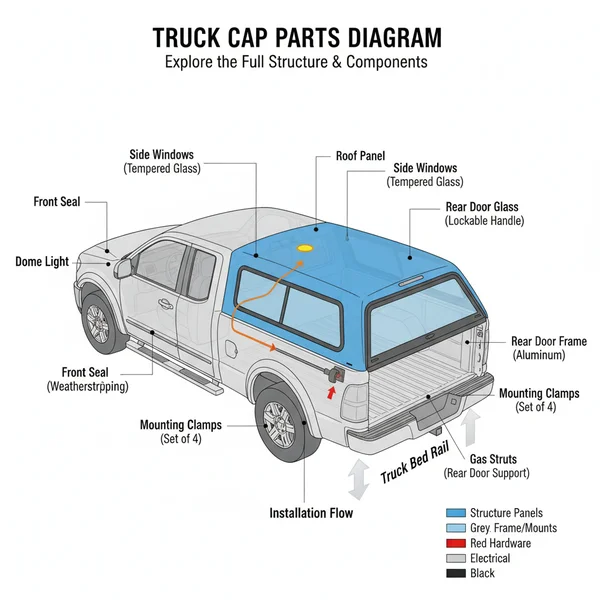
A truck cap parts diagram illustrates the internal and external structure of a camper shell, detailing every critical component like the rear door, struts, and seals. This visual layout helps owners identify the specific configuration of their system, making it easier to order replacement parts or perform routine maintenance and repairs.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides a visual roadmap of the camper shell assembly for maintenance.
- The rear glass door and gas struts are the most important components to identify for safety.
- Always check the mounting clamps to prevent the cap from shifting during transit.
- Use the diagram to identify weather stripping locations to prevent bed leaks.
- Use this diagram when replacing broken glass, repairing locks, or installing new hardware.
Navigating the complexities of vehicle accessories requires a clear roadmap, especially when you are performing maintenance or repairs on your vehicle’s topper. Understanding exactly what the standard components are in a truck cap parts diagram is vital for any truck owner looking to ensure their cargo stays protected and their shell remains secure. Having access to a correct diagram helps you identify specific hardware, seal types, and glass configurations that might otherwise seem indistinguishable. In the following sections, you will learn how to interpret these technical layouts, identify every major component from the struts to the seals, and execute repairs with professional precision.
A truck cap diagram serves as a structural blueprint, categorizing parts into four main systems: the exterior shell, the window/glass assembly, the rear door hardware, and the mounting/sealing infrastructure. Misidentifying a single fastener or seal type can lead to water leaks or structural instability.
Understanding the Truck Cap Parts Diagram Layout
A comprehensive diagram for a truck cap or camper shell is designed to provide a transparent look at the hidden architecture of the unit. The primary component is the shell or “canopy” itself, which is typically constructed from reinforced fiberglass, heavy-duty aluminum, or high-density polymers. In a standard diagram, this is the central anchor point from which all other parts radiate. Surrounding the shell, you will find detailed callouts for the window systems. These include the front window—which sits closest to the truck cab—and the side windows, which may be fixed, sliding, or “windoors” that flip upward for side access.
The rear of the diagram focuses heavily on the rear door assembly, the most mechanical portion of the system. This section illustrates the interaction between the glass pane, the aluminum frame (if applicable), the gas struts, and the locking mechanism. Color-coding in these diagrams often highlights moving parts versus static parts. For example, seals and gaskets might be labeled in blue to denote weatherproofing zones, while mechanical hardware like T-handles or hinges might be highlighted in red or bold black to indicate points of frequent maintenance. Variations in diagrams often depend on whether the cap is a “cab-hi” model, which sits flush with the truck roof, or a “high-rise” model designed for maximum interior volume. Each configuration requires specific strut lengths and glass shapes, which are clearly demarcated in a high-quality schematic.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER – A detailed technical illustration showing a 3D exploded view of a truck cap with labeled callouts for: 1. Fiberglass Shell, 2. Gas Struts, 3. Rear Door Glass, 4. T-Handle Lock, 5. Side Sliders, 6. Bulb Seal, 7. Mounting Clamps, 8. Third Brake Light.]
Step-by-Step Guide to Interpreting and Using the Diagram

Reading a technical layout can be intimidating, but following a logical sequence ensures you find the exact information you need for your repair or installation. Use these steps to navigate your truck cap parts diagram effectively.
- 1. Orient the Perspective: Most diagrams use an “exploded view” perspective. This means parts are shown slightly detached from where they actually sit. Start by identifying the rear door—this is your primary landmark. Once you locate the door, you can easily distinguish the left (driver) and right (passenger) sides of the shell.
- 2. Identify the Material System: Look at the callouts for the shell. If the diagram mentions “gelcoat” or “chopped strand,” you are working with fiberglass. If it mentions “skin” and “internal frame,” it is an aluminum unit. Knowing the material is essential for choosing the right adhesives or repair resins.
- 3. Locate the Hardware Specifications: Pay close attention to the “Gas Struts” or “Prop Arms.” The diagram will often list a “poundage” or “force rating” (e.g., 40 lbs). This is critical; using a strut with too much force can shatter the rear glass, while one with too little will fail to hold the door open.
- 4. Analyze the Sealing Strategy: The diagram should show a “Base Rail Seal” or “Bulb Seal.” Note how the seal is oriented. Some seals are designed to sit on the truck bed rails, while others are integrated into the cap’s bottom lip. Proper orientation as shown in the diagram is the difference between a dry bed and a flooded one.
- 5. Trace the Electrical Path: Most modern caps include a Center High Mount Stop Light (CHMSL). Find the wiring harness in the diagram. It will show the path from the light, through the interior pillar, and down to the truck’s electrical system. This helps you find hidden disconnects if your brake light stops working.
- 6. Match the Fasteners: Diagrams include a legend for screws, bolts, and clamps. Do not substitute hardware unless specified. For instance, using a standard bolt where a specialized J-clamp is required can damage your truck’s bed rails.
When replacing rear door glass as shown in the diagram, always have a second person assist you. The weight of the glass combined with the tension of the gas struts makes this a dangerous solo task. Ensure the struts are disconnected before attempting to unscrew the hinges.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with the Diagram

Even the highest quality truck caps encounter wear and tear. Using the diagram to troubleshoot can save you hundreds of dollars in professional labor. One of the most frequent issues is water intrusion. By consulting the diagram’s seal layout, you can identify if the leak is coming from the window “molding” (the frame around the glass) or the “base seal” (where the cap meets the truck). If the diagram shows a double-bulb seal but you only see a flat foam tape on your truck, you have identified the source of the failure.
Another common problem involves the rear door latching system. The diagram will illustrate the “Strike Plates” and the “Rotary Latches.” Over time, the truck bed may flex, causing these to move out of alignment. By looking at the configuration in the diagram, you can determine which way to adjust the mounting bolts to restore a secure latch. If the door is difficult to close, the diagram can help you locate the specific “T-handle” set screws that may have vibrated loose, preventing the locking rods from engaging properly.
If you are struggling to find a replacement part, look for the “Serial Number” usually located on the inside roof or near the rear door of the shell. Manufacturers use this number to provide the exact diagram for your specific build configuration.
Tips and Best Practices for Component Longevity
Maintenance is the key to ensuring your truck cap components last as long as the vehicle itself. Beyond simply following the truck cap parts diagram for repairs, you should implement a routine care schedule based on the layout’s most vulnerable points.
- ✓ Lubricate Moving Parts: Every six months, apply a dry graphite lubricant to the lock cylinders and a silicone-based lubricant to the window tracks and hinge points identified in your diagram.
- ✓ Check Clamp Torque: Vibration from the road can loosen the mounting clamps. Refer to your diagram to locate all 4 to 6 attachment points and ensure they are tightened to the manufacturer’s torque specifications.
- ✓ Protect the Seals: UV rays are the enemy of rubber seals. Apply a UV protectant spray to the exterior seals twice a year to prevent cracking and shrinking.
- ✓ Strut Maintenance: Never wipe the shafts of your gas struts with degreaser. They require a thin film of oil to keep the internal seals lubricated. Simply wipe them with a clean, soft cloth to remove dust.
- ✓ Glass Alignment: If you notice your side sliders are sticking, check the diagram to see if the window is “mitered” or “radius.” This tells you if the frame can be adjusted or if the entire unit needs to be reseated.
By treating your truck cap as a system of integrated parts rather than a single solid object, you extend its utility and resale value. Whether you are replacing a broken T-handle or completely resealing the unit for the winter, having a detailed truck cap parts diagram ensures that your DIY efforts are grounded in technical accuracy. Always prioritize high-quality replacement components that match the specifications found in your diagram to maintain the structural integrity and weatherproofing of your truck’s topper.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a truck cap parts diagram?
A truck cap parts diagram is a visual schematic showing the full configuration of a camper shell. It identifies every essential component, including the fiberglass or aluminum body, windows, door handles, and mounting system, allowing users to understand how the entire structure fits together for maintenance or repair.
How do you read a truck cap parts diagram?
To read the diagram, start by identifying the main shell body and follow the numbered callouts to individual parts. Observe the layout to see how components like seals and windows interface with the main structure. It provides a clear roadmap for disassembling or upgrading your truck’s cargo system.
What are the parts of a truck cap?
Key parts include the main shell, front and side windows, rear door glass, and gas struts. Critical hardware includes the T-handle locks, mounting clamps, and bulb seals. This integrated system works together to protect your truck bed from the elements while providing secure, weatherproof storage for gear.
Why is the gas strut component important?
Gas struts are vital components because they provide the necessary lift and support for the rear glass door. Without functioning struts, the door’s heavy structure becomes difficult to open and dangerous to hold, potentially causing injury or damage. The diagram helps you locate the correct mounting points.
What is the difference between cab-high and high-rise configurations?
Cab-high configurations sit level with the truck’s roof for better aerodynamics, while high-rise versions offer increased interior volume for larger cargo. The diagram for each layout will differ primarily in the height of the side windows and the overall slope of the shell’s roof structure and rear door.
How do I use a truck cap parts diagram?
Use the diagram to identify broken or worn-out components by matching the visual representation to the parts on your actual truck cap. It serves as a reference for ordering the correct replacement hardware and ensures that the assembly configuration remains structurally sound after any DIY repairs or upgrades.