7 Wire Trailer Plug Diagram: Wiring and Installation
A 7 wire trailer plug diagram illustrates the connection points for tail lights, turn signals, electric brakes, and auxiliary power. It identifies the common terminal for the ground wire and maps out the standard color codes to ensure your vehicle and trailer systems communicate effectively for safe highway operation.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Standardizes electrical signals between the towing vehicle and the trailer
- The white ground wire is the most critical component for completing the circuit
- Always ensure clean, corrosion-free contact points to prevent signal loss
- Use a circuit tester to verify power at the hot wire and lighting pins
- Refer to this diagram when installing hitches or repairing damaged harnesses
Towing a heavy-duty trailer requires more than just a hitch and a ball; it demands a reliable electrical connection to ensure your safety and the safety of everyone on the road. Whether you are hauling a horse trailer, a large boat, or a multi-axle camper, understanding a 7 wire trailer plug diagram is essential for a successful setup. This comprehensive guide provides the specific wiring schematics you need to connect your vehicle to your trailer, ensuring that turn signals, brake lights, electric brakes, and auxiliary power all function in perfect harmony. By following the correct diagram, you will eliminate the guesswork that often leads to blown fuses or flickering lights. In the sections below, you will learn about wire color codes, terminal assignments, and the step-by-step process of installing or repairing a 7-way connector to keep your towing experience stress-free and compliant with road regulations.
Understanding the 7-Way RV Standard Connector
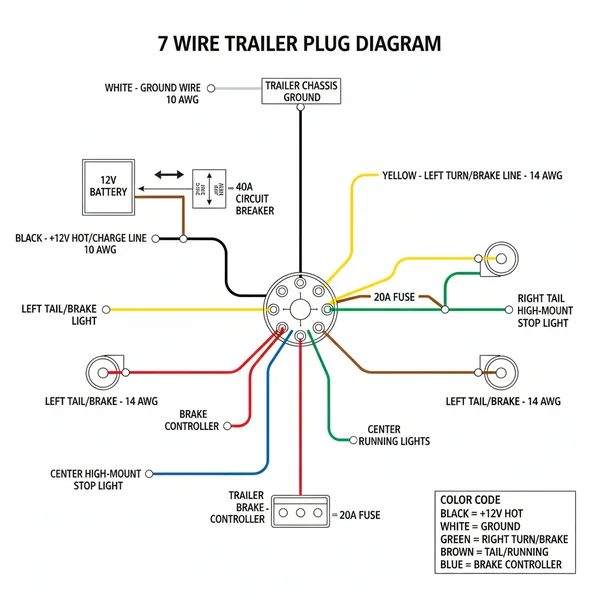
The 7-way trailer plug is the industry standard for trailers equipped with electric brakes and additional power needs. Unlike simpler 4-way or 5-way flat plugs, the 7-way round plug provides a dedicated circuit for several high-demand functions. The diagram essentially maps out how voltage is distributed from your tow vehicle’s battery and lighting system to the trailer’s components. Most modern 7-way plugs follow the “RV Standard” North American wiring pattern, though it is always wise to verify your specific manufacturer’s manual.
In a standard 7 wire trailer plug diagram, each pin inside the housing has a specific assignment. The layout is designed to prevent cross-connection, but because different manufacturers sometimes use different wire colors, looking at the terminal position is often more reliable than looking at the wire jacket alone. The central pin is typically reserved for backup lights or an auxiliary traveler wire, while the six pins arranged in a circle around it handle the primary functions like ground, brakes, and lighting.
The components within the plug are often secured using a brass screw for each terminal. These screws provide a high-conductivity connection point that resists vibration, which is crucial for maintaining a steady flow of current while traveling over rough terrain. Understanding which wire goes to which terminal—such as identifying the common terminal for the ground wire—is the first step toward a successful installation.
The most common 7-way plug is the “RV Blade” style. If you are working on commercial or heavy agricultural equipment, you may encounter a “7-Way Round Pin” plug, which uses a different pin configuration. Always match your plug type to the socket on your vehicle before beginning the wiring process.
Step-by-Step Installation and Wiring Guide

Installing a 7-way plug may seem daunting, but when broken down into logical steps, it becomes a manageable DIY project. Before you begin, ensure you have the correct gauge of wire for each circuit. Typically, the ground wire and the hot wire (battery charge) require a heavier 10 or 12-gauge wire to handle the higher amperage, while the lighting circuits can use 14 or 16-gauge wire.
- ✓ 7-Way Trailer Plug (Vehicle Side or Trailer Side)
- ✓ Wire Strippers and Crimping Tool
- ✓ Multimeter or 12V Circuit Tester
- ✓ Dielectric Grease
- ✓ Heat Shrink Tubing or Electrical Tape
Always disconnect the tow vehicle’s battery or pull the trailer’s 12V fuse before working on the wiring. A short circuit during installation can damage the vehicle’s electrical system or cause the electric brakes to lock up unexpectedly.
Step 1: Prepare the Cable
Begin by stripping back about 2 to 3 inches of the outer jacket from your trailer wire harness. Be careful not to nick the insulation on the individual wires inside. Once the wires are exposed, strip approximately half an inch of insulation from the end of each colored wire. If your plug uses a compression fitting, slide the housing of the plug onto the cable before you start connecting the wires to the interior terminals.
Step 2: Identify and Map Your Wires
Refer to your 7 wire trailer plug diagram. In most standard RV configurations, the colors are:
– White: Ground (The common terminal)
– Blue: Electric Brakes
– Green: Tail and Running Lights
– Black: 12V Battery Charge (The hot wire)
– Red: Left Turn and Brake Lights
– Brown: Right Turn and Brake Lights
– Yellow: Reverse Lights or Auxiliary Traveler Wire
Step 3: Connect the Ground Wire
The white ground wire is the most critical connection. It serves as the return path for all other circuits. Locate the terminal marked “Ground” or “WH” and loosen the brass screw. Insert the bare wire and tighten the screw firmly. In DC systems, this acts as the neutral wire equivalent, providing the necessary path back to the battery.
Step 4: Connect the Lighting Circuits
Connect the Green, Red, and Brown wires to their respective terminals according to the diagram. These control the basic safety lighting. If you find that your signals are swapped (left signal blinks when you turn right), you will need to reverse the Red and Brown wire positions on the terminals.
Step 5: Connect the Power and Brakes
The Black wire is your hot wire, providing a constant 12V charge to the trailer battery. Connect this to the terminal usually located at the 1 o’clock position. The Blue wire is for the electric brake controller. Ensure this connection is exceptionally secure, as it is vital for stopping the trailer.
Step 6: The Auxiliary/Traveler Wire
The center pin is often used for reverse lights, which is helpful when backing a large trailer into a dark campsite. Some older systems use this as a traveler wire for various auxiliary functions. Connect the Yellow wire here. If your trailer does not have reverse lights, this terminal can be left empty, but ensure the wire is capped off to prevent a short.
Step 7: Final Assembly and Testing
Slide the plug housing back over the terminal block and tighten any set screws or clamps. Use a 12V circuit tester or a multimeter to check the voltage at each pin on the vehicle side before plugging in the trailer. This ensures the vehicle is sending the correct signals to the right pins.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting

Even with a perfect 7 wire trailer plug diagram, issues can arise due to environmental factors or wear and tear. The most frequent problem users encounter is a “bad ground.” Because the ground wire is the common terminal for all circuits, a loose or corroded white wire can cause all the lights to dim, flicker, or act erratically (such as the tail lights flashing when you use the turn signal).
Another common issue is corrosion on the brass screw terminals. Road salt and moisture can enter the plug housing, leading to high resistance and a drop in voltage. If your electric brakes feel “weak” or your trailer battery isn’t charging, use a multimeter to check the voltage at the black and blue pins. If you see significantly less than 12V while the vehicle is running, you likely have a corrosion issue or a wire gauge that is too thin for the length of the run.
If you are experiencing intermittent light failure, check the “blades” or “pins” inside the plug. Over time, they can spread apart. Gently squeezing the female terminals with needle-nose pliers can restore a tight, reliable connection.
Tips and Best Practices for Trailer Wiring
To ensure your trailer wiring lasts for years, maintenance and quality components are key. When selecting a new plug, look for one with a built-in “pull handle” and a weather-sealed cover. This makes it easier to disconnect and keeps moisture out when the trailer is parked.
One of the best practices for any 7 wire trailer plug setup is the generous use of dielectric grease. Apply a small amount to the terminals before inserting the wires and to the face of the plug before connecting it to the vehicle. This grease does not conduct electricity but acts as a waterproof barrier that prevents oxidation on the metal surfaces.
Furthermore, always pay attention to wire gauge. For the 12V hot wire and the ground wire, using 10-gauge wire is highly recommended, especially for trailers with large batteries or multiple axles with electric brakes. Thinner wires can overheat or cause a voltage drop that prevents your equipment from operating at peak efficiency.
Finally, periodically inspect the wiring harness for “traveler wire” fatigue. This happens where the cable flexes during turns. If the outer jacket is cracked, moisture can wick up into the plug, causing internal shorts that are difficult to diagnose without taking the entire assembly apart. By following these maintenance tips and keeping a copy of the 7 wire trailer plug diagram in your glovebox, you can ensure that every towing journey is a safe one. Using a high-quality connector and ensuring every brass screw is tight will save you time, money, and frustration at the boat ramp or the campsite.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 7 wire trailer plug diagram?
A 7 wire trailer plug diagram is a visual schematic used to identify the wiring positions for a 7-way round plug. It provides a roadmap for connecting essential functions like turn signals, reverse lights, and electric brakes, ensuring the trailer lighting mimics the vehicle’s actions for road safety.
How do you read 7 wire trailer plug diagram?
To read the diagram, match the color-coded wires to their corresponding pin positions. Locate the common terminal at the center or specific notch and identify the ground wire, usually white. Follow the clockwise or numbered sequence provided in the schematic to ensure each circuit is wired to its correct pin.
What are the parts of 7 wire trailer plug?
The plug consists of a housing, a protective boot, and seven metal pins or blades. Internally, it features a common terminal for grounding and individual terminals for the hot wire, brake signal, traveler wire for auxiliary power, and specific pins for the left, right, and tail light circuits.
Why is ground wire important?
The white ground wire is crucial because it provides the return path for electrical current back to the vehicle’s battery. Without a solid ground connection, the entire electrical system can fail, causing flickering lights, weak signals, or a complete loss of power across the trailer’s lighting and braking systems.
What is the difference between 4-way and 7-way plugs?
A 4-way plug provides basic lighting functions like tail lights and turn signals. In contrast, a 7-way plug adds three additional wires for electric brakes, a 12V hot wire for battery charging, and backup lights. This makes the 7-way plug essential for larger trailers equipped with braking systems.
How do I use 7 wire trailer plug diagram?
Use the diagram by stripping a small portion of insulation from each wire and securing it to the correct terminal as shown. Start with the neutral wire or ground to establish a circuit, then systematically connect the remaining functions like the auxiliary traveler wire and tail light leads.