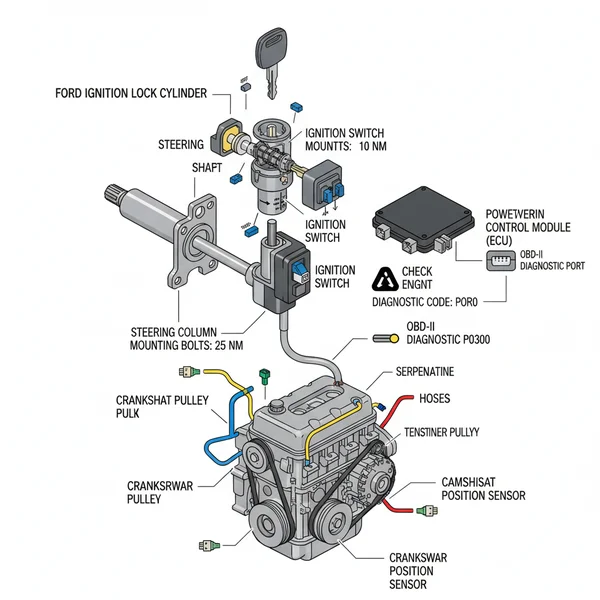
A Ford ignition lock cylinder diagram illustrates the internal components, mechanical tumblers, and electrical switch connections within the steering column. It helps identify how the key rotates to trigger the ECU and start the engine. Referencing this layout is essential when resolving mechanical key jams or electrical failures that prevent vehicle ignition.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Visually map the physical and electrical links between the key and the ignition switch.
- Identify the release pin location required for cylinder removal.
- Ensure the battery is disconnected to prevent short circuits or SRS deployment.
- Compare diagram wire colors to your specific harness for accurate troubleshooting.
- Use this diagram when the key won’t turn or the vehicle fails to crank.
If you are currently facing a key that refuses to turn or a vehicle that will not initiate the cranking process, understanding a Ford ignition lock cylinder diagram is essential for a successful repair. Many Ford owners encounter mechanical wear within the lock housing, leading to frustration and potential stranding. By utilizing a clear schematic, you can visualize the relationship between the key, the tumblers, and the ignition switch. This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of the assembly, offering a detailed guide on how to interpret the diagrams, troubleshoot common failures, and perform a replacement that ensures your vehicle starts reliably every time.
Understanding the Ford Ignition Lock Cylinder Assembly
The Ford ignition lock cylinder is more than just a hole for your key; it is a sophisticated mechanical-to-electrical interface. When you look at a Ford ignition lock cylinder diagram, you are seeing the primary gateway to your vehicle’s power systems. The assembly is typically housed within the steering column and consists of several critical layers. At the core is the cylinder itself, which contains a series of spring-loaded tumblers. These tumblers must align perfectly with the “bits” or cuts on your key to allow the cylinder to rotate.
Surrounding the mechanical cylinder is the transceiver ring. In most modern Ford vehicles, this ring communicates with a chip inside your key. This data is then sent to the ECU (Engine Control Unit) to verify that a programmed key is being used. If the ECU does not receive the correct signal, the vehicle will engage the Passive Anti-Theft System (PATS), preventing the engine from firing even if the mechanical lock turns.
The diagram also illustrates the connection to the ignition switch, which is a separate electrical component located behind or below the mechanical cylinder. While the cylinder provides the physical rotation, the switch translates that movement into electrical signals that engage the starter motor and power the dashboard. It is important to distinguish between these two; a failure in the cylinder usually results in a key that won’t turn, whereas a failure in the switch often results in a key that turns but produces no electrical response or a check engine light due to voltage drops.

Most Ford ignition diagrams utilize a color-coded system where blue or green lines represent the mechanical path of the actuator rod, and red or yellow lines indicate the electrical signal path to the starter relay and fuel pump.
Step-by-Step Interpretation and Installation Guide
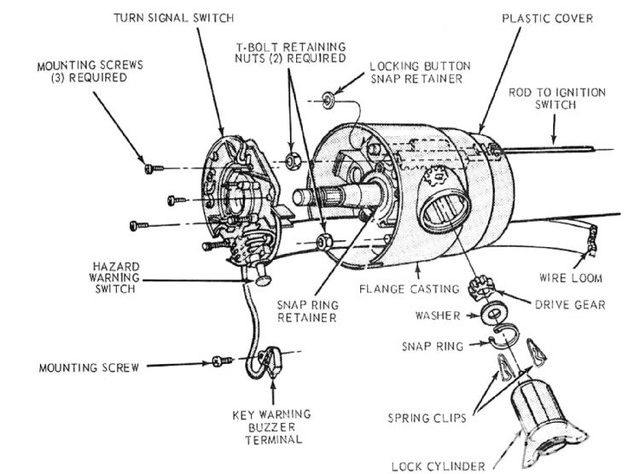
Reading a Ford ignition lock cylinder diagram requires a systematic approach. Before you begin any work, ensure you have gathered the necessary tools, including a small pin punch or a 1/8-inch drill bit, a set of screwdrivers (Phillips and Torx), and potentially a socket set for steering column shroud removal. Unlike working on the engine’s timing chain or adjusting the accessory belt, this task requires precision and patience rather than brute force.
- ✓ Step 1: Disconnect the Battery: Safety is paramount. Disconnect the negative battery terminal to prevent accidental airbag deployment or electrical shorts while working inside the steering column.
- ✓ Step 2: Remove the Column Shrouds: Use your screwdriver to remove the fasteners holding the upper and lower plastic covers around the steering wheel. This reveals the ignition housing shown in your diagram.
- ✓ Step 3: Locate the Release Hole: Referencing your Ford ignition lock cylinder diagram, find the small access hole on the bottom of the lock housing. This is usually only accessible when the shroud is removed.
- ✓ Step 4: Rotate the Key to the ‘Run’ Position: Insert your key and turn it to the ‘Run’ (ON) position. This aligns the internal locking pin with the access hole. If your key is stuck and won’t turn, you may need to gently tap the cylinder with a mallet to vibrate the tumblers into place.
- ✓ Step 5: Depress the Release Pin: Insert your pin punch into the access hole and press firmly. While holding the pin down, pull the ignition lock cylinder straight out of the housing.
- ✓ Step 6: Inspect the Actuator Rod: Look inside the housing. The diagram will show an actuator rod that connects the cylinder to the electrical switch. Ensure this rod is not snapped or bent.
- ✓ Step 7: Install the New Cylinder: Ensure the new cylinder is in the ‘Run’ position. Slide it into the housing until the release pin clicks into place. Test the rotation before reassembling the shrouds.
- ✓ Step 8: Reconnect and Program: Reattach the battery. If your vehicle uses a transponder key, you may need to follow a specific programming sequence to link the new lock to the ECU.
Do not force the key if it will not turn. Applying excessive torque can snap the key inside the cylinder or damage the internal actuator rod, turning a simple cylinder swap into a much more expensive repair involving the entire steering column.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with the Diagram
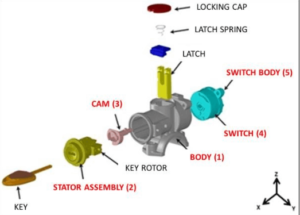
When troubleshooting Ford ignition problems, the diagram serves as a diagnostic map. One of the most common issues is a “dead” feel when turning the key. By looking at the assembly diagram, you can see that the cylinder rotates a gear which moves the actuator rod. If the rod is broken, the cylinder will turn freely, but the vehicle will remain silent.
Another frequent problem involves the anti-theft system. If the vehicle cranks but shuts off immediately, or won’t crank at all, you should use an OBD-II scanner to look for a specific diagnostic code such as P1260 (Theft Detected). While a mechanical diagram helps with the physical replacement, these codes point toward the electronic transceiver ring shown in the schematic.
It is also worth noting that symptoms of a failing ignition cylinder can sometimes mimic other engine issues. For example, if your check engine light is on, it is rarely caused by the lock cylinder itself, but rather by the electronic switch failing to provide constant power to the ECU. Always verify the mechanical integrity of the lock before diving into complex engine diagnostics like checking coolant flow or sensor voltages.
Pro Tips and Best Practices for Longevity
To ensure your Ford ignition system remains reliable, maintenance is key. Many owners make the mistake of using heavy keychains. The weight of numerous keys and accessories pulls down on the cylinder, causing the tumblers to wear prematurely. By referencing the Ford ignition lock cylinder diagram, you can see how delicate the internal brass tumblers are. Keeping your ignition key on a separate, lightweight ring can double the lifespan of the lock.
Never use oil or WD-40 in an ignition lock. These attract dust and grime, which eventually turn into a thick paste that jams the tumblers. Instead, use a dry graphite lubricant specifically designed for automotive locks.
When purchasing replacement parts, always opt for High-Quality OE (Original Equipment) components. While aftermarket cylinders are cheaper, they often lack the precise tolerances shown in the original manufacturer’s diagram, leading to sticking issues within months of installation. If you are performing a full steering column overhaul, take the time to check other nearby components. For instance, while you have the column disassembled, inspect the steering shaft U-joints and ensure any mounting bolts are tightened to the correct torque spec.
Finally, keep a copy of your OBD-II diagnostic code history. If you notice a recurring issue with the security system, it may indicate that the transceiver ring (shown in your diagram) is beginning to fail, rather than the mechanical lock cylinder. Addressing these small issues early can prevent the need for an emergency tow and a much more stressful repair scenario. Just as you monitor your accessory belt for cracks or your timing chain for noise, paying attention to the “feel” of your ignition key is a vital part of proactive vehicle maintenance. Understanding the Ford ignition lock cylinder diagram empowers you to take control of these repairs, saving you hundreds of dollars in dealership labor costs while ensuring your Ford remains a dependable mode of transportation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ford ignition lock cylinder diagram?
A Ford ignition lock cylinder diagram is a visual schematic showing the assembly of the lock cylinder, housing, and ignition switch. It highlights the mechanical interface between the physical key and the electronic starter system. This guide is vital for diagnosing starting failures and ensuring proper alignment during a replacement.
How do you read Ford ignition lock cylinder diagram?
Start by locating the steering column and identifying the cylinder housing. Trace the wires from the ignition switch to the main harness. Look for labels indicating power, ground, and signal wires that communicate with the ECU. Matching the diagram symbols to physical components ensures an accurate and safe repair process.
What are the parts of Ford ignition lock cylinder?
The system includes the lock cylinder, key tumblers, ignition switch, and anti-theft transceiver. These parts work together to turn the engine over. If the ignition switch fails, it may trigger a check engine light or store a diagnostic code in the system, requiring further inspection using an OBD-II scanner.
Why is Ford ignition lock cylinder important?
The ignition lock cylinder is the primary gateway for starting your vehicle and securing the steering column. It ensures that only the correct key can activate the electronics. If it malfunctions, the ECU may not receive the necessary signal to engage the fuel pump or the starter motor for ignition.
What is the difference between the cylinder and the switch?
The lock cylinder is the mechanical part where you insert the key, whereas the ignition switch is the electrical component behind it. The cylinder turns the switch to complete circuits. If the switch fails, you might see a diagnostic code, but the key will still turn mechanically inside the cylinder.
How do I use Ford ignition lock cylinder diagram?
Use the diagram to locate the small access hole for the release pin on the steering column. Follow the wiring paths to test for continuity with a multimeter if you suspect an electrical fault. Always check for a check engine light first to see if an OBD-II scan is needed.