7 Pin Trailer Plug Wiring Diagram USA: Complete Hookup Guide
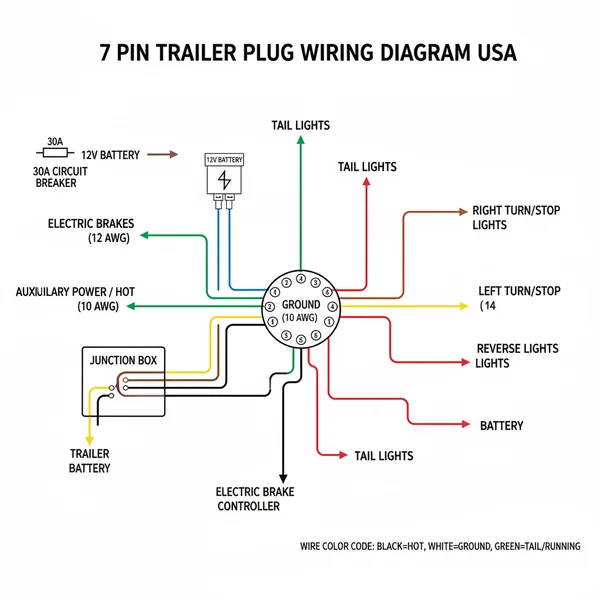
The 7 pin trailer plug wiring diagram USA standard provides the schematic for connecting lights, brakes, and power. It identifies the ground wire for the circuit, the hot wire for auxiliary power, and specific pins for blinkers, tail lights, and electric brakes to ensure safe vehicle-to-trailer communication.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Main purpose of this diagram is to standardize electrical connections for heavy-duty towing.
- The ground wire is the most important component to identify for electrical stability.
- Always ensure the hot wire is fused to protect the vehicle’s charging system.
- Use dielectric grease on the common terminal to prevent corrosion and signal loss.
- Use this diagram when installing brake controllers or replacing damaged trailer plugs.
When you are preparing to tow a heavy-duty trailer, camper, or boat, ensuring that your electrical connections are flawless is a matter of both safety and legal necessity. The 7 pin trailer plug wiring diagram usa is the definitive standard for North American towing, providing a robust interface for lights, electric brakes, and auxiliary power. Whether you are installing a new hitch system or repairing a faulty connection, having a clear understanding of this diagram prevents costly electrical shorts and ensures your trailer mimics your vehicle’s signals perfectly. In this comprehensive guide, you will learn the specific pinout configurations, the importance of wire gauges, and how to master the installation process from start to finish.
The 7-way “RV Standard” blade connector is the most common 7-pin configuration used in the United States. It is designed to provide power for tail lights, turn signals, brake lights, electric trailer brakes, a 12V hot wire for battery charging, and reverse lights.
The 7-way trailer plug consists of seven distinct terminals arranged in a circular pattern around a central pin. In the North American RV standard, these terminals are housed in a durable plastic or metal casing designed to withstand road debris and weather. When looking at the face of the vehicle-side socket (the female end), the configuration follows a specific color-coded logic. The central pin is typically reserved for the auxiliary or reverse light function. The surrounding pins handle the primary lighting and power needs. Each connection point usually features a high-conductivity brass screw to secure the wire, ensuring a low-resistance path for the electrical current.
Understanding the internal architecture of the plug is vital. Each wire serves a dedicated purpose, and its thickness, or gauge, must be appropriate for the current it carries. For instance, the ground wire and the 12V hot wire require a heavier gauge (usually 10 to 12 gauge) because they handle the highest current loads. Conversely, signal wires for turn indicators can typically use 14 or 16 gauge wire. While most modern harnesses follow a standardized color scheme—White for ground, Blue for electric brakes, Green for tail lights, Black for the 12V battery feed, Red for left turn/brake, Brown for right turn/brake, and Yellow for reverse—it is essential to verify these with a multimeter, as some manufacturers may use proprietary variations.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: 7-Pin Trailer Plug Wiring Map – USA RV Standard]
(Visualizing a circular plug with 7 terminals: Center = Yellow; 12 o’clock = White; 1 o’clock = Blue; 3 o’clock = Brown; 5 o’clock = Black; 7 o’clock = Red; 9 o’clock = Green)
To interpret the 7 pin trailer plug wiring diagram usa correctly, you must distinguish between the vehicle-side socket and the trailer-side plug. They are mirror images of one another. If you misinterpret the orientation, you may inadvertently wire the “hot wire” to the “ground wire” terminal, which will result in a blown fuse or damage to your vehicle’s integrated towing module.
Always disconnect the vehicle battery and the trailer’s onboard battery before beginning any wiring work. A short circuit involving the 12V hot wire can cause immediate sparks and potential fire hazards.
Reading and implementing a wiring diagram requires a methodical approach. Follow these steps to ensure a professional-grade installation:
- ✓ Step 1: Preparation and Tool Gathering – Collect a wire stripper, a high-quality crimping tool, a multimeter, and dielectric grease. Ensure you have the correct 7-way connector for your application, preferably one with a spring-loaded dust cover.
- ✓ Step 2: Strip and Tin the Wires – Strip approximately half an inch of insulation from each wire in the harness. If you are using a plug with a brass screw terminal, twisting the copper strands tightly is essential. For maximum durability, some technicians prefer to “tin” the ends with solder to prevent fraying.
- ✓ Step 3: Connect the Ground Wire – Locate the common terminal, which is usually at the 12 o’clock position and marked as “White” or “GND.” This is the most critical connection. Without a solid ground, the entire system will fail or behave erratically. Use a heavy 10-gauge wire for this terminal.
- ✓ Step 4: Wire the Lighting Functions – Connect the Brown wire to the Right Turn/Brake terminal and the Red wire to the Left Turn/Brake terminal. The Green wire attaches to the Tail/Running light terminal. Ensure the strands are fully seated under the brass screw before tightening.
- ✓ Step 5: Connect the Power and Brakes – Attach the Blue wire to the Electric Brake terminal. Then, connect the Black wire (the hot wire) to the battery charge terminal. This pin provides a constant 12V voltage to the trailer’s battery while the vehicle is running.
- ✓ Step 6: Auxiliary and Reverse Lights – The center pin is typically used for auxiliary power or reverse lights (Yellow wire). In some specialized configurations, this may act as a traveler wire for complex signaling, but in standard USA RV plugs, it is almost always for reverse functionality.
- ✓ Step 7: Weatherproofing and Assembly – Apply a liberal amount of dielectric grease to each terminal to prevent corrosion. Slide the outer housing over the wired core and tighten the strain relief clamp to ensure the wires aren’t pulled out of their terminals during use.
- ✓ Step 8: Final Testing – Use a multimeter or a 7-way circuit tester to verify that each pin is receiving the correct voltage when the vehicle’s lights and brakes are activated. Check that the “neutral wire” equivalent (the ground) has perfect continuity with the vehicle frame.
Even with a perfect 7 pin trailer plug wiring diagram usa, issues can arise due to environmental factors or wear and tear. The most frequent problem users encounter is “dim lights” or lights that flash out of sync. This is almost always caused by a poor ground wire connection. Because the trailer frame is often used as a secondary path, corrosion at the ground point can cause the electrical current to seek a path through other bulbs, creating a ghosting effect.
Another common issue is a “No Brake” signal. This can be traced back to the Blue wire or the brake controller inside the vehicle. If you notice a sudden drop in voltage at the trailer brakes, check the brass screw terminals inside the plug; they often loosen over time due to road vibrations. If you see green or white powdery residue on the pins, corrosion has set in, which increases resistance and can eventually melt the plastic housing of the plug. If you encounter complex issues like a total power failure that a multimeter cannot identify, it may be time to seek professional help to inspect the vehicle’s integrated Power Distribution Center.
To extend the life of your 7-way plug, always use a mounting bracket that keeps the socket angled slightly downward. This prevents rainwater from pooling inside the socket housing and causing terminal corrosion.
For a truly reliable setup, consider these maintenance recommendations and best practices. First, always prioritize wire gauge. While it might be tempting to use thinner wire for the hot wire or ground to save money, doing so creates significant voltage drops that can prevent your trailer battery from charging or, worse, prevent your electric brakes from engaging with full force. High-quality 7-way harnesses often use molded plugs rather than user-serviceable ones because they are hermetically sealed against moisture.
Maintenance is the key to longevity. At the start of every towing season, spray the terminals with an electrical contact cleaner and reapply dielectric grease. This simple step can save you hours of troubleshooting on the side of the road. Additionally, always check the “common terminal” (Ground) for a secure connection to the trailer frame. A self-tapping screw into a clean, paint-free section of the frame is the gold standard for grounding.
In conclusion, mastering the 7 pin trailer plug wiring diagram usa is a foundational skill for any trailer owner. By understanding the specific role of the hot wire, the necessity of a thick-gauge ground wire, and the proper placement of signal wires on the brass screw terminals, you ensure that your towing setup is safe, efficient, and reliable. Regular inspections and the use of quality components will keep your trailer’s electrical system functioning perfectly for years to come. Whether you are navigating busy highways or backing into a tight campsite, a properly wired 7-pin plug provides the peace of mind you need for every journey.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the 7 Pin Trailer Plug Wiring Diagram Usa: Complete Hookup Guide
Identify the standard color-coding used in the 7 pin trailer plug wiring diagram USA.
Locate the common terminal designated for the white ground wire to ensure a closed circuit.
Understand how the traveler wire connections distribute signals for left and right turn indicators.
Connect the black hot wire to the constant power pin for charging trailer batteries.
Verify that the neutral wire configuration effectively manages the return current for all lighting functions.
Complete the installation by testing each pin with a multimeter to ensure correct voltage output.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 7 pin trailer plug wiring diagram USA?
This diagram is the standard schematic for North American towing systems, detailing how to connect seven specific functions. It covers the ground wire, tail lights, left and right turn signals, electric brakes, backup lights, and a hot wire for constant 12V power, ensuring full trailer functionality and road safety.
How do you read 7 pin trailer plug wiring diagram USA?
To read the diagram, orient the plug by its center keyway or notch. Match each numbered pin to its designated function and wire color. Identify the common terminal for the ground and follow the path of the traveler wire signals for indicators to ensure the trailer mimics the vehicle’s actions.
What are the parts of 7 pin trailer plug?
The plug consists of a durable housing, seven internal brass pins, and a weather-sealed rear entry. Key internal parts include the common terminal for grounding, the 12V hot wire for battery charging, and individual circuits for brakes and lighting, all organized to prevent short circuits during heavy use.
Why is ground wire important?
The ground wire is critical because it completes the electrical circuit back to the vehicle’s battery. Without a solid ground, the trailer lights will flicker, brakes may malfunction, or the circuit might attempt to ground through the hitch ball, leading to inconsistent performance and potential electrical damage to both.
What is the difference between 4-pin and 7-pin?
A 4-pin plug provides basic lighting like stop and turn signals. The 7-pin version adds three essential functions: a hot wire for auxiliary power, a connection for electric trailer brakes, and backup lights. This makes the 7-pin plug necessary for larger trailers equipped with their own braking systems.
How do I use 7 pin trailer plug wiring diagram USA?
Use the diagram as a visual map when stripping and connecting wires to a new plug. Align the white neutral wire equivalent to the ground pin and ensure the traveler wire for each signal is in its correct slot to prevent cross-wired turn signals or brakes.