Coolster 125cc ATV Wiring Diagram: Repair & Setup Guide
A Coolster 125cc ATV wiring diagram provides a visual representation of the vehicle’s electrical paths, including the battery, ignition system, and lighting. It helps mechanics identify the hot wire for power distribution and the ground wire for circuit completion, ensuring that components like the common terminal on switches function correctly for reliable engine starting.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Essential for diagnosing no-start conditions or lighting failures
- Identifying the CDI unit and its pinout is crucial for ignition
- Always ensure a clean, secure connection to the green ground wire
- Use a multimeter to verify voltage at the common terminal of switches
- Ideal for DIY repairs, part replacements, or adding accessories
Starting a repair or custom project on your off-road vehicle often begins with a sense of frustration, especially when the engine refuses to turn over or the lights flicker intermittently. Understanding the electrical system through a comprehensive coolster 125cc atv wiring diagram is the most effective way to demystify the complex web of colored cables running beneath the plastics. For many DIY enthusiasts, the electrical system is the “black box” of the machine, yet it follows a very logical path from the power source to the ignition. Having a reliable diagram ensures you aren’t guessing which wire controls the spark and which manages the charging system. In this guide, we will break down the entire electrical architecture, explore the role of each component, and provide you with the technical knowledge needed to troubleshoot or rewire your ATV with confidence.
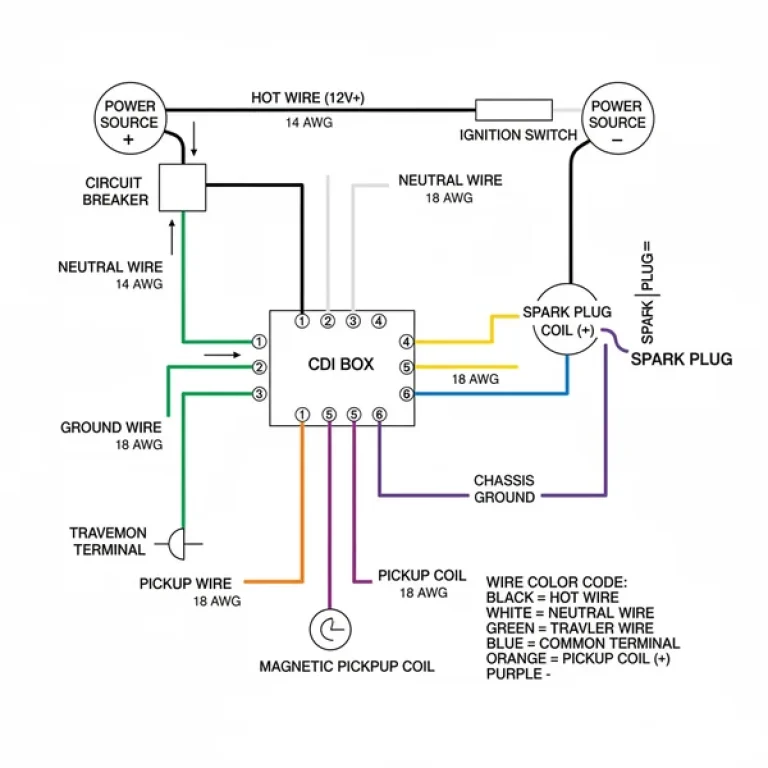
The electrical system of a Coolster 125cc ATV is centered around a few critical hubs: the stator, the CDI (Capacitor Discharge Ignition) box, the regulator/rectifier, and the starter solenoid. When looking at a coolster 125cc atv wiring diagram, you will notice that the system is primarily a 12-volt DC setup, though the stator produces AC voltage that must be converted. The diagram typically uses a color-coded legend to help users identify the path of current. For instance, a solid green wire almost universally represents the ground wire, which is essential for completing any circuit. The hot wire, often colored red, carries the 12V positive charge directly from the battery to the ignition switch.
Most Coolster 125cc models utilize a 5-pin CDI box. The pins are designated for the kill switch, ignition coil, ground, AC ignition power (from the stator), and the trigger pulse (pickup coil). Knowing this pinout is 80% of the battle when solving “no spark” issues.
The visual layout of the diagram also highlights the charging circuit. You will see two wires (usually yellow and white) coming from the stator and heading into the regulator/rectifier. This component is responsible for keeping the battery topped up and ensuring the voltage does not spike and blow out the bulbs. In some custom configurations or older switch replacements, you might encounter a common terminal on the back of the ignition switch, where the main power is distributed to the various subsystems. While automotive wiring differs slightly from household wiring, the principles of a neutral wire or return path remain constant to ensure a closed loop.
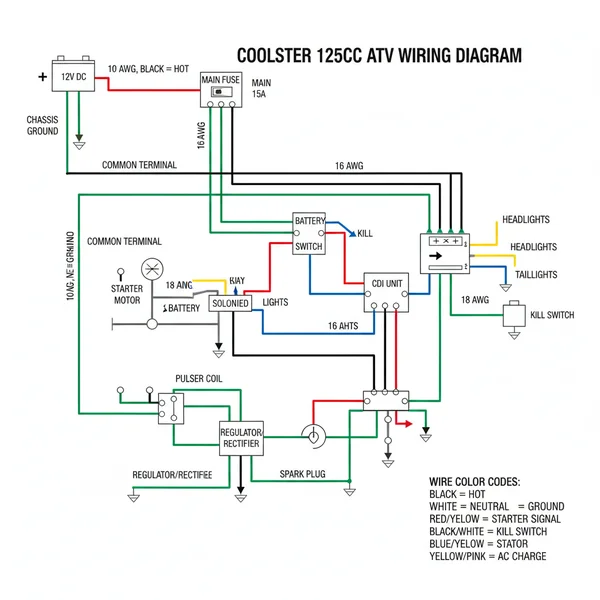
Navigating a coolster 125cc atv wiring diagram requires a systematic approach. If you are replacing a harness or simply trying to find a break in the line, follow these steps to interpret and apply the diagram effectively:
- ✓ Identify the Battery and Main Fuse: Start at the source. Locate the red hot wire leaving the battery. Ensure it passes through the main fuse (usually 10A or 15A) before it reaches the ignition switch.
- ✓ Trace the Ignition Switch: The switch acts as the gatekeeper. When turned to the “On” position, it connects the hot wire to the rest of the harness. Some switches use a brass screw terminal for the ground connection to the frame, ensuring the kill circuit is functional.
- ✓ Map the CDI and Coil: Locate the CDI box in your diagram. Ensure the black/yellow wire is running directly to the ignition coil. This is the wire that delivers the high-voltage pulse necessary for the spark plug to fire.
- ✓ Locate the Safety Switches: Many Coolster models have a neutral wire connected to a safety switch on the transmission or the brake lever. The ATV will not start unless this circuit is closed, preventing the vehicle from jumping forward unexpectedly.
- ✓ Check the Lighting Circuit: Follow the wires from the handlebar switch to the headlights. In complex setups involving high and low beams, a traveler wire may be used to toggle the current between the different filaments of the bulb.
- ✓ Verify Ground Points: A common failure point is a loose ground wire. Ensure every green wire in the diagram is securely fastened to a clean, unpainted part of the metal frame.
To perform these steps, you will need a few basic tools: a digital multimeter (to measure voltage and continuity), wire strippers, electrical tape, and high-quality 16 or 18-gauge automotive wire for any necessary repairs.
Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before cutting or splicing wires. A short circuit can not only blow fuses but can also permanently damage the sensitive electronics inside the CDI box or the stator windings.
Even with a perfect coolster 125cc atv wiring diagram, common issues can arise. One of the most frequent complaints is a “crank but no start” condition. Using the diagram, you can narrow this down to the ignition circuit. Check for voltage at the black/white wire on the CDI; if this wire is grounded when the key is on, the machine will never spark. This is often caused by a faulty kill switch or a pinched wire in the handlebar assembly.
Another common issue is a dead battery that won’t charge. By referencing the charging section of the diagram, you can test the AC output from the stator. If the stator is producing power but the battery remains flat, the regulator/rectifier is likely the culprit. Look for signs of melted plastic or burnt smells around the connectors, as these components generate significant heat during operation. If you see consistent fuse failure, you likely have a hot wire rubbing against the frame, creating a short circuit. The diagram helps you trace the path of that specific color-coded wire to find the abrasion.
When testing for “no spark,” use your multimeter to check the resistance of the ignition coil. A healthy coil should show a specific ohm reading (usually between 0.4 and 5.0 ohms on the primary side). If the reading is infinite, the internal windings are broken.
To keep your Coolster 125cc ATV running smoothly, maintenance of the electrical system is just as important as changing the oil. One best practice is to apply dielectric grease to all multi-pin connectors. This prevents moisture from entering the plugs and causing corrosion, which is the leading cause of “phantom” electrical issues in off-road vehicles. When replacing wires, always match the original gauge. Using a wire that is too thin can lead to overheating and potential fires, while a wire that is too thick may be difficult to route through the tight spaces of the frame.
For those looking to save costs, purchasing a universal wiring harness can be tempting. However, ensure that the pinout matches your coolster 125cc atv wiring diagram exactly. Chinese ATVs often have slight variations in the CDI plug (rounded vs. square corners). Quality components, such as NGK spark plug caps and high-output coils, are relatively inexpensive upgrades that can significantly improve the reliability of the system. Finally, always secure your wiring harness with UV-resistant zip ties. A loose harness can vibrate against the engine or exhaust, melting the insulation and leading to a catastrophic failure in the middle of a trail ride.
In conclusion, while the electrical system of a small-engine vehicle might seem intimidating, the coolster 125cc atv wiring diagram provides the clarity needed to tackle any repair. By understanding the relationship between the hot wire, the ground wire, and the various control modules, you transform from a frustrated owner into a capable mechanic. Whether you are chasing a voltage drop or installing a new ignition switch, keep your diagram handy, work methodically, and always prioritize safety and clean connections. With a bit of patience and the right roadmap, your ATV’s electrical system will remain reliable for years to come.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the Coolster 125Cc Atv Wiring Diagram: Repair & Setup Guide
Identify the main power source by locating the battery and the primary hot wire connected to the starter solenoid.
Locate the ignition switch and trace the wires back to the CDI box and stator to ensure signal flow.
Understand how the common terminal on the handlebar switch directs current between the kill switch and the starter button.
Connect the multimeter to the ground wire and various points to check for continuity and proper voltage across the harness.
Verify that the neutral wire signal is reaching the safety relay, allowing the ignition system to engage the starter motor.
Complete the repair by securing all loose traveler wire connections and insulating any exposed copper to prevent future short circuits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Coolster 125cc ATV wiring diagram?
A Coolster 125cc ATV wiring diagram is a visual map showing how electrical power flows through the vehicle. It outlines the path from the battery to components like the starter motor and CDI. This schematic is vital for identifying where a traveler wire or power lead connects to specific switches or terminals.
How do you read a Coolster 125cc ATV wiring diagram?
To read the diagram, start at the power source, usually the battery. Follow the lines representing wires to each component, noting color codes. Look for labels like the neutral wire or ground wire to understand circuit completion. Symbols denote parts like the ignition switch, relay, stator, and various lighting systems.
What are the parts of a Coolster 125cc ATV wiring system?
The primary parts include the battery, ignition coil, stator, voltage regulator, and CDI box. It also features a wiring harness containing the hot wire for current delivery, the ground wire for stability, and various connectors that link the handlebar controls and safety switches to the main electrical power grid.
Why is the ground wire important?
The ground wire is critical because it provides a return path for electrical current to the battery. Without a solid ground connection, the circuit remains open, preventing components from functioning. Ensuring the green ground wire is securely fastened to the frame prevents intermittent power loss and potential electrical surges.
What is the difference between a hot wire and a neutral wire in an ATV?
In an ATV’s DC electrical system, the hot wire carries the positive charge from the battery to the ignition system. The neutral wire typically refers to the safety circuit lead that indicates the transmission state, ensuring the engine only cranks when it is in the neutral position for safety.
How do I use a Coolster 125cc ATV wiring diagram?
Use the diagram to trace electrical paths during repairs. Start by locating the common terminal on the ignition switch to see where power is distributed. By following the lines to the ground wire and CDI, you can use a probe to find breaks in the circuit or faulty components.