Ford Escape Coolant Hose Diagram: Routing and Layout
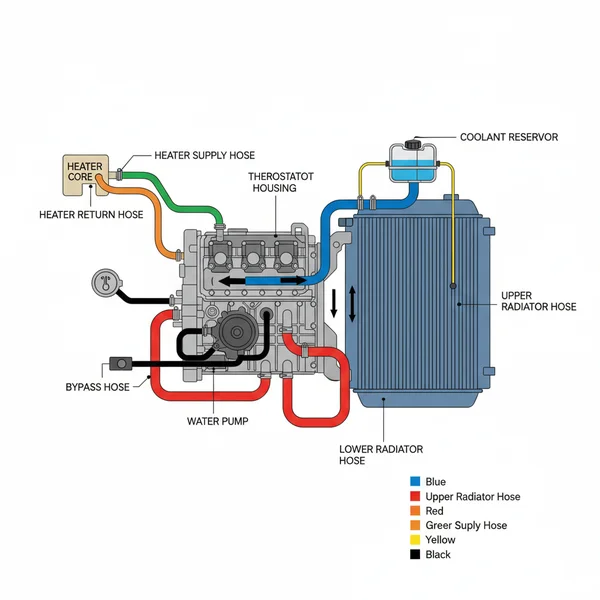
A Ford Escape coolant hose diagram illustrates the intricate system of hoses transferring fluid between the engine, radiator, and heater core. This visual layout helps identify critical components like the upper and lower radiator hoses, expansion tank lines, and bypass hoses, ensuring proper coolant flow and engine temperature regulation.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Map the flow path of engine coolant to prevent overheating
- Identify the radiator hoses and heater core connections
- Always check for pressure leaks at the connection points
- Use the diagram to verify the correct configuration after repairs
- Use this guide when replacing worn hoses or flushing the system
Navigating the complex cooling system of a modern SUV requires precision, especially when dealing with the intricate 2014 Ford Escape coolant hose diagram. Whether you are performing a routine maintenance check or diagnosing a sudden overheat, understanding how coolant circulates through your engine is essential for the longevity of your vehicle. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of the coolant hose layout, detailing every major component from the radiator to the heater core. You will learn how to identify specific hoses, interpret the routing system, and gain the confidence needed to perform repairs or replacements safely. By mastering this diagram, you ensure your EcoBoost or naturally aspirated engine remains at the optimal operating temperature, preventing costly internal damage.
Understanding the 2014 Ford Escape Coolant Hose Diagram Layout
The 2014 Ford Escape features a sophisticated cooling system configuration that varies slightly depending on whether your vehicle is equipped with the 1.6L EcoBoost, 2.0L EcoBoost, or the 2.5L Duratec engine. Despite these variations, the core structure remains consistent. The primary purpose of the coolant hose diagram is to illustrate the path of the engine coolant as it travels from the radiator, through the engine block, and into the passenger cabin via the heater core. Understanding this layout is the first step in identifying which specific component may be failing.
Most 2014 Ford Escape models utilize a “degas” system, which uses a pressurized expansion tank rather than a traditional radiator cap. This means the hoses connected to the plastic tank are just as critical as the main radiator hoses.
The diagram typically breaks down into three main circuits. First is the primary radiator circuit, which includes the large diameter upper and lower radiator hoses. The upper hose carries hot coolant from the thermostat housing to the radiator, while the lower hose returns cooled fluid back to the water pump. Second is the heater circuit, consisting of two hoses that pass through the firewall to provide warmth to the cabin. Finally, there is the bypass and degas circuit, which includes smaller-diameter hoses designed to bleed air from the system and maintain consistent pressure. On EcoBoost models, you will also notice additional coolant lines running to and from the turbocharger, which are vital for cooling the turbine bearings.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A detailed 2014 Ford Escape coolant hose diagram showing the radiator, thermostat, water pump, and heater core connections for EcoBoost engines.]
When viewing the diagram, pay close attention to the labeling of connectors. Ford often uses “quick-connect” fittings on these hoses rather than traditional worm-gear clamps. These fittings are color-coded or shape-specific in the diagram to ensure that the return line is never swapped with the feed line, which could cause a significant disruption in the cooling system’s thermal efficiency.
How to Read and Interpret the Coolant Hose System

Reading a 2014 Ford Escape coolant hose diagram can feel overwhelming at first glance due to the density of components in the engine bay. To effectively use the diagram for a repair or inspection, follow these systematic steps to interpret the configuration and flow of the system.
Step 1: Identify Your Engine Specification
Before looking at the diagram, confirm your engine type. The 1.6L EcoBoost engine has a notably different hose layout near the cylinder head compared to the 2.0L version. The diagram will often have specific sub-sections or legends indicating which lines are specific to the turbocharger system. Ensuring you are looking at the correct engine variant is the most important preparatory step.
Step 2: Locate the Radiator as the Anchor Point
In the diagram, the radiator serves as the primary reference point. Find the radiator at the front of the layout. From here, you can trace the two largest hoses. The upper hose usually connects to the thermostat housing near the top of the engine, while the lower hose leads toward the water pump inlet at the bottom. These are the most common points of failure due to the high pressure they sustain.
Step 3: Trace the Directional Flow
Most diagrams use arrows to indicate the direction of coolant flow. Coolant exits the engine hot, travels through the thermostat (once open), moves through the upper hose into the radiator, cools down, and is pulled back into the engine by the water pump via the lower hose. If your diagram does not have arrows, remember: “Top is Hot, Bottom is Cool.”
Never attempt to disconnect coolant hoses while the engine is hot. The 2014 Ford Escape system is under high pressure, and opening a connection can result in severe steam burns.
Step 4: Identify the Degas (Expansion) Tank Lines
The 2014 Escape uses a pressurized tank. The diagram will show several small hoses connecting this tank to the radiator and the engine block. These hoses are critical for removing air bubbles (burping) from the system. If these small lines are clogged or cracked, the engine may overheat even if the main radiator hoses are in perfect condition.
Step 5: Isolate the Heater Core Circuit
Locate the two hoses that disappear toward the back of the engine bay near the firewall. One is the heater inlet and the other is the outlet. These provide the heat for your HVAC system. In the diagram, these are often grouped together. If you have no heat in the cabin but the engine is running at the correct temperature, these hoses or the heater control valve are the components to inspect.
Required Tools for Hose Maintenance
- ✓ Long-reach hose clamp pliers (for those hard-to-reach spring clamps)
- ✓ Flathead screwdriver or pick tool (for quick-connect clips)
- ✓ Large drain pan (minimum 2-gallon capacity)
- ✓ Distilled water and Ford-approved Motorcraft coolant
Common Issues and Troubleshooting the Cooling System

The 2014 Ford Escape is known for specific cooling system vulnerabilities that the hose diagram can help you diagnose. One of the most frequent problems is a failure in the coolant bypass valve, particularly on the 1.6L EcoBoost models. This valve controls the flow between the engine and the heater core. If you notice a “Coolant Over Temperature” warning but the radiator is cold, the diagram will help you locate this valve to check for electrical or mechanical failure.
Another common issue involves the plastic “T-connectors” and quick-connect fittings. Over time, the plastic becomes brittle due to constant heat cycles. By using the diagram, you can pinpoint these junction points. If you see white or orange crusty residue around a hose end, that is a clear indicator of a slow leak. The diagram allows you to identify the specific part number or hose section needed for replacement without having to guess which “black tube” is leaking.
Air pockets are a third frequent hurdle. If you have recently replaced a hose and the car is now overheating, there is likely air trapped in the system. Referencing the diagram helps you find the highest point in the cooling system—usually a bleeder valve or the degas bottle return line—where air can be successfully purged.
Tips and Best Practices for Cooling System Maintenance
Maintaining the integrity of your 2014 Ford Escape’s coolant hoses requires more than just knowing where they are; it requires a proactive approach to automotive care. Follow these professional tips to ensure your system remains leak-free and efficient.
When replacing a hose, always replace the constant-tension spring clamp if it shows signs of rust. While many DIYers switch to worm-gear screw clamps, spring clamps are often better at maintaining a seal as the rubber expands and contracts with heat.
First, always use the correct coolant specification. For the 2014 model year, Ford originally specified Motorcraft Orange Antifreeze, though this has largely been superseded by Motorcraft Yellow in newer service bulletins. Check your owner’s manual or the label on the degas bottle to confirm. Never mix green “universal” coolant with the specialized OAT (Organic Acid Technology) coolant used by Ford, as this can lead to “sludging,” which will clog the narrow passages shown in your hose diagram.
Second, perform a “squeeze test” during every oil change. With the engine off and cool, squeeze the radiator hoses. They should feel firm but pliable. If a hose feels “crunchy” (indicating internal scale buildup) or excessively soft and “spongy” (indicating oil contamination or internal breakdown), it is time to replace it. A hose that fails while driving can lead to total engine failure within minutes.
Finally, consider a “complete system refresh” if your Escape has surpassed 100,000 miles. Rubber components have a finite lifespan. Using your 2014 ford escape coolant hose diagram as a shopping list, replacing the upper and lower radiator hoses, the degas bottle cap, and the thermostat as a preventative measure can save you from an expensive breakdown on the road. High-quality silicone or reinforced EPDM hoses are recommended for long-term durability and resistance to electrochemical degradation.
In conclusion, the 2014 ford escape coolant hose diagram is an invaluable tool for any owner or mechanic. By understanding the routing, identifying the components, and following a structured approach to troubleshooting, you can maintain the thermal health of your vehicle for years to come. Remember that a small investment in a new hose today is far cheaper than an engine replacement tomorrow.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the Ford Escape Coolant Hose Diagram: Routing And Layout
Identify the main radiator hoses and the expansion tank connection on the diagram.
Locate the heater core hoses leading toward the vehicle’s firewall within the engine structure.
Understand how the bypass hoses integrate with the thermostat housing and water pump configuration.
Connect the visual representation of the layout to the actual hose routing in your vehicle.
Verify that all hose clamps are positioned correctly according to the system schematic provided.
Complete the inspection by tracing the entire coolant flow path to ensure no obstructions exist.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ford Escape coolant hose diagram?
A Ford Escape coolant hose diagram is a visual representation of the cooling system’s plumbing. It shows the specific routing and structure of hoses that carry coolant from the radiator to the engine block and heater core, helping owners identify specific parts for maintenance or repair tasks.
How do you read Ford Escape coolant hose diagram?
To read the diagram, start at the radiator and follow the lines to the engine. Identify arrows indicating flow direction and labels marking each component. Pay attention to the layout of bypass hoses and the expansion tank to understand how the pressurized system circulates fluid throughout the vehicle.
What are the parts of Ford Escape coolant system?
The system includes the radiator, water pump, thermostat housing, expansion tank, heater core, and various hoses. The configuration also features a cooling fan and temperature sensors. Each component works together within the structure to dissipate heat from the engine and maintain an optimal operating temperature during driving.
Why is the expansion tank hose important?
The expansion tank hose is critical because it manages the system’s pressure and allows for coolant expansion as it heats up. This component prevents air pockets from forming and ensures that the coolant level remains consistent, which is vital for the overall health and safety of the engine.
What is the difference between upper and lower radiator hoses?
The upper radiator hose carries hot coolant from the engine to the radiator for cooling, while the lower radiator hose returns cooled fluid back to the water pump. This specific configuration ensures a continuous loop of heat exchange, preventing the engine from seizing due to extreme temperatures.
How do I use Ford Escape coolant hose diagram?
Use the diagram as a reference to locate specific hoses when searching for leaks or performing replacements. Match the physical layout of your engine bay to the schematic to ensure every component is connected correctly, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of the vehicle’s cooling system.