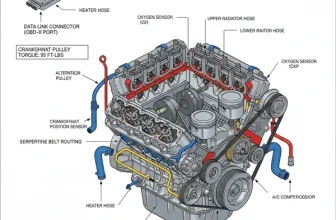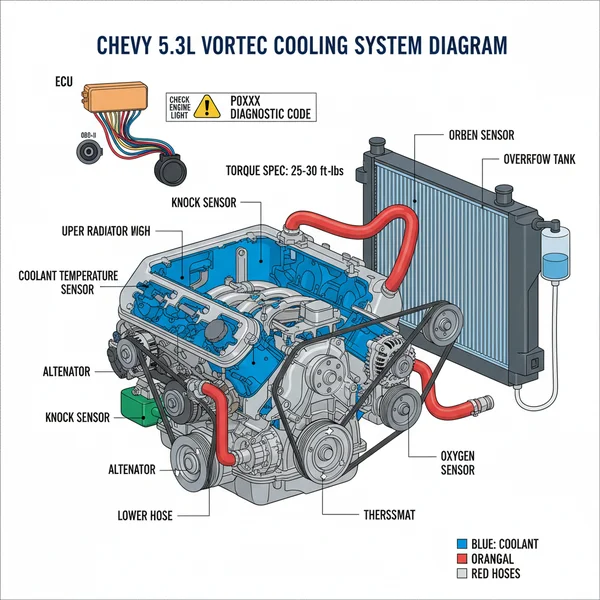
The Chevy 5.3 Vortec cooling system diagram illustrates the flow of coolant from the radiator through the water pump, engine block, and heater core. It identifies critical parts like the thermostat, hoses, and sensors that prevent overheating and maintain optimal engine temperatures for peak performance and long-term engine longevity.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Explains the pressurized flow of coolant through the 5.3L V8 engine.
- The water pump is the central hub for circulating coolant throughout.
- Always check for leaks at the quick-connect heater hose fittings.
- Use the diagram to locate sensors when a diagnostic code appears.
- Essential for cooling system flushes, thermostat replacement, or hose routing.
Understanding the engine 5.3 liter Chevy 5.3 Vortec cooling system diagram is essential for any truck or SUV owner looking to maintain vehicle longevity and peak performance. Whether you are dealing with a small leak or performing a complete water pump replacement, having a clear visual and conceptual map of how coolant moves through your Small Block Chevy V8 is the first step toward a successful repair. This guide provides a detailed breakdown of the coolant flow, identifies every critical component from the radiator to the heater core, and explains how the system interacts with the engine’s electronic controls. By the end of this article, you will have the technical confidence to diagnose cooling issues, interpret diagnostic codes, and perform maintenance using professional-grade specifications.
The Anatomy of the 5.3 Vortec Cooling System
The cooling system in a 5.3L Vortec engine is a pressurized, closed-loop system designed to maintain an optimal operating temperature, typically between 195°F and 210°F. Unlike older engine designs, the 5.3L (part of the LS engine family) utilizes a specific coolant flow pattern that prioritizes even heat distribution across the cylinder heads to prevent warping.
The engine 5.3 liter Chevy 5.3 Vortec cooling system diagram typically illustrates a “reverse flow” influenced design where the water pump acts as the central hub. Driven by the accessory belt, the water pump pulls cooled fluid from the bottom of the radiator and pushes it through the engine block and cylinder heads. A unique feature of this system is the inclusion of “steam holes” or crossover vents at the top of the heads, which allow trapped air and steam to escape back to the surge tank, preventing localized hot spots.
The diagram identifies several key zones:
- ✓ The Cold Side: Includes the lower radiator hose and the thermostat housing, where coolant enters the pump.
- ✓ The Hot Side: Includes the upper radiator hose where hot coolant exits the engine to be cooled by the radiator.
- ✓ The Bypass Loop: The heater core circuit that provides cabin heat and allows coolant circulation even when the thermostat is closed.
- ✓ The Pressurized Surge Tank: Unlike older “overflow” bottles, this tank is under full system pressure and is where you check and add coolant.
Most 5.3L Vortec engines utilize a thermostat located on the inlet side of the water pump. This means the thermostat regulates the temperature of the coolant entering the engine, rather than the coolant leaving it, which allows for more precise temperature management and reduced thermal shock.
Step-by-Step Guide to Interpreting and Servicing the System

Reading an engine 5.3 liter Chevy 5.3 Vortec cooling system diagram requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to navigate the system for inspection or repair.
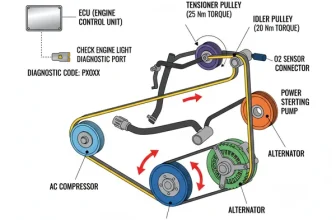
Step 1: Locate the Water Pump and Accessory Belt
The water pump is the large aluminum component bolted to the front of the engine block. Before you can service any part of the cooling system, you must inspect the accessory belt. If the belt is slipping or snapped, the water pump won’t turn, leading to immediate overheating. Ensure the belt tensioner is applying adequate pressure.
Step 2: Identify the Thermostat Housing
On the 5.3L Vortec, the thermostat is housed inside a housing attached to the water pump where the lower radiator hose connects. When reading the diagram, note that the thermostat remains closed until the coolant reaches roughly 187°F to 195°F. If your vehicle takes too long to warm up, the thermostat may be stuck open.
Step 3: Trace the Coolant Flow Path
Start at the bottom of the radiator. Follow the lower hose to the water pump. From there, visualize the coolant split: most goes into the engine block, while a smaller portion is diverted to the heater core via the two smaller hoses on the passenger side of the pump. The coolant then travels up through the cylinder heads and exits through the large upper radiator hose back to the radiator.
Step 4: Inspect the Steam Vent Tubes
Look at the top of the cylinder heads. You will see a small metal tube (the steam crossover) connecting the two heads. This line runs to the top of the radiator or the surge tank. This is a critical point on the diagram; if this line is plugged, air pockets will form in the heads, causing the ECU to detect high temperatures even if the radiator is cold.
Step 5: Check the Surge Tank and Cap
The surge tank is the highest point in the system. The cap is designed to release pressure if it exceeds 15 PSI. When interpreting the diagram, remember that the surge tank is “active,” meaning coolant constantly circulates through it to self-bleed air from the system.
Step 6: Apply Correct Torque Specs
If you are replacing the water pump or thermostat, you must use a torque wrench. The water pump bolts for a 5.3L Vortec generally require two passes: a first pass at 11 lb-ft and a final pass at 22 lb-ft. Over-tightening can crack the aluminum housing or strip the threads in the engine block.
Never open the surge tank cap while the engine is hot. The system is under high pressure, and the coolant can reach temperatures well over 200°F, which will cause severe burns if sprayed.
Common Issues and Diagnostic Troubleshooting

The 5.3L Vortec is a robust engine, but its cooling system has specific failure points that often trigger a check engine light or specific diagnostic code.
One of the most frequent issues is the “P0128” diagnostic code, which indicates the engine is not reaching its target operating temperature quickly enough. This is almost always caused by a thermostat that has failed in the open position. Using an OBD-II scanner is the most efficient way to monitor real-time coolant temperatures and confirm if the sensor data matches the physical symptoms.
Another common problem involves the plastic heater hose connectors. Over time, these become brittle and can snap unexpectedly, leading to rapid coolant loss. If you see a puddle of orange or red Dex-Cool fluid on the passenger side of the engine bay, check these connectors first. Additionally, the ECU monitors the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor to adjust fuel trim and spark timing. If the ECT sensor fails or the wiring is damaged, you may experience poor fuel economy and a rough idle.
If your check engine light is on for an overheating condition, use your OBD-II tool to check the “Freeze Frame” data. This shows exactly what the engine was doing when the fault occurred, helping you determine if the issue is a failing fan clutch or a blocked radiator.
Maintenance Tips and Best Practices
To keep your 5.3L Vortec running cool for hundreds of thousands of miles, follow these professional maintenance recommendations:
- ✓ Use the Correct Coolant: These engines are designed for Dex-Cool (orange) coolant. Do not mix it with traditional green silicated coolant, as this can lead to “sludging” that clogs the narrow passages in the radiator and heater core.
- ✓ Burp the System: After any cooling system repair, you must remove air pockets. Start the engine with the surge tank cap off, turn the cabin heat to maximum, and let the engine reach operating temperature. Watch for air bubbles in the tank and top off the fluid as needed.
- ✓ Inspect the Accessory Belt: Since the water pump relies on this belt, look for cracks, fraying, or glazing every 30,000 miles. A failing belt tensioner can also cause the pump to spin inefficiently.
- ✓ Timing Chain Considerations: While the cooling system is external, if you are performing a high-mileage water pump replacement, it is a good time to inspect the front timing cover area for oil leaks, as the timing chain and gears sit directly behind the pump.
Quality components are vital. When replacing a water pump or thermostat, opt for AC Delco or high-quality aftermarket brands that meet OEM specifications. Cheap plastic-impeller pumps are prone to cavitation and premature failure compared to those with metal impellers.
By following the engine 5.3 liter Chevy 5.3 Vortec cooling system diagram and understanding the nuances of coolant flow, you can ensure your vehicle remains reliable under heavy loads and extreme temperatures. Regular inspection of hoses, monitoring for a check engine light, and adhering to strict torque specs during repairs will save you thousands of dollars in potential engine damage and keep your Chevy V8 running strong.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is engine 5.3 liter chevy 5.3 vortec cooling system diagram?
An engine 5.3 liter Chevy 5.3 Vortec cooling system diagram is a visual map showing how coolant moves through the engine. It highlights the radiator, water pump, thermostat, and reservoir. This schematic is essential for diagnosing leaks, replacing worn hoses, or understanding the cooling path during a complex engine repair.
How do you read engine 5.3 liter chevy 5.3 vortec cooling system diagram?
To read the diagram, trace the lines representing coolant hoses from the radiator to the water pump. Arrows usually indicate flow direction. Identify key junctions like the thermostat housing and heater core. This helps you understand where hot coolant leaves the engine and where cooled fluid returns from the radiator.
What are the parts of engine 5.3 liter chevy 5.3 vortec cooling system?
Main components include the radiator, water pump, thermostat, upper and lower radiator hoses, heater core, and the expansion tank. The system also relies on the ECT sensor, which communicates with the ECU to manage fan operation and monitor temperatures to ensure the engine operates within safe and efficient limits.
Why is the thermostat important?
The thermostat is vital because it regulates the engine’s operating temperature. It stays closed during warm-up to reach heat quickly and opens once the engine is hot to allow coolant to flow to the radiator. A failure can trigger a check engine light or cause severe engine overheating and damage.
What is the difference between the radiator and heater core?
The radiator is located at the front of the vehicle to dissipate engine heat into the atmosphere. In contrast, the heater core is a smaller heat exchanger inside the dashboard that uses hot engine coolant to provide warmth to the cabin interior when the vehicle heater is turned on by users.
How do I use engine 5.3 liter chevy 5.3 vortec cooling system diagram?
Use the diagram to locate specific components when troubleshooting an OBD-II diagnostic code related to temperature. It guides you in identifying which hose to remove or where a sensor is located. It is also helpful for ensuring every bolt meets the specific torque spec during a new water pump installation.