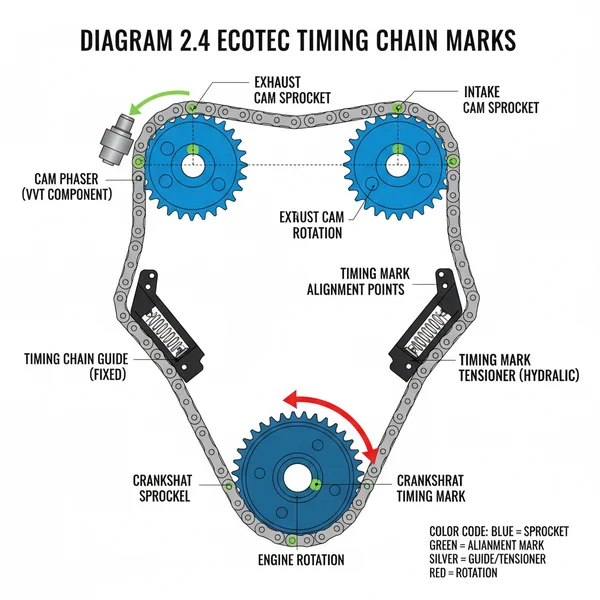
The diagram for 2.4 Ecotec timing chain marks illustrates the alignment between the crankshaft sprocket and the intake and exhaust camshaft phasers. It shows the specific colored links on the chain matching the timing marks on the sprockets to ensure the internal engine structure is perfectly synchronized for optimal performance.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Ensures precise synchronization between the crankshaft and camshafts
- Identification of three distinct colored links is the most important component
- Never rotate the engine counter-clockwise during the alignment process
- Always replace the chain guides and tensioner as a complete set
- Essential for engine rebuilds or when correcting timing-related fault codes
Performing a timing service on a General Motors 2.4L engine requires precision, as this is an interference engine design where a single tooth of misalignment can lead to catastrophic valve-to-piston contact. Finding an accurate diagram 2.4 ecotec timing chain marks is essential for any DIY mechanic or professional technician looking to restore engine synchronization. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the timing system structure, explaining how the colored links on the chain correlate with the physical marks on the sprockets. You will learn the exact layout of the components, the correct installation sequence, and the critical troubleshooting steps needed to ensure your engine runs smoothly without timing-related fault codes.
Comprehensive Overview of the 2.4 Ecotec Timing System Layout
The internal configuration of the 2.4 Ecotec timing system is designed to synchronize the crankshaft’s rotation with the intake and exhaust camshafts. This system utilizes a series of sprockets, guides, and a hydraulic tensioner to maintain tension across the chain. The diagram for this engine is unique because it relies on a color-coded chain system. Unlike older engines that might use simple dots or lines on the block, the Ecotec system uses three distinct colored links on the timing chain—typically two chrome or silver links and one copper or dark-colored link—to indicate precise alignment points.
[EXHAUST CAM SPROCKET] [INTAKE CAM SPROCKET]
(Mark at 10:00) (Mark at 2:00)
\ /
[Silver Link] [Silver Link]
\ /
\ /
\ [GUIDE RAIL] /
\ /
\ /
\ /
\ /
[CRANK SPROCKET]
(Mark at 5:00)
[Copper Link]
Figure 1: Conceptual layout of the 2.4 Ecotec timing chain marks and component alignment.
The crankshaft sprocket features a small circular “dot” or “dimple.” According to the standard system layout, when the engine is at the proper timing position, this mark should point toward the 5 o’clock position, aligning perfectly with a notch or tab on the oil pump housing. The intake camshaft sprocket (right side when facing the engine) has a mark that must align with a colored link at approximately the 2 o’clock position. Conversely, the exhaust camshaft sprocket (left side) has a mark that aligns with the second colored link at the 10 o’clock position. Understanding this triangular orientation is the foundation of a successful installation.
While the main timing chain controls the valves, there is a secondary “balance shaft chain” located behind it. This secondary chain drives the water pump and balance shafts. Always ensure the primary timing chain is removed first when performing a full overhaul of the system.
Step-by-Step Guide to Aligning Diagram 2.4 Ecotec Timing Chain Marks

Successfully interpreting the timing diagram requires a methodical approach to the assembly process. Before beginning, ensure you have a 24mm wrench to rotate the camshafts and a torque wrench for the final bolt specifications. Follow these steps to ensure the diagram 2.4 ecotec timing chain marks are perfectly aligned.
- ✓ Step 1: Set the Engine to Top Dead Center (TDC) – Rotate the crankshaft until the number one piston is at the top of its compression stroke. In this configuration, the keyway on the crankshaft should be facing the 12 o’clock position, while the actual timing mark on the sprocket faces 5 o’clock.
- ✓ Step 2: Inspect the Sprocket Marks – Locate the diamond or triangle etched into the intake and exhaust cam actuators (phasers). Ensure these marks are visible and clean. If you are using aftermarket phasers, verify that the marks match the original equipment manufacturer (OEM) locations.
- ✓ Step 3: Align the Crankshaft Link – Take the new timing chain and find the single dark-colored or copper link. Drape this link over the crankshaft sprocket so that the link straddles the timing mark at the 5 o’clock position.
- ✓ Step 4: Align the Intake Camshaft – Feed the chain upward toward the intake (rear) camshaft. Place one of the two chrome/silver links directly over the timing mark on the intake sprocket. You may need to use a 24mm wrench on the camshaft hex to slightly rotate the cam until the mark meets the link.
- ✓ Step 5: Align the Exhaust Camshaft – Pull the chain across to the exhaust (front) camshaft. Align the remaining chrome/silver link with the timing mark on the exhaust sprocket. Ensure there is no slack in the chain between the two camshaft sprockets.
- ✓ Step 6: Install Guides and Tensioner – Mount the fixed timing chain guide and the adjustable tensioner guide. Once the guides are bolted down (using blue thread locker is recommended), install the hydraulic tensioner.
- ✓ Step 7: Release the Tensioner – Pull the retaining pin from the new tensioner. You should hear a “click” or see the tensioner arm extend to take up the slack on the exhaust side of the chain.
- ✓ Step 8: Final Verification – Rotate the crankshaft by hand for two full revolutions. Note that the colored links will no longer align with the marks after rotation (this is normal), but the physical marks should return to their 5, 2, and 10 o’clock relative positions.
Never use an impact wrench on the camshaft actuator bolts or the crankshaft bolt while the timing chain is connected. The sudden torque can cause the chain to jump teeth or damage the internal vanes of the VVT phasers.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting Timing Failures

The 2.4 Ecotec engine is known for specific timing-related issues that often stem from improper maintenance or component wear. One of the most frequent problems is “chain stretch.” Over time, the pins and rollers of the chain wear down, effectively lengthening the chain. This causes the diagram 2.4 ecotec timing chain marks to drift out of sync, leading to Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) such as P0016 (Crankshaft-Camshaft Correlation) or P0017.
Another common failure point is the plastic timing chain guides. These components can become brittle and shatter, falling into the oil pan and causing the chain to slap against the timing cover. If you hear a “rattle” sound upon cold start, it is a primary warning sign that the tensioner or guides have failed. Using the diagram to inspect the system can reveal if the chain has jumped a tooth. If the marks do not align as described in the 10, 2, and 5 o’clock positions during teardown, the timing has already shifted, and a full component replacement is required. If you find metal shavings in the oil or the chain has snapped, professional mechanical intervention is necessary to check for bent valves.
When replacing the timing chain, always replace the Variable Valve Timing (VVT) solenoids located on top of the valve cover. These solenoids control oil flow to the phasers and are often clogged with debris when a timing chain begins to fail.
Maintenance Tips & Best Practices
To ensure the longevity of your 2.4 Ecotec timing system, consistent maintenance is the most effective strategy. Because the timing tensioner relies on hydraulic oil pressure, the quality and cleanliness of your engine oil are paramount. Using a high-quality full synthetic oil and following a strict 5,000-mile change interval can prevent the sludge buildup that often leads to tensioner failure and subsequent chain stretch.
When performing a timing chain replacement, it is highly recommended to install a complete kit rather than just the chain. A comprehensive kit should include:
- • New primary timing chain with colored links
- • New hydraulic tensioner (updated design)
- • Intake and exhaust guide rails
- • New crankshaft sprocket
- • New timing cover gasket and front crank seal
Additionally, since the water pump is driven by the balance shaft chain (located behind the main timing chain), many technicians recommend replacing the water pump and the balance shaft chain components at the same time. This “while you’re in there” approach saves significant labor costs in the future, as accessing these parts requires removing the same front-engine structure. Always choose OEM or high-grade aftermarket components, as lower-quality chains are prone to stretching within a few thousand miles, rendering your hard work useless and risking engine damage.
In conclusion, mastering the diagram 2.4 ecotec timing chain marks is a matter of understanding the relationship between the colored chain links and the sprocket indicators. By maintaining a clean environment, using the correct tools, and following the 5, 2, and 10 o’clock alignment configuration, you can successfully restore the timing structure and ensure your engine remains reliable for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a diagram 2.4 ecotec timing chain marks?
This diagram is a visual representation of the alignment points within the GM 2.4L Ecotec engine. It illustrates the exact positioning of the timing chain relative to the crankshaft and camshaft sprockets, ensuring that the engine’s valves open and close at the precise moment during the combustion cycle.
How do you read a diagram 2.4 ecotec timing chain marks?
To read this layout, locate the three colored links on the timing chain and match them to the corresponding marks on the sprockets. The intake and exhaust camshaft phasers have specific diamond or triangle symbols, while the crankshaft sprocket features a distinct dot for alignment with the chain.
What are the parts of the 2.4 ecotec timing system?
The primary components include the timing chain, intake and exhaust camshaft actuators (phasers), a crankshaft sprocket, and various guides and tensioners. This complex system configuration works together to manage engine synchronization, ensuring that the internal mechanical structure maintains high efficiency and prevents catastrophic valve-to-piston contact.
Why is the timing chain tensioner important?
The tensioner is a critical component that maintains constant pressure on the timing chain, preventing it from skipping or jumping off the marks. A failure in this system can cause the chain to become loose, leading to incorrect timing, severe engine damage, and poor performance characteristics.
What is the difference between primary and balance shaft chains?
In the 2.4 Ecotec structure, the primary timing chain controls the camshafts, while a separate balance shaft chain reduces engine vibration. Both systems feature their own set of marks and colored links, but they serve different functions within the overall engine layout to ensure smooth operation.
How do I use a diagram 2.4 ecotec timing chain marks?
Use this diagram as a reference during the assembly phase of an engine repair. By visually verifying the alignment of the colored links with the sprocket marks, you can confirm that the system is properly timed before rotating the engine manually to ensure no mechanical interference exists.