device that manages several independent circuits simultaneously. When you examine the diagram, you will notice several terminals, often labeled with letters like B, H, P, and R. These correspond to the Battery (power in), Headlights, Parking lights, and Rear/Taillights.
Understanding the color-coding is paramount. Traditionally, a heavy-gauge red or orange wire serves as the primary hot wire, feeding 12-volt power directly from the battery or a fusible link to the common terminal on the switch. From there, the switch acts as a gatekeeper. When pulled to the first position, it directs current to the parking light circuit (often a brown wire). In the second position, it energizes the headlight circuit (often a yellow or light green wire).
In vintage GM configurations, the headlight switch also incorporates a rheostat—a coiled spring of wire—to control the brightness of the instrument cluster. Rotating the knob changes the resistance, which in turn adjusts the voltage sent to the dashboard bulbs.
The diagram also illustrates the integration of the dimmer switch, which functions similarly to a traveler wire setup in residential three-way lighting. The headlight switch sends power to the dimmer switch (located on the floor or the steering column), which then selects between the high-beam and low-beam circuits. Proper grounding is represented by the ground wire, usually black, which must be securely fastened to a clean metal surface or a dedicated ground terminal to complete the circuit.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A detailed schematic showing a 7-pin GM headlight switch. Labels: Terminal B (Red, 12V Hot), Terminal H (Yellow, Headlights), Terminal P (Brown, Parking), Terminal I (Gray, Instrument Lights), Terminal D (White, Dome Ground), Terminal R (Orange, Fused Power). The diagram shows the flow from the battery through the fuse block to the switch and out to the various lamp assemblies.]
Step-by-Step Guide to Installation and Interpretation

Interpreting a gm headlight switch wiring diagram and applying it to your vehicle requires a methodical approach. Whether you are replacing a faulty unit or installing a completely new harness, follow these steps to ensure a professional-grade installation.
1. Gather Essential Tools and Materials
Before beginning, ensure you have the following tools:
- ✓ Digital Multimeter (for checking voltage and continuity)
- ✓ Wire strippers and crimping tool
- ✓ Heat shrink tubing and high-quality electrical tape
- ✓ Correct gauge automotive primary wire (12-14 gauge for headlights, 16-18 for markers)
- ✓ Dielectric grease for terminal protection
2. Disconnect the Power Source
Safety is the first priority. Always disconnect the negative battery cable before touching any part of the dash wiring. This prevents accidental shorts that could damage your new switch or, worse, cause a fire.
3. Map the Existing Harness
Using your gm headlight switch wiring diagram, identify each wire in your vehicle’s harness. If you are working on an older vehicle where the wire colors have faded, use your multimeter to perform a continuity test. Label each wire with masking tape according to its function: Battery, Headlights, Park, Tail, and Dimmer.
4. Connect the Constant Hot Wire
Locate the common terminal on the back of the switch, usually marked with a ‘B’ or ‘BAT’. Connect the thickest red or orange wire here. This is your hot wire that provides constant 12-volt power. If your switch uses a screw-type terminal, ensure the wire is wrapped clockwise around the brass screw before tightening to ensure a secure mechanical connection.
5. Wire the Output Circuits
Connect the remaining wires to their designated terminals based on the diagram:
- ✓ Attach the headlight output wire to the terminal marked ‘H’.
- ✓ Attach the parking/tail light wire to the ‘P’ or ‘R’ terminal.
- ✓ Connect the instrument panel light wire (usually gray) to the ‘I’ terminal.
Ensure that the wire gauge you use is appropriate for the current load. Headlights draw significant amperage; using a wire that is too thin (high gauge number) will cause the wire to overheat and drop voltage, resulting in dim headlights.
6. Establish the Ground Connections
While the headlights themselves are grounded at the radiator support or frame, the switch often requires a ground wire for the dome light circuit. In many GM switches, the dome light is activated by turning the knob fully counter-clockwise, which completes the circuit to ground. Ensure the switch body or the dedicated ground terminal is making clean contact with the chassis.
7. Test the Voltage and Function
Reconnect the battery and use your multimeter to check the voltage at the switch. You should see roughly 12.6V at the hot wire terminal. Pull the switch to the first position and verify that the parking lights and tail lights illuminate. Pull to the second position to verify the headlights. Finally, rotate the knob to ensure the instrument lights dim and the dome light activates.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting

Even with a perfect gm headlight switch wiring diagram, you may encounter obstacles during the repair process. One of the most common issues in GM vehicles is the “flickering headlight” syndrome. This often occurs because the internal circuit breaker in the switch is tripping due to excessive heat or a short circuit. If your lights go out and then come back on after a few minutes, the switch is likely failing or being overloaded by high-wattage aftermarket bulbs.
Another frequent problem is the loss of instrument cluster lights. This is typically caused by a corroded rheostat. If you look at the back of the switch and see a ceramic or metal coil that looks rusted or broken, the switch must be replaced. Additionally, check for melted plastic around the connector. GM switches are known for carrying the full current of the headlights through the switch itself, which generates significant heat. If you find melted wires, you may need to replace the pigtail connector along with the switch.
If you are upgrading to high-output halogen or LED bulbs, do not run them directly through the factory switch. Install a relay harness that uses the switch only as a trigger. This takes the heavy electrical load off the switch and delivers full battery voltage directly to the bulbs.
Tips & Best Practices for Wiring Success
When working with your gm headlight switch wiring diagram, longevity should be your goal. Start by using high-quality connectors. While many DIYers rely on “butt connectors,” a soldered joint protected by heat shrink is the gold standard for automotive applications. This prevents moisture from entering the wire and causing “green rot” corrosion, which increases resistance and lowers performance.
Maintenance is also key. Periodically check the back of the switch for signs of heat stress. If you notice the brass screw terminals or pins are turning blue or black, it indicates a high-resistance connection that needs attention. Applying a small amount of dielectric grease to the terminals can prevent oxidation and ensure a consistent flow of electricity.
Finally, consider the age of your wiring. If your vehicle is several decades old, the original copper wires may have become brittle. If the insulation cracks when you bend it, it is time to replace that section of the harness. Investing in a factory-style replacement harness can save you hours of troubleshooting in the future and ensures that your gm headlight switch wiring diagram matches the physical reality of your car.
By following this guide and utilizing a proper gm headlight switch wiring diagram, you ensure that your vehicle’s lighting system remains a reliable safety feature. Whether you are navigating a dark highway or just making sure your dashboard glows properly at dusk, a well-wired switch is the heart of your vehicle’s nighttime capabilities. Proper planning, the right wire gauge, and attention to detail will keep your lights burning bright for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is GM headlight switch wiring diagram?
A GM headlight switch wiring diagram is a visual map showing the electrical connections between the dashboard switch and the vehicle’s lighting system. It displays how the hot wire delivers power through various fuses and relays to activate the headlamps, taillights, and interior dash illumination during operation.
How do you read GM headlight switch wiring diagram?
To read the diagram, start at the power source and trace the hot wire through the switch to the load. Look for symbols representing the common terminal and ground wire connections. Standardized color codes help identify which wires control specific functions like high beams or parking lights.
What are the parts of GM headlight switch?
The primary parts include the internal actuator, the common terminal for power distribution, and specific pins for the dimmer and light circuits. It connects to the hot wire for power and utilizes a ground wire to ensure the internal rheostat and illumination functions operate correctly and safely.
Why is hot wire important?
The hot wire is the lifeblood of the circuit, carrying 12-volt battery power directly to the switch. Without a secure connection to the hot wire, the headlights will not receive any electricity. Identifying this wire is the first step in diagnosing power loss or switch failure issues.
What is the difference between traveler wire and common terminal?
In specialized automotive relays or three-way lighting setups, a traveler wire carries current between two switching points. The common terminal serves as the main entry or exit point for current within the switch assembly itself, ensuring that power is routed to the correct output based on the switch position.
How do I use GM headlight switch wiring diagram?
Use the diagram to identify wire colors and pin locations when testing for voltage or ground. By comparing the diagram to your vehicle’s harness, you can determine if a failure exists in the switch, the neutral wire return path, or the power supply line, enabling targeted repairs.