Chevy 4.3 V6 Engine Diagram: Identification and Repair
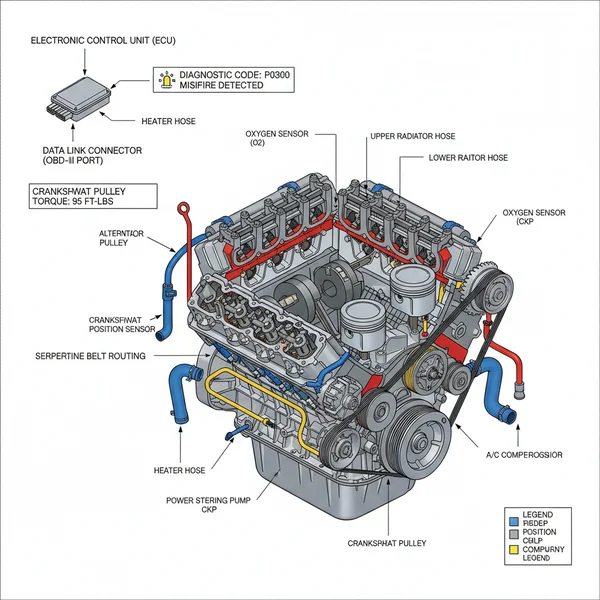
A Chevy 4.3 V6 engine diagram illustrates the layout of internal and external components, including the intake manifold, cylinder heads, and accessory drive. It is essential for locating sensors that trigger a check engine light and for ensuring every bolt meets the proper torque spec during assembly and maintenance tasks.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Visualizes component locations for maintenance and repair
- Identifying the distributor and fuel injectors is critical for timing
- Always follow specific torque spec values for head bolts
- Use the diagram alongside an OBD-II scanner for faster repairs
- Use this when performing rebuilds or electrical troubleshooting
Understanding the internal and external architecture of your powerplant is the first step toward successful maintenance, and a comprehensive chevy 4.3 v6 engine diagram serves as your essential roadmap. Whether you are performing a simple tune-up or a complex overhaul, having a clear visual reference ensures that every sensor, bolt, and belt is exactly where it needs to be. This guide provides a detailed breakdown of the 4.3L Vortec layout, explaining component locations, vital systems, and diagnostic pathways. By the end of this article, you will be equipped to navigate your engine bay with professional-level confidence and technical accuracy.
Understanding the Chevy 4.3 V6 Engine Diagram Layout
The 4.3L V6, often referred to as the “90-degree V6,” is fundamentally a 5.7L 350 small-block V8 with two cylinders removed. Because of this heritage, the diagram layout is remarkably logical but features specific nuances unique to the V6 configuration. When viewing a standard chevy 4.3 v6 engine diagram, the first thing you will notice is the accessory drive system located at the front. This area includes the accessory belt, also known as the serpentine belt, which powers the alternator, power steering pump, and water pump.
A detailed diagram will also highlight the fuel delivery system, specifically the Central Sequential Fuel Injection (CSFI) or the later Multi-Port Fuel Injection (MPFI) setups. Centered between the cylinder banks is the intake manifold, which houses the fuel spider assembly. The diagram typically color-codes the coolant flow paths, showing how fluid moves from the radiator through the lower intake manifold and cylinder heads to maintain stable operating temperatures.
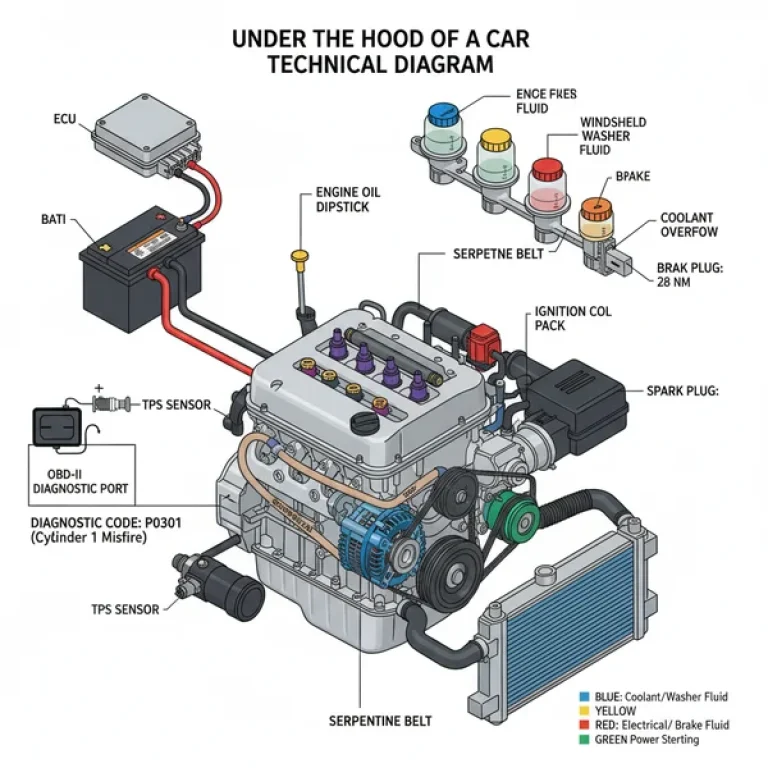
Furthermore, the diagram identifies critical electronic components. You will find the ECU (Engine Control Unit) mapping, which illustrates how wiring harnesses connect various sensors—like the Mass Air Flow (MAF) and Oxygen sensors—back to the central computer. For those working on the internal assembly, the diagram will detail the timing chain location behind the front cover, illustrating the alignment marks necessary for maintaining perfect synchronization between the crankshaft and camshaft. This visual breakdown is vital for distinguishing between different production eras, such as the pre-1996 “LB4” versions and the post-1996 “L35” or “LF6” Vortec iterations.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER – High-resolution technical illustration of a Chevy 4.3L V6 showing the front accessory drive, intake manifold, and sensor locations]
How to Interpret and Use the Engine Diagram

Reading a technical diagram might seem daunting, but it becomes straightforward once you break it down into functional systems. Follow these steps to use your chevy 4.3 v6 engine diagram effectively for your next repair or inspection.
Before starting any work, ensure the engine is cool to the touch. Always disconnect the negative battery terminal when working near electrical components or the fuel system to prevent accidental shorts or fires.
- Identify the Orientation: Most diagrams view the engine from the front (radiator side). Locate the “front of engine” arrow to ensure you are not confusing the driver-side (Bank 1) with the passenger-side (Bank 2).
- Locate the Accessory Belt Routing: Use the diagram to trace the path of the serpentine belt. Note the position of the tensioner pulley; this is the component you must rotate to release tension for belt removal or installation.
- Map the Ignition System: On older models, find the distributor at the rear of the intake manifold. On newer models, identify the coil packs. The diagram will show the firing order (1-6-5-4-3-2), which is crucial for preventing misfires.
- Trace the Vacuum Lines: Vacuum leaks are common on the 4.3L. Use the diagram to follow lines from the PCV valve and brake booster back to the throttle body. A misplaced vacuum line can lead to a rough idle and poor performance.
- Find the OBD-II Diagnostic Ports: While the OBD-II port is inside the cabin, the diagram will show the sensors (like the Crankshaft Position Sensor) that feed data to it. This helps you locate the physical source of a diagnostic code.
- Verify Fluid Circuits: Trace the coolant flow from the water pump through the block. This is essential if you are troubleshooting overheating or replacing the thermostat.
- Reference Torque Specs: A high-quality diagram will often include a torque spec table for critical fasteners, such as cylinder head bolts or intake manifold bolts. Never guess these values; use a calibrated torque wrench.
The intake manifold bolts on the 4.3L V6 are notorious for losing tension or being over-tightened. Always follow the specific tightening sequence provided in the diagram to avoid cracking the manifold or causing a coolant leak.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with the Diagram

The Chevy 4.3L V6 is a workhorse, but it has specific “weak points” that the diagram can help you diagnose. One of the most frequent complaints is a persistent check engine light. By using the diagram to locate the OBD-II related sensors, you can quickly move from a generic diagnostic code to a physical component. For example, a P0300 (random misfire) code often points toward the distributor cap or the fuel spider assembly located under the upper intake plenum.
Another common issue involves the timing chain. While these chains are robust, they can stretch over high mileage. A diagram helps you locate the timing cover and understand the relationship between the crank sensor and the cam timing. If you notice a “slapping” sound at the front of the engine, the diagram will guide you to the area requiring inspection.
Coolant leaks are also a hallmark of this engine family, specifically around the lower intake manifold gaskets. By studying the coolant flow section of your chevy 4.3 v6 engine diagram, you can identify the exact “valley” where coolant tends to pool. This allows you to differentiate between a simple hose leak and a more serious gasket failure.
- ✓ Misfires: Use the diagram to check spark plug wire routing to ensure no cross-firing is occurring.
- ✓ Rough Idle: Locate the Idle Air Control (IAC) valve on the throttle body using the diagram for cleaning or replacement.
- ✓ Fuel Pressure Loss: Identify the fuel pressure test port (Schrader valve) on the fuel rail.
Pro Tips and Best Practices for Maintenance
To keep your 4.3L V6 running for hundreds of thousands of miles, follow these professional maintenance tips derived from years of collective mechanic experience.
When replacing the intake manifold gaskets, upgrade to the “problem-solver” metal-core gaskets rather than the standard plastic ones. This prevents future leaks caused by plastic degradation.
First, always prioritize the health of your accessory belt. A frayed belt can snap and take out the cooling fan or radiator hoses. Inspect the belt for cracks every 10,000 miles. Second, pay close attention to the ECU connections. Corrosion in the wiring harness can trigger phantom diagnostic code readings that lead to unnecessary parts replacement. Periodically cleaning the electrical connectors with specialized contact cleaner can save you hundreds of dollars in “ghost” repairs.
When it comes to the timing chain, consistency with oil changes is your best defense. Sludge buildup can accelerate wear on the chain tensioner and guides. Use a high-quality synthetic oil and a premium filter to keep the internal components lubricated and clean. Finally, always keep a printed copy of the chevy 4.3 v6 engine diagram in your glovebox or workshop. In an emergency situation, being able to quickly identify a blown fuse or a disconnected sensor can be the difference between being stranded and getting back on the road.
Regarding the cooling system, ensure the coolant flow is never obstructed. The 4.3L is sensitive to air pockets in the system. When refilling the coolant, use the bleeder screw (if equipped) or a “no-spill” funnel to ensure all air is purged, preventing localized hotspots in the cylinder heads. Following these best practices, backed by a solid understanding of the engine’s diagram, ensures your Chevy remains a reliable performer for years to come.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the Chevy 4.3 V6 Engine Diagram: Identification And Repair
Identify the primary engine orientation to distinguish between the driver and passenger side components.
Locate the specific sensors linked to the OBD-II system to address any active fault codes.
Understand how the wiring harness connects the fuel injectors directly to the central ECU module.
Apply the correct torque spec to all structural bolts as indicated by the technical diagram’s legend.
Verify that the vacuum lines and cooling hoses follow the exact routing paths shown in the illustration.
Complete the inspection by scanning for a diagnostic code to ensure all components are communicating correctly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Chevy 4.3 V6 engine diagram?
A Chevy 4.3 V6 engine diagram is a detailed visual representation of the engine’s architecture, showcasing the arrangement of pistons, valves, and electronic sensors. It serves as a roadmap for mechanics, helping them identify specific parts like the ECU or spark plug wires to facilitate efficient repairs and part replacements.
How do you read a Chevy 4.3 V6 engine diagram?
To read the diagram, start by identifying the front of the engine, typically where the fan and belts are located. Use the provided legend to match numbered components with their names. Look for flow lines to understand fluid paths and check for electrical connectors linked to the main ECU system.
What are the parts of a Chevy 4.3 V6?
Primary parts include the engine block, cylinder heads, intake manifold, and the Vortec fuel injection system. Essential electronic components integrated into the diagram are the crankshaft position sensor, the throttle body, and various sensors that relay data back to the OBD-II system for performance monitoring and emissions control.
Why is the ECU important?
The ECU, or Engine Control Unit, is the brain of the Chevy 4.3 V6. It monitors sensor inputs to adjust fuel delivery and ignition timing. Understanding its location on the diagram is vital for troubleshooting electrical faults or when a specific diagnostic code indicates a communication failure within the powertrain.
What is the difference between TBI and Vortec 4.3 V6?
The TBI version uses a simpler fuel delivery system located atop the intake, whereas the later Vortec models feature central port injection. Their diagrams differ significantly in fuel rail layout and sensor placement, which affects how you interpret a check engine light and perform diagnostics on the fuel system.
How do I use a Chevy 4.3 V6 engine diagram?
Use the diagram to guide your disassembly and reassembly processes. It helps you verify the correct placement of gaskets, the routing of the serpentine belt, and the specific sequence for tightening bolts. This ensures you maintain the required torque spec, preventing leaks and long-term mechanical engine failure during operation.