GM 3.4 V6 Engine Diagram: Repair and Maintenance Guide
A GM 3.4 V6 engine diagram illustrates the layout of internal and external components, including the intake manifold, cylinder heads, and sensor locations. This visual map is essential for diagnosing issues when a check engine light appears, allowing owners to locate the ECU and interpret OBD-II data for efficient, accurate repairs.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides a visual reference for locating critical sensors and mechanical parts.
- Identifying the intake manifold gasket is vital due to common leakage issues.
- Always verify specific torque spec values to prevent bolt failure or leaks.
- Use the diagram to trace wiring between the ECU and various engine sensors.
- Apply this diagram when diagnosing performance drops or identifying parts for replacement.
Navigating the complexities of a GM 3.4 V6 engine requires more than just mechanical intuition; it demands a precise gm 3.4 v6 engine diagram to ensure every bolt, sensor, and hose is correctly placed. Whether you are performing a routine maintenance check or diving into a deep repair like replacing the intake manifold gaskets, having a visual roadmap is indispensable. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the engine’s architecture, helping you identify critical components, understand fluid paths, and master the intricate wiring that connects to the vehicle’s computer system. By studying the correct diagram, you will learn how to troubleshoot common failures and maintain the longevity of this widely used powerplant.
Main Diagram Component Breakdown
The GM 3.4L V6, part of the 60-degree engine family (specifically the LA1 3400), features a distinct layout that emphasizes a compact design for transverse mounting in front-wheel-drive vehicles. When looking at a comprehensive gm 3.4 v6 engine diagram, the first thing you will notice is the split between the upper and lower intake manifolds. The upper plenum is typically made of lightweight alloy or composite, while the lower intake manifold (LIM) houses the fuel injectors and connects directly to the cylinder heads.
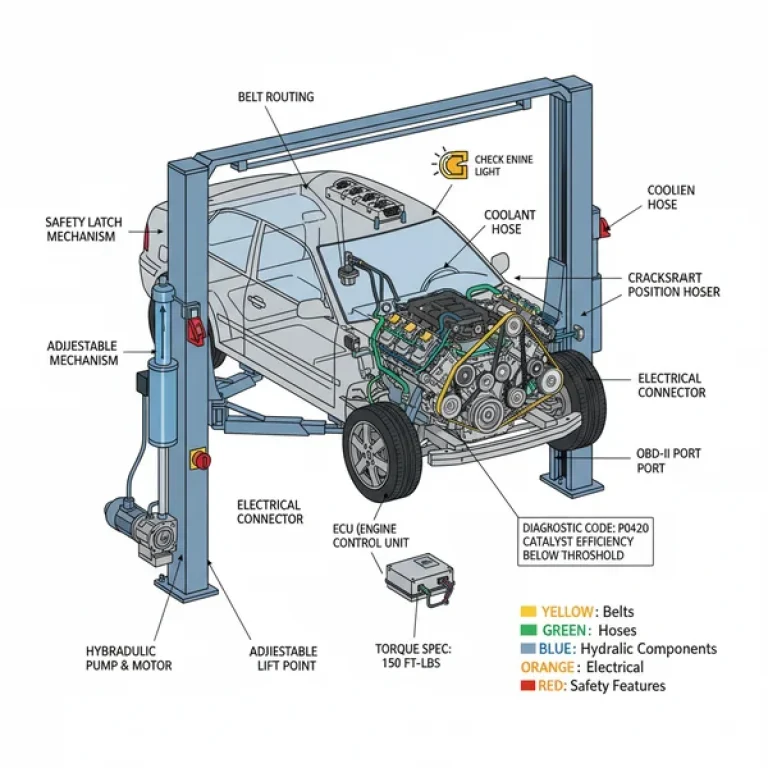
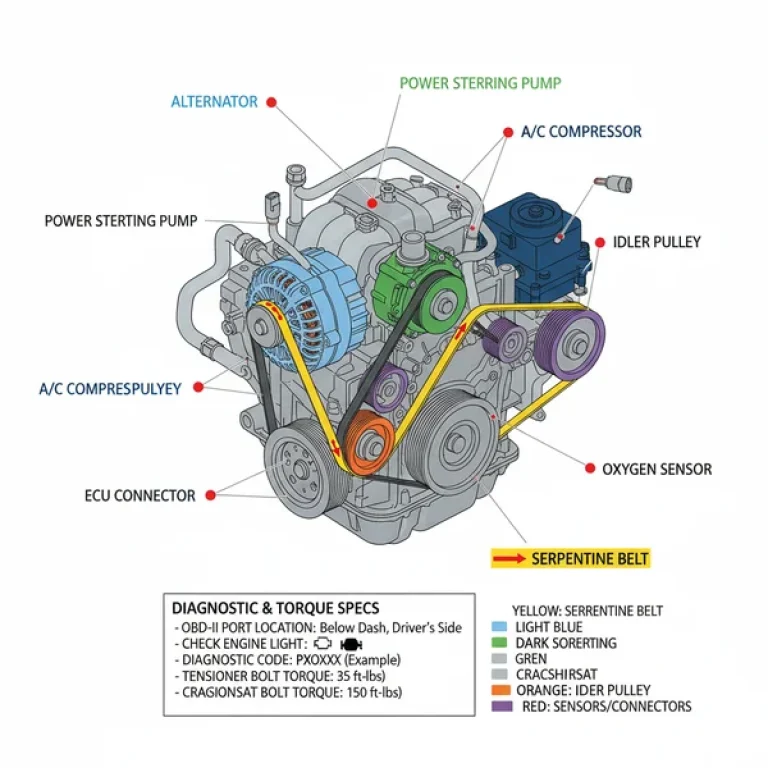
Key elements of the diagram include the accessory belt routing, which winds around the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and the water pump. The water pump is driven by the back of the serpentine belt, a critical detail often missed without a diagram. Fluid paths are another vital component; the coolant flow moves from the radiator through the lower radiator hose, into the engine block, up through the cylinder heads, and back through the thermostat housing located near the top of the engine.
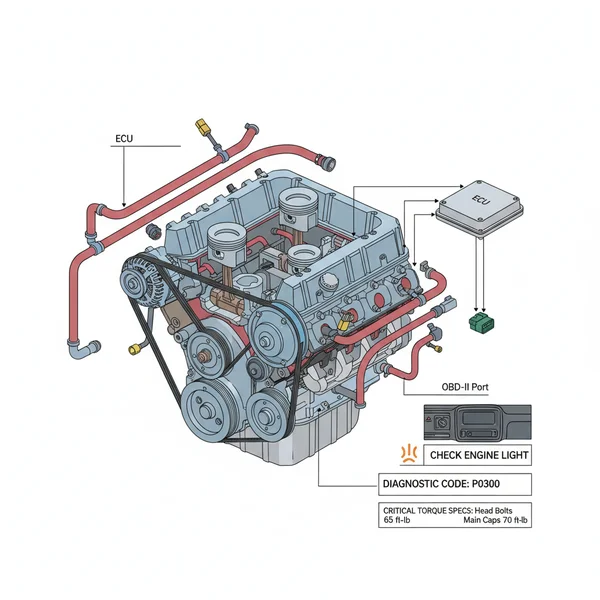
The electrical side of the diagram highlights the Ignition Control Module (ICM) and the three coil packs mounted at the rear of the engine block. These are connected via a wiring harness to the ECU (Engine Control Unit), which manages fuel injection and spark timing based on sensor feedback. Identifying these locations on a diagram is essential for pinpointing the source of a misfire or a faulty sensor reading.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A detailed technical illustration of the GM 3.4L V6 engine. The image displays a 3/4 view of the engine with labels for the Upper Intake Manifold, Alternator, Accessory Belt Path, Thermostat Housing, and Spark Plug Wire Routing. Color-coded lines indicate Coolant Flow (Blue) and Fuel Lines (Green). A sub-diagram shows the Serpenting Belt tensioner direction and pulley alignment.]
The GM 3.4L V6 uses a “waste spark” ignition system. This means one coil fires two spark plugs simultaneously, which is why the diagram shows wires paired across the engine bank.
Step-by-Step Guide: Interpreting and Using the Diagram

To effectively use a gm 3.4 v6 engine diagram for repairs or maintenance, follow these structured steps to ensure accuracy and safety.
-
1. Orient the Diagram to the Vehicle:
Open your hood and identify the front of the engine (where the belts are) versus the rear (where the transmission attaches). Most diagrams are drawn from the perspective of looking at the belts, so rotate your understanding accordingly. -
2. Identify the Accessory Belt Path:
Locate the tensioner pulley on the diagram. Use a long-handled wrench to release tension on the accessory belt. Follow the diagram’s “S-curve” to ensure the belt passes over the ribbed pulleys and under the smooth idler pulleys correctly. -
3. Trace the Coolant Flow for Bleeding:
The 3.4 V6 is notorious for trapping air in the cooling system. Use the diagram to find the two brass bleeder valves—one is usually on the thermostat housing and the other on the bypass pipe above the water pump. Opening these while filling the system ensures air escapes. -
4. Locate Sensors for OBD-II Diagnostics:
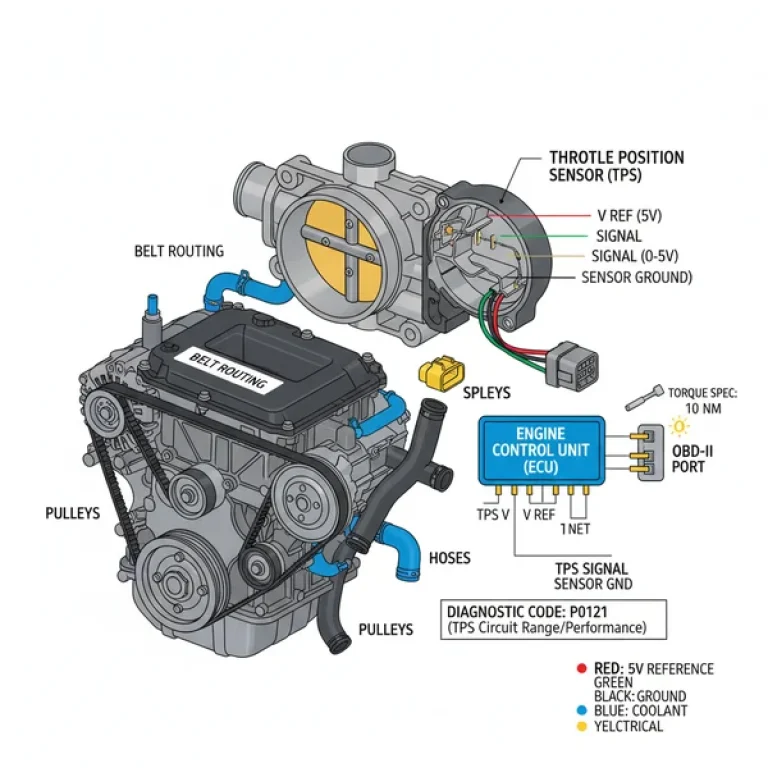
When a check engine light appears, use the diagram to find the sensor corresponding to the diagnostic code. For example, the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor is located on the intake bellows, while the Oxygen (O2) sensors are found in the exhaust manifold and downpipe. -
5. Verify Torque Spec Applications:
Using the diagram’s component list, identify the specific torque spec for the part you are installing. For the lower intake manifold, this is typically around 115 lb-in (not lb-ft) for the vertical bolts. Following a specific sequence (usually starting from the center and working out) is vital to prevent leaks. -
6. Inspect the Timing Chain Area:
While the timing chain is internal, the diagram shows the location of the timing cover behind the harmonic balancer. If you hear a rattling sound, use the diagram to confirm if the noise is coming from the front-center of the block where the chain resides.
Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on electrical components shown in the diagram, especially the ECU or alternator, to prevent short circuits.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
The GM 3.4 V6 is a robust engine, but it has specific “weak points” that a diagram can help you resolve. The most frequent issue is the failure of the lower intake manifold gaskets. These gaskets often degrade, leading to coolant entering the oil valley or leaking externally. By referring to the gm 3.4 v6 engine diagram, you can identify the exact perimeter of the intake where these leaks occur.
Another common problem involves the check engine light being triggered by the EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) valve or the Idle Air Control (IAC) valve. The diagram allows you to locate these valves on the throttle body and intake plenum for easy cleaning or replacement. If your OBD-II scanner returns a “lean” code, the diagram helps you trace the vacuum lines that might have become brittle and cracked over time.
Finally, overheating is a major concern. If your temperature gauge spikes, use the coolant flow diagram to check for obstructions. A common failure point is the plastic coolant bypass elbows, which can be located on the diagram near the alternator bracket. Replacing these with metal versions is a standard fix for this engine series.
Tips & Best Practices for Maintenance
Maintaining the GM 3.4L V6 requires attention to detail and high-quality parts. When replacing gaskets, always opt for premium “problem-solver” versions, such as those made from aluminized steel with viton rubber coatings. These are far more durable than the original plastic-frame gaskets that frequently failed in early models.
When performing an oil change, always check the underside of the oil fill cap for a “milky” substance. This is a sign of coolant mixing with oil, indicating a failing intake gasket or head gasket—both of which are easier to diagnose if you have your gm 3.4 v6 engine diagram handy.
For optimal performance, keep the throttle body clean. Carbon buildup on the butterfly valve can cause a rough idle or stalling. Use the diagram to safely remove the air intake ducting and spray a dedicated throttle body cleaner while avoiding sensitive electrical connectors.
Furthermore, pay close attention to the accessory belt. A worn belt can snap and cause immediate overheating or loss of power steering. Check the belt for “rib cracking” (more than three cracks in a one-inch span) and ensure the pulleys are aligned according to the diagram’s specifications. Lastly, always keep a record of your diagnostic code history; this allows the ECU to provide a better long-term picture of the engine’s health, making future troubleshooting significantly faster and more cost-effective.
By combining the visual data from a gm 3.4 v6 engine diagram with these practical maintenance tips, you can ensure your vehicle remains reliable for many miles to come. Understanding the relationship between the mechanical hardware and the electronic control system is the key to mastering this classic GM engine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a GM 3.4 V6 engine diagram?
A GM 3.4 V6 engine diagram is a technical illustration showing the arrangement of mechanical parts, electrical sensors, and fluid passages. It helps mechanics identify specific locations for components like the intake manifold, spark plugs, and various sensors, facilitating easier maintenance and more accurate repairs for vehicle owners.
How do you read a GM 3.4 V6 engine diagram?
Start by identifying the front of the engine, usually where the drive belt is located. Follow the labels to locate the upper and lower intake manifolds. Use the legend to distinguish between electrical connections to the ECU and physical hardware components to navigate the engine bay effectively.
What are the parts of a GM 3.4 V6?
Key parts include the cylinder heads, intake manifold, water pump, and fuel injectors. It also features several electronic components, such as the ECU, oxygen sensors, and ignition coils. Understanding these parts’ locations via a diagram is crucial for performing common maintenance tasks and ensuring the engine runs efficiently.
Why is the ECU important in this diagram?
The ECU, or Engine Control Unit, is the brain that monitors sensors and manages engine performance. In a diagram, it shows how wiring harnesses connect to the ECU, which is essential for troubleshooting a check engine light or resolving complex electrical issues through the OBD-II system.
What is the difference between an exploded view and a wiring diagram?
An exploded view diagram shows individual mechanical parts separated to illustrate how they fit together, which is ideal for assembly. A wiring diagram focuses on electrical connections between sensors, the ECU, and the OBD-II port, which is better for diagnosing electrical faults and sensor communication errors.
How do I use a GM 3.4 V6 engine diagram?
Use the diagram as a roadmap by matching the visual symbols to the physical parts in your vehicle’s engine bay. It helps you locate components for testing, find the correct torque spec for fasteners, and trace vacuum or electrical lines when diagnosing a specific diagnostic code.