Engine Throttle Position Sensor Diagram: Diagnostics Guide
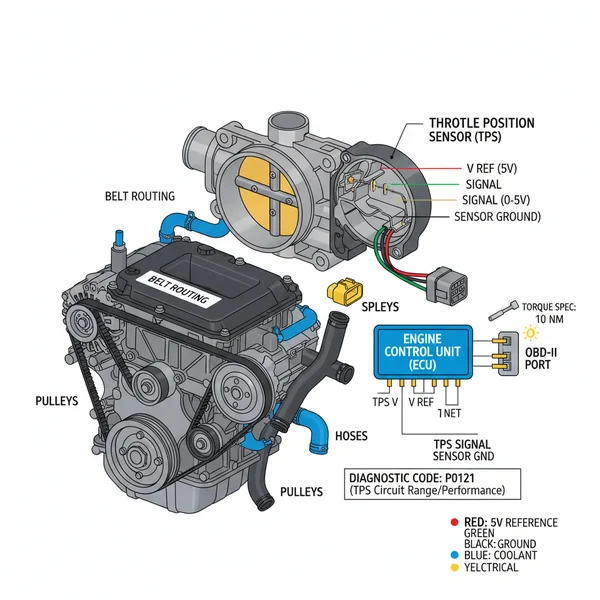
An engine throttle position sensor diagram illustrates the electrical connections between the TPS and the ECU. It typically identifies the 5V reference wire, the signal wire, and the ground. This visual guide is essential for troubleshooting diagnostic codes and ensuring the throttle blade angle is accurately reported for proper fuel injection.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides a visual map of the electrical pinout and signal flow
- The signal wire is the most critical for monitoring voltage changes
- Always disconnect the battery before testing sensitive electronic components
- Compare live sensor data with the diagram to isolate wiring faults
- Use this diagram when diagnosing limp mode or erratic idling issues
Whether you are dealing with a sudden drop in fuel economy, a stumbling engine, or a frustrating hesitation when you press the gas pedal, understanding your vehicle’s air-intake system is the first step toward a successful repair. Most of these issues trace back to a small but vital component known as the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS). Having a clear and accurate engine throttle position sensor diagram allows you to pinpoint the exact location of the sensor, understand its wiring configuration, and verify how it communicates with your vehicle’s computer. In this guide, you will learn how to interpret a TPS diagram, use it to diagnose electrical faults, and perform a professional-grade replacement that restores your engine’s performance and throttle response.
Understanding the Engine Throttle Position Sensor Diagram Components
An engine throttle position sensor diagram serves as a technical roadmap for one of the most critical sensors in the fuel management system. The TPS is typically a potentiometer—a type of variable resistor—mounted directly onto the throttle body. As you press the accelerator, the throttle plate rotates, and the TPS monitors this movement, converting the mechanical angle into an electrical signal sent to the Engine Control Unit (ECU).
The diagram illustrates how the sensor is integrated into the engine’s architecture. Most modern diagrams show a three-pin or four-pin connector. The first pin usually carries a 5-volt reference signal from the ECU. The second pin is the signal return, which varies in voltage based on the position of the butterfly valve. The third pin provides a dedicated ground to complete the circuit. If your vehicle features an electronic throttle control (drive-by-wire), the diagram may show dual sensor tracks (TPS 1 and TPS 2) used for redundancy and safety.
In the diagram, you will also see the physical proximity of the sensor to other engine components. While the TPS is mounted to the throttle body, it resides near the coolant flow bypass hoses and the intake manifold. Understanding these surroundings is vital, as heat or moisture from nearby systems can often cause connector corrosion or wire insulation failure. The diagram helps you distinguish the TPS wiring from other nearby harnesses, such as those for the idle air control valve or the fuel injectors, ensuring you don’t probe the wrong circuit during testing.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A detailed automotive schematic showing a throttle body assembly with the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) highlighted. The diagram labels the 5V reference wire, signal wire, and ground wire leading to the ECU. It also shows the mechanical linkage between the accelerator cable/motor and the internal potentiometer.]
How to Interpret and Use the Diagram for Repairs

Using an engine throttle position sensor diagram effectively requires a systematic approach. Whether you are a weekend warrior or an aspiring technician, following a logical sequence ensures safety and accuracy.
Before beginning any work, always consult the specific wiring colors listed in your vehicle’s factory service manual, as wire colors can vary significantly between different manufacturers and model years.
- Locate the Sensor: Refer to the diagram to find the throttle body. On most engines, this is located between the air filter box and the intake manifold. Ensure the engine is cool before touching any components.
- Identify the Wiring Pins: Use the diagram to identify which wire is the 5V reference and which is the signal. This is crucial because testing the wrong wire with a probe could potentially short out the ECU.
- Check for Physical Obstructions: Inspect the area around the sensor. Ensure that no stray components, such as a loose accessory belt or poorly routed vacuum lines, are interfering with the sensor’s connector.
- Perform a Voltage Sweep: With the ignition on but the engine off, use a multimeter to back-probe the signal wire. Slowly open the throttle. The voltage should rise smoothly (typically from 0.5V to 4.5V) without any “dead spots” or sudden drops.
- Disconnect and Inspect: Turn off the ignition and disconnect the harness. Use the diagram to verify that the pins on the sensor side are not bent or corroded.
- Remove the Old Sensor: Most sensors are held by two small screws. Use a high-quality screwdriver to avoid stripping the heads, which are often softened by engine heat over time.
- Install and Align: Some TPS units are “clockable,” meaning they must be rotated slightly to find the correct base voltage. Refer to your diagram or manual for the specific base voltage setting at idle.
- Apply Proper Torque: Once aligned, tighten the mounting screws to the manufacturer’s torque spec. Over-tightening can crack the plastic housing of the sensor.
Never spray cleaning solvent directly into the TPS electrical connector. This can cause internal short circuits or dissolve the conductive material inside the potentiometer.
Troubleshooting Common TPS Issues

When the TPS begins to fail, the ECU can no longer accurately calculate the air-fuel ratio, leading to a variety of driveability problems. The most common indicator is the illumination of the check engine light. By using an OBD-II scanner, you can retrieve a diagnostic code that points toward the throttle system. Common codes include P0121 (TPS Range/Performance Problem) or P0122 (TPS Circuit Low Input).
The diagram helps in troubleshooting by allowing you to perform a “wiggle test.” While monitoring the voltage on your multimeter or OBD-II live data, gently wiggle the wiring harness. If the signal jumps erratically, you have a wiring break rather than a sensor failure. This distinction can save you hundreds of dollars in unnecessary parts. Furthermore, while the TPS is often blamed for surging, always check the integrity of your timing chain or timing belt. If the mechanical timing is off, the engine may struggle to idle regardless of how well the TPS is functioning. Similarly, ensure that the coolant flow is consistent; some throttle bodies use engine coolant to prevent icing, and a leak here can contaminate the TPS electronics.
If your vehicle has a “dead spot” in acceleration, it is often due to a worn resistive track inside the TPS at the specific angle where you normally hold your foot during highway cruising.
Best Practices and Maintenance Tips
To ensure your engine throttle position sensor remains functional for the life of the vehicle, follow these maintenance best practices. First, always keep the throttle body clean. Carbon buildup around the butterfly valve can cause the valve to stick, putting mechanical strain on the TPS and leading to premature failure. Use a dedicated throttle body cleaner and a soft brush every 30,000 miles to maintain smooth operation.
When replacing a sensor, always opt for High-Quality (OEM) components. Inexpensive aftermarket sensors often have lower-quality resistive elements that provide “noisy” signals to the ECU, which can cause subtle hesitations even when new. Additionally, check the condition of your accessory belt. A slipping or vibrating belt can create electrical interference or excessive vibration that vibrates the throttle assembly, potentially loosening the TPS mounting screws.
- ✓ Check Grounds: Ensure the engine block ground straps are clean and tight to prevent voltage offsets in the TPS circuit.
- ✓ Seal Connections: Use a small amount of dielectric grease on the connector seal to keep moisture out of the pins.
- ✓ Reset the ECU: After replacement, disconnect the battery for 15 minutes to clear the learned idle values in the ECU memory.
- ✓ Inspect Vacuum Lines: Leaks in the vacuum system can mimic TPS failure; always inspect lines while you have the diagram handy.
In summary, a comprehensive engine throttle position sensor diagram is an indispensable tool for maintaining modern vehicle performance. By understanding the electrical relationship between the sensor and the ECU, and by following methodical diagnostic steps using an OBD-II scanner and multimeter, you can accurately identify faults. Whether you are dealing with a check engine light or simply performing routine maintenance, a clear understanding of the TPS ensures your engine remains efficient, responsive, and reliable on the road.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the Engine Throttle Position Sensor Diagram: Diagnostics Guide
Identify the throttle body assembly and the sensor mounting location using the provided diagram.
Locate the electrical connector and match the wire colors to the schematic for accurate testing.
Understand how the 5V reference signal flows from the ECU to the sensor’s input pin.
Connect a digital multimeter to the signal wire to monitor voltage changes as the throttle opens.
Verify that the sensor is securely fastened according to the manufacturer’s specific torque spec.
Complete the diagnostic process by clearing any stored OBD-II codes with a scanning tool.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is engine throttle position sensor diagram?
An engine throttle position sensor diagram is a technical schematic showing how the sensor interacts with the engine control unit. It highlights the internal potentiometer and the three-wire configuration common in most vehicles. This map helps technicians identify where voltage enters and exits the sensor to manage air-fuel ratios.
How do you read engine throttle position sensor diagram?
To read the diagram, locate the sensor housing and trace the colored lines representing the reference, signal, and ground wires. Check the pin numbers against the connector face. This allows you to use a multimeter to verify that the signal changes smoothly as the throttle plate moves.
What are the parts of engine throttle position sensor?
The main parts include the sensor body, the internal resistive track, and the wiper arm connected to the throttle shaft. Externally, it features a mounting flange and a harness connector. Understanding these components through a diagram helps diagnose mechanical wear that triggers a check engine light.
Why is ECU important?
The ECU is the brain of the vehicle that interprets the TPS signal to calculate fuel delivery and ignition timing. If the ECU receives an inconsistent voltage reading, it will store a diagnostic code and may put the vehicle into a reduced power mode to prevent engine damage.
What is the difference between TPS and MAF?
While both affect fuel trim, the TPS measures the physical opening of the throttle plate, whereas the MAF sensor measures the actual mass of air entering the intake. A diagram shows the TPS is mechanically linked to the pedal, while the MAF is located in the air ducting.
How do I use engine throttle position sensor diagram?
Use the diagram to perform a sweep test with a voltmeter to ensure there are no dead spots in the sensor range. By identifying the correct pins, you can confirm the 5V reference from the ECU is present and the ground circuit is intact during troubleshooting.