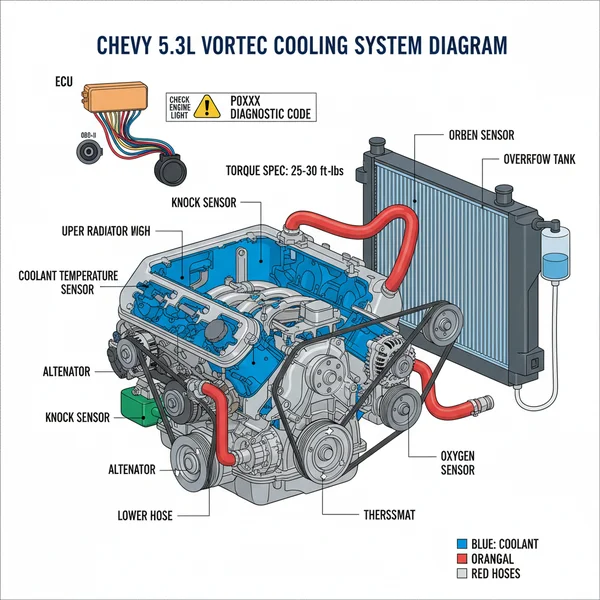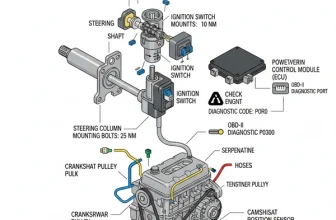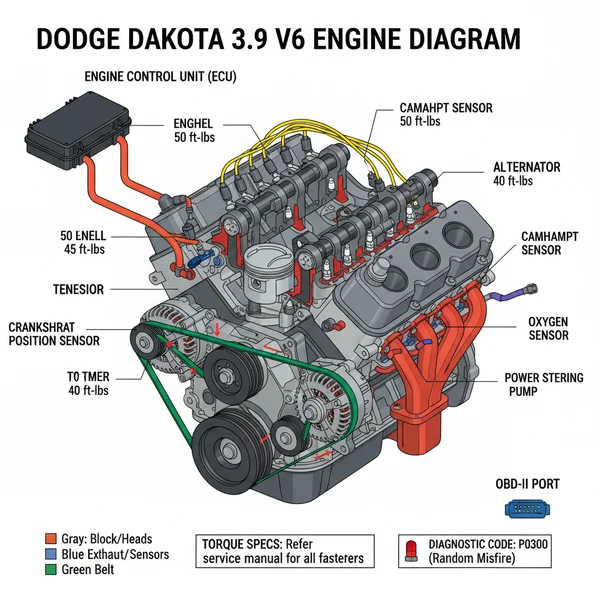
The Dodge Dakota 3.9 V6 engine diagram illustrates the layout of internal components, vacuum lines, and electrical sensors. It helps owners identify parts like the fuel injectors and ECU, facilitating troubleshooting when a check engine light appears or when performing repairs that require specific torque spec measurements for proper reassembly.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Simplifies the identification of sensor locations and routing
- Focus on the ECU and ignition system for diagnostic accuracy
- Always disconnect the battery before working on electrical components
- Use the diagram to verify vacuum line routing to prevent leaks
- Essential for interpreting OBD-II codes during routine maintenance
If you are a Dodge Dakota owner, you know that the 3.9-liter Magnum V6 is a legendary workhorse, providing a balance of power and durability for decades. However, even the most reliable engines require maintenance and occasional repair, which is where a comprehensive dodge dakota 3.9 v6 engine diagram becomes an essential tool in your garage. Understanding the layout of this specific engine is the first step in diagnosing mysterious noises, replacing worn components, or performing routine tune-ups. This guide provides a detailed breakdown of the engine’s architecture, helping you navigate the complex web of sensors, belts, and mechanical parts that keep your truck on the road. By the end of this article, you will have the knowledge to interpret engine schematics with confidence, ensuring your Dakota continues to perform at its peak.
Decoding the Dodge Dakota 3.9 V6 Engine Diagram
The 3.9-liter V6 engine is essentially a 90-degree V6 architecture, often described as a shortened version of the venerable 5.2L V8. When looking at a dodge dakota 3.9 v6 engine diagram, the most prominent feature is the front-mounted accessory drive system. This layout utilizes a single serpentine accessory belt to power the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and the water pump. The diagram typically highlights the “path of power,” showing exactly how the belt winds around various pulleys to ensure every sub-system receives the mechanical energy it needs to function.
Another critical element of the diagram is the intake and fuel delivery system. The 3.9L V6 features a “keggy” style intake manifold, so named for its barrel-like shape. A detailed diagram will illustrate the placement of fuel injectors, the throttle body, and essential sensors like the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) and the Idle Air Control (IAC) valve. Below the intake, the diagram reveals the lifter valley and the cylinder heads. Because this is an overhead valve (OHV) engine, the diagram will show the pushrod configuration and the rocker arms located beneath the valve covers. Understanding these layers is vital if you are performing a gasket replacement or investigating a top-end tick.
The cooling system is another major focus area. A proper schematic outlines the coolant flow, beginning at the radiator, moving through the lower radiator hose into the water pump, and circulating through the engine block and cylinder heads before reaching the thermostat housing. Seeing this flow visually helps you identify where air pockets might form or where a leak is likely to originate. Finally, diagrams for this engine often include the ignition system layout, specifically the distributor location at the rear of the engine block and the routing of the spark plug wires, which is crucial for maintaining the correct firing order.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A detailed technical illustration of a 3.9L V6 Magnum engine showing the front accessory drive, intake manifold, and sensor locations.]
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the Engine Diagram

Reading an engine diagram for the first time can feel like looking at a foreign map. However, by breaking it down into logical steps, you can use the dodge dakota 3.9 v6 engine diagram to perform almost any repair. Follow these steps to master the interpretation of your engine’s layout.
Before starting any work, ensure the engine is completely cool to the touch. Working on a hot engine increases the risk of burns from the radiator or exhaust manifolds.
Step 1: Orient Your Perspective
The first thing you must do when looking at a diagram is determine the “front” and “rear” of the engine. In a Dodge Dakota, the engine is mounted longitudinally. The front of the engine faces the radiator, where the fan and belts are located. The rear of the engine faces the firewall and connects to the transmission. Most diagrams are drawn from the front-facing perspective, but some may offer a “top-down” view for vacuum line routing.
Step 2: Trace the Accessory Belt Routing
If you are replacing your accessory belt, locate the belt routing section of the diagram. Identify the tensioner pulley, which is usually spring-loaded. Use the diagram to verify that the ribbed side of the belt touches the pulleys with grooves (like the alternator and crank) while the smooth side of the belt touches the smooth idler pulleys.
Step 3: Locate Electrical and Sensor Components
Use the diagram to find the ECU (Engine Control Unit) connection points and primary sensors. If your check engine light is on, the diagram will help you find the MAP sensor, O2 sensors, and the crank position sensor. The crank sensor is notoriously difficult to find on the 3.9L V6, as it is tucked away on the passenger side near the back of the engine block where it meets the transmission bellhousing.
Step 4: Identify Fluid Paths and Capacities
Trace the coolant flow and oil galleries. This is particularly helpful when you are trying to flush the system. The diagram will show you where the drain petcock on the radiator is located and where the block drain plugs are positioned. This ensures a complete flush rather than just a partial radiator drain.
Step 5: Reference Mechanical Fasteners
A comprehensive diagram often includes a torque spec table. When reassembling components like the intake manifold or valve covers, you must follow a specific tightening sequence and reach a specific foot-pound or inch-pound measurement. For example, the intake plenum bolts on this engine have a very specific torque sequence to prevent the common “plenum leak” issue.
Step 6: Check Vacuum Line Integrity
The 3.9L V6 relies heavily on vacuum pressure for everything from brake boosting to emission controls. Use the vacuum schematic portion of your diagram to ensure every plastic line and rubber elbow is connected to the correct port. A single loose line can cause a rough idle or a diagnostic code related to lean fuel mixtures.
Never over-tighten bolts on the aluminum components of the 3.9L V6. Using a torque wrench is mandatory to avoid stripping threads in the engine block or manifold.
Troubleshooting Common 3.9 V6 Issues

Even with a perfect dodge dakota 3.9 v6 engine diagram, you still need to know what symptoms to look for. One of the most frequent problems with this engine is the “plenum gasket failure.” Because the intake manifold is made of two different metals (aluminum top, steel bottom plate), they expand at different rates, eventually blowing out the gasket. This allows oil to be sucked into the combustion chamber.
The diagram helps here by showing you the exact location of the manifold bolts and the PCV system. If you notice a check engine light with codes indicating a misfire or an oxygen sensor failure, check the bottom of the intake through the throttle body using a flashlight. If you see standing oil, your plenum gasket is gone.
Another common issue involves the OBD-II system throwing a diagnostic code for the crankshaft or camshaft position sensors. These sensors synchronize the ignition timing. Using the diagram to locate these sensors can save you hours of “blind” searching in the cramped engine bay. If your truck cranks but won’t start, the diagram directs you straight to the ignition coil and the distributor cap to check for spark.
Maintenance Tips and Best Practices
To keep your Dakota running for 300,000 miles or more, you must look beyond the basic diagram and adopt a proactive maintenance schedule. The 3.9L V6 is an “interference” style engine in some configurations, meaning the timing chain is a critical failure point. While the chain is much stronger than a belt, it can stretch over time.
If you have over 150,000 miles, consider replacing the timing chain and gears. A stretched chain can cause sluggish performance and poor fuel economy long before it actually breaks.
- ✓ Use High-Quality Sensors: The ECU on these trucks is very sensitive to voltage. Always use OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) sensors rather than cheap aftermarket alternatives to avoid “ghost” codes.
- ✓ Monitor the Cooling System: Inspect your water pump for weeping every 30,000 miles. A failure in the coolant flow can lead to cracked cylinder heads, which are expensive to replace.
- ✓ Dielectric Grease: Use dielectric grease on all electrical connectors shown in the diagram, especially the OBD-II port and sensor plugs, to prevent corrosion in humid environments.
- ✓ Ground Straps: Ensure all engine-to-chassis ground straps are clean and tight. A bad ground can cause the ECU to behave erratically, leading to multiple false diagnostic code readings.
In conclusion, mastering the dodge dakota 3.9 v6 engine diagram is about more than just identifying parts; it is about understanding the synergy of the engine’s systems. Whether you are chasing down a check engine light or performing a full timing chain service, the diagram is your roadmap to success. By combining technical visuals with the torque spec requirements and maintenance best practices outlined here, you can ensure your Dodge Dakota remains a reliable partner for all your hauling and commuting needs. Always remember that a little time spent studying the diagram today can save you hundreds of dollars in professional repair bills tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Dodge Dakota 3.9 V6 engine diagram?
This diagram is a visual map of the 3.9-liter Magnum V6 engine, showing the placement of the intake manifold, spark plugs, and sensors. It serves as a blueprint for mechanics and DIYers to navigate the engine bay during repairs, ensuring every hose and wire is correctly positioned for optimal performance.
How do you read Dodge Dakota 3.9 V6 engine diagram?
Start by identifying major landmarks like the alternator or power steering pump to orient yourself. Follow the lines representing wiring or vacuum hoses from the source to the destination. Use the legend to correlate numbers or symbols with specific parts like the ECU or fuel rails for pinpoint accuracy.
What are the parts of Dodge Dakota 3.9 V6?
The 3.9 V6 consists of the engine block, cylinder heads, intake manifold, and throttle body. It also includes critical electronics like the ECU, oxygen sensors, and ignition coil. Supporting systems include the cooling fan, serpentine belt assembly, and the OBD-II port for connecting diagnostic tools to the vehicle’s computer.
Why is ECU important?
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) acts as the brain of the vehicle, managing fuel injection, ignition timing, and emission controls. It monitors engine performance and triggers a check engine light if it detects a fault, providing a specific diagnostic code that can be read through the vehicle’s standard diagnostic port.
What is the difference between OBD-II and ECU?
The ECU is the computer that manages engine functions, while OBD-II is the standardized diagnostic system used to access data from that computer. When the ECU detects a malfunction, it stores a diagnostic code that is retrieved through the OBD-II port using a scanner to identify the exact problem.
How do I use Dodge Dakota 3.9 V6 engine diagram?
Use the diagram as a reference guide while inspecting the engine bay or replacing parts. Cross-reference the visual layout with your physical engine to confirm component locations. It is particularly useful for verifying the firing order of spark plugs or ensuring every bolt meets its required torque spec during reassembly.