GM Fuel Pump Wiring Harness Diagram: Troubleshooting & Repair
A GM fuel pump wiring harness diagram illustrates the electrical connections between the relay, ECM, and fuel pump. It helps identify the 12V hot wire, ground wire, and sender circuits. Understanding these paths is essential for diagnosing power loss, faulty grounds, or sensor failures that prevent your vehicle from starting.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Identifies the specific pinouts for power, ground, and fuel level signals
- The fuel pump relay is the most critical switching component to locate
- Always disconnect the battery before probing the harness to prevent shorts
- Use a multimeter to check for 12V at the pump connector during prime
- Essential for diagnosing ‘crank but no start’ conditions in GM vehicles
Navigating the complexities of a GM vehicle’s electrical system can be a daunting task for even the most seasoned DIY mechanic. When your engine cranks but refuses to fire, the culprit is often a failure within the fuel delivery system, specifically the electrical path. Understanding a gm fuel pump wiring harness diagram is the essential first step in diagnosing whether your pump has failed or if there is a simple break in the electrical circuit. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the wiring architecture, explaining how power travels from the battery through the relay and down to the tank. By the end of this article, you will have the knowledge to trace circuits, identify wire functions, and perform professional-grade repairs on your vehicle’s fuel system.
Understanding the GM Fuel Pump Wiring Architecture
The standard gm fuel pump wiring harness diagram typically illustrates a four-wire or five-wire configuration, depending on the specific model and whether the fuel level sender is integrated into the same connector. At its core, the system relies on a high-current circuit to drive the pump motor and a low-current circuit to transmit fuel level data to the dashboard. Unlike residential wiring where you might look for a brass screw or a neutral wire, automotive systems use color-coded insulation and specific pin layouts to define circuit paths.
In a typical GM setup, the harness is divided into four primary functions. The most critical is the hot wire, usually colored gray, which carries the 12-volt load to the pump motor. This is paired with a heavy-gauge black ground wire that completes the circuit to the vehicle’s chassis. The remaining wires, often purple and black/white, handle the fuel level sending unit. The purple wire acts as the signal carrier, while the black/white wire serves as the sensor ground. In some advanced configurations, you may encounter a fifth wire used for an internal pressure sensor, which helps the Engine Control Module (ECM) monitor evaporative emissions.
Most GM fuel pumps do not run constantly when the key is in the ‘On’ position. The ECM primes the system for two to three seconds to build pressure, then cuts power unless it receives a signal that the engine is actually rotating. This is a critical distinction when testing for voltage at the harness.

The visual representation above highlights the pinout of the connector. Pin A is generally the fuel pump power (Gray), Pin B is the fuel level signal (Purple), Pin C is the sensor ground (Black/White), and Pin D is the main pump ground (Black). Understanding this layout prevents the common mistake of probing the wrong terminal and potentially shorting out the sensitive ECM signal wires.
How to Interpret and Utilize the Wiring Diagram
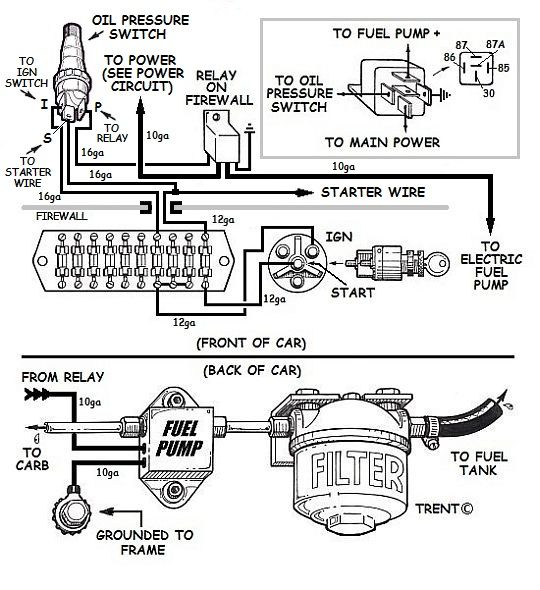
Reading a gm fuel pump wiring harness diagram requires an understanding of how electricity “travels” through the vehicle. While a house circuit might use a traveler wire to connect two switches, an automotive fuel circuit uses a trigger wire from the ECM to activate a relay. The relay acts as the gateway; when it receives a low-current signal, it closes a “common terminal” inside the relay box, allowing high-amperage current to flow directly from the battery to the fuel pump.
To effectively use the diagram for installation or repair, follow these structured steps:
- ✓ Identify the Relay Location: Locate the fuel pump relay in the under-hood fuse block. The diagram will show the relay pins, usually numbered 30, 85, 86, and 87. Pin 30 is the constant hot wire from the battery.
- ✓ Verify Fuse Integrity: Before diving into the harness, check the fuel pump fuse. A blown fuse often indicates a short circuit in the wiring or a pump motor that is drawing too much amperage due to internal wear.
- ✓ Test for Prime Voltage: Have an assistant turn the ignition to the “Run” position while you use a multimeter on the gray wire at the fuel tank connector. You should see roughly 12.6 volts for a brief two-second window.
- ✓ Inspect the Ground Path: Use your diagram to find the chassis ground point for the black wire. In many GM trucks and SUVs, this is located on the frame rail. Corrosion here is a leading cause of intermittent pump failure.
- ✓ Check Wire Gauge and Condition: Ensure the harness has not been pinched or melted. If you are replacing a section of wire, always use the same or a thicker gauge to handle the current load without overheating.
- ✓ Signal Simulation: For the fuel level sender (purple wire), the diagram helps you understand resistance. By checking the ohms between the signal and ground, you can determine if your fuel gauge issues are in the tank or the dashboard.
Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before cutting or splicing into the fuel pump wiring harness. Fuel vapors are highly flammable, and a single spark from a hot wire can lead to a catastrophic fire or explosion.
To perform these steps, you will need a digital multimeter, a test light, wire strippers, and high-quality heat-shrink connectors. Avoid using “T-taps” or “Scotch locks,” as these allow moisture to enter the wire, leading to green crusty corrosion that will eventually break the circuit.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Techniques

When the gm fuel pump wiring harness diagram doesn’t match what you see on the vehicle, or if the pump still won’t run despite having power, you are likely facing one of several common GM-specific issues. One frequent problem is “connector pin tension.” Over time, the female terminals in the plastic plug can stretch out, leading to a loose connection that arcs and eventually melts the plastic housing. If you see discoloration or warping on the harness plug, the entire connector must be replaced.
Another common failure point is the ground wire circuit. In the automotive world, the ground is just as important as the power. If the ground wire has high resistance due to a rusty frame bolt, the pump may run slowly or not at all, even if you see 12 volts on the hot side. Use your multimeter to check for “voltage drop” on the ground side; any reading over 0.2 volts suggests a poor connection that needs cleaning.
If you have power at the fuse but not at the pump, check the bulkhead connector where the harness passes through the body or frame. These areas are prone to debris buildup and wire chafing.
Best Practices for Wiring Maintenance and Repair
To ensure your repair lasts the life of the vehicle, follow industry best practices when working with your gm fuel pump wiring harness diagram. First, always use automotive-grade TXL or GXL wire. These types of wire have thin-wall cross-linked polyethylene insulation that is resistant to heat, oil, and gasoline. Standard primary wire from a hardware store may degrade quickly when exposed to the harsh environment under a vehicle.
When splicing wires, soldering is the gold standard, followed by adhesive-lined heat shrink tubing. This creates a waterproof seal that prevents oxygen and moisture from reaching the copper strands. If you are replacing the entire pump, many modern kits include a new pumper-end harness. It is highly recommended to use this new connector rather than plugging the old, potentially heat-damaged connector into a brand-new pump.
- ✓ Use Dielectric Grease: Apply a small amount of dielectric grease to the connector pins to prevent corrosion and facilitate a better seal.
- ✓ Secure the Harness: Use UV-resistant zip ties to secure the harness away from moving parts like the driveshaft or hot components like the exhaust system.
- ✓ Match the Gauge: If you must extend a wire, never use a smaller gauge than what the factory provided. A smaller wire will increase resistance, lower the voltage to the pump, and can cause the wire to catch fire.
In summary, a gm fuel pump wiring harness diagram is more than just a set of lines on a page; it is a vital tool for maintaining the heart of your vehicle’s engine. By identifying the hot wire, ensuring a solid ground, and verifying the relay’s common terminal operation, you can diagnose fuel delivery issues with confidence. Proper maintenance of the wiring harness ensures that your GM vehicle remains reliable, preventing the frustration and cost of being stranded by a simple electrical failure. Whether you are performing a routine inspection or a complete pump replacement, respecting the electrical specifications of your harness is the key to a successful and safe repair.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the Gm Fuel Pump Wiring Harness Diagram: Troubleshooting & Repair
Identify the main power source and hot wire originating from the fuel pump fuse.
Locate the fuel pump relay and identify the common terminal used for power switching.
Understand how the traveler wire carries the switched current from the relay to the tank.
Connect a digital multimeter to the ground wire to verify circuit continuity and low resistance.
Verify that the neutral wire equivalent (chassis ground) is securely fastened and free of rust.
Complete the diagnosis by testing for 12V at the pump connector while the ignition is cycled.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is GM fuel pump wiring harness diagram?
A GM fuel pump wiring harness diagram is a visual schematic showing the electrical path from the battery to the fuel pump. It details the routing of the hot wire, ground wire, and signal lines for the fuel level sender, allowing technicians to trace circuits and locate electrical faults accurately.
How do you read GM fuel pump wiring harness diagram?
To read this diagram, start at the fuse box to find the hot wire source. Follow the circuit through the fuel pump relay to the common terminal, then trace the traveler wire as it runs to the fuel tank. Check the schematic for ground symbols to ensure proper earthing.
What are the parts of GM fuel pump wiring harness?
Key parts include the fuel pump relay, the primary hot wire for power, the ground wire for circuit completion, and the fuel pressure sensor connections. The harness also contains wires for the fuel level sending unit and various connectors that link the fuel system to the vehicle’s computer.
Why is the ground wire important?
The ground wire is critical because it completes the electrical circuit. Without a clean connection to the chassis, the pump cannot draw current, leading to intermittent operation or total failure. Ensuring the ground is free of corrosion is a primary step in any automotive electrical troubleshooting process.
What is the difference between hot and neutral wires in this harness?
In this DC system, the hot wire provides 12V power while the ground wire acts as the return path. Unlike AC systems that use a neutral wire, automotive circuits rely on the vehicle chassis as the return. Identifying the hot wire versus the ground is vital for safe testing.
How do I use GM fuel pump wiring harness diagram?
Use the diagram to perform voltage drop tests and continuity checks across the harness. By identifying which wire is the hot wire or the traveler wire leading to the tank, you can use a multimeter to pinpoint exactly where power is lost or where a short exists.