7 Pin Brake Controller Wiring Diagram: Installation Guide
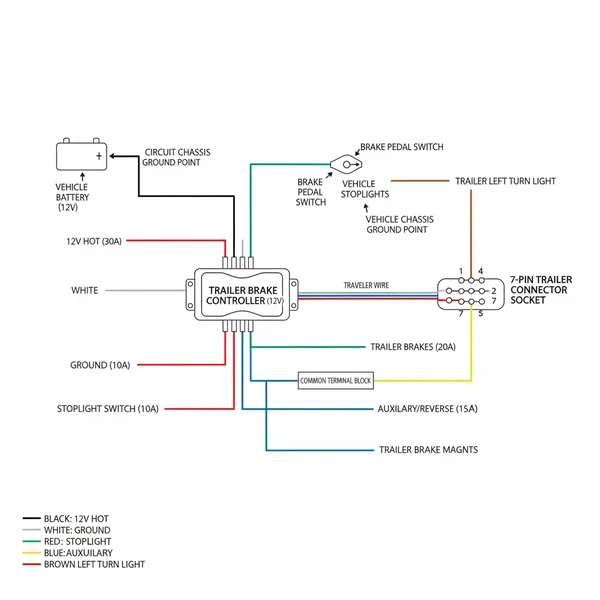
A 7-pin brake controller wiring diagram illustrates how to connect your vehicle’s electric brakes, lights, and power. It links the controller to the trailer plug using a ground wire for stability and a hot wire for 12V power, ensuring synchronized braking between the towing vehicle and the trailer for safe transit.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides a visual map for synchronizing vehicle and trailer brakes
- Identification of the blue brake signal wire is the most essential step
- Always use a circuit breaker to protect the hot wire connection
- Ensure all connections are weatherproofed to prevent electrical shorts
- Essential for heavy-duty towing requiring electric trailer brakes
Starting your journey into heavy-duty towing requires more than just a hitch and a trailer; it demands a sophisticated electrical interface to ensure safety on the road. Understanding a 7 pin brake controller wiring diagram is the first step toward achieving a synchronized braking experience between your tow vehicle and your trailer. This guide is designed to demystify the complex web of wires, providing you with a clear roadmap for installation and maintenance. Whether you are a DIY enthusiast or a first-time tower, you will learn how to identify each circuit, select the correct wire gauge, and ensure your system maintains the proper voltage to keep your trailer brakes responsive and reliable.
A 7-way trailer plug does more than just power lights. It facilitates a high-current connection for electric brakes and provides a 12V auxiliary line to charge trailer batteries while driving. Precision in wiring these components is vital for preventing electrical fires and brake failure.
Decoding the 7 Pin Brake Controller Wiring Diagram
The 7 pin brake controller wiring diagram represents a standardized layout used across the North American towing industry. Unlike simpler 4-flat or 5-flat connectors, the 7-way round plug includes dedicated circuits for electric brakes and auxiliary power. The diagram functions as a top-down view of the connector, usually from the perspective of looking directly at the face of the vehicle-side socket.
The central component of this system is the common terminal, which typically sits in the middle or is assigned to the largest pin to handle the return current. Each pin is assigned a specific color and function to prevent cross-wiring. While there are slight variations in aftermarket wire colors, the standard industry layout is as follows:
- ✓ White (Pin 1): The ground wire, which must be connected to a clean, unpainted part of the vehicle frame.
- ✓ Blue (Pin 2): The electric brake output, often referred to as the traveler wire that carries the modulated signal from the controller to the trailer magnets.
- ✓ Green (Pin 3): Tail lights and running lights.
- ✓ Black (Pin 4): The hot wire, providing 12V auxiliary power to charge trailer batteries.
- ✓ Yellow (Pin 5): Left turn signal and stop light.
- ✓ Brown (Pin 6): Right turn signal and stop light.
- ✓ Purple (Pin 7): Reverse lights or auxiliary backup power.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A circular 7-way trailer plug diagram showing Pin 1 at the 7 o’clock position (White/Ground), Pin 2 at 9 o’clock (Blue/Brake), Pin 3 at 11 o’clock (Green/Tail), Pin 4 at 1 o’clock (Black/Battery), Pin 5 at 3 o’clock (Yellow/Left), Pin 6 at 5 o’clock (Brown/Right), and Pin 7 in the center (Purple/Reverse).]
Inside the physical plug, these wires are usually secured to a brass screw terminal. These terminals are chosen for their excellent conductivity and resistance to the harsh environments found behind a rear bumper. When examining your diagram, always ensure you are distinguishing between the “vehicle side” (socket) and the “trailer side” (plug), as they are mirror images of each other.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide

Properly installing a brake controller requires attention to detail and the right materials. Before beginning, gather your tools: a wire stripper, crimping tool, a multi-meter to check voltage, and a circuit tester. You will also need high-quality primary wire of the appropriate gauge—typically 10-gauge for the power and ground, and 12-gauge for the brake output.
Always disconnect the negative battery terminal before starting any electrical work on your vehicle. This prevents accidental shorts that could damage your vehicle’s sensitive Electronic Control Unit (ECU).
Step 1: Mounting the Controller
Choose a location within reach of the driver but out of the way of your knees and the airbag deployment zones. Most controllers can be mounted at various angles, but check the manufacturer’s manual to ensure it doesn’t need to be perfectly level to function correctly.
Step 2: Connecting the Hot Wire and Ground
Run a 10-gauge hot wire from the positive terminal of the battery to the “Battery” input on the controller. You must install an in-line circuit breaker (usually 20A or 30A) as close to the battery as possible. Next, connect the ground wire from the controller to the common terminal or a solid metal ground point on the chassis. In a 12V DC automotive system, the ground acts as the neutral wire or return path, completing the electrical loop.
Step 3: Tapping the Brake Switch Signal
Locate the brake light switch near the top of your brake pedal arm. Use your circuit tester to find the wire that only shows voltage when the pedal is depressed. This is the “cold side” of the switch. Tap into this wire to send a signal to the controller that the brakes are being applied.
Step 4: Running the Brake Output Wire
Run the blue wire (the brake output) from the controller all the way to the back of the vehicle. This is the critical traveler wire that carries the variable power to the trailer’s magnetic brakes. Secure this wire along the frame rail using zip ties, ensuring it is away from hot exhaust components or moving suspension parts.
Step 5: Wiring the 7-Way Socket
Follow your 7 pin brake controller wiring diagram to connect the wires to the back of the 7-way socket. Strip approximately half an inch of insulation from each wire, insert it into the correct terminal, and tighten the brass screw firmly. Ensure no stray wire strands are touching adjacent terminals.
Step 6: Testing the System
Once everything is connected, reconnect the battery. Use a multi-meter to check for 12V at the hot wire pin on the socket. Have an assistant step on the brakes while you check for a signal on the blue pin. The voltage on the blue pin should increase as the manual override on the controller is moved.
When running wires under the vehicle, use plastic wire loom (conduit) to protect against road debris and moisture. This small investment prevents 90% of future electrical “ghost” issues caused by frayed insulation.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting

Electrical problems are the most common headache in towing. If your brakes are weak or non-existent, the first place to look is the 7 pin brake controller wiring diagram to verify your pinouts. A frequent mistake is swapping the auxiliary power and brake output pins, which can lead to the trailer brakes being “locked on” as soon as the trailer is plugged in.
Another common issue is a “floating ground.” If the ground wire is not properly bonded to the frame, the electricity will try to find a path back through the hitch ball. This results in flickering lights and intermittent brake performance. If you notice a drop in voltage at the trailer plug, check the brass screw connections inside the plug for corrosion. Green or white powdery buildup indicates moisture intrusion, which creates resistance and heat. If you find your controller showing an “NC” (No Connection) error, it usually means the traveler wire has a break or the trailer magnets have failed.
Tips and Best Practices for Long-Term Reliability
To ensure your wiring remains in peak condition, maintenance is key. Every season, open the back of the 7-way socket and inspect the brass screw terminals. Applying a small amount of dielectric grease to the terminals and the plug face can prevent oxidation and ensure a consistent flow of voltage.
When it comes to wire selection, always prioritize gauge over cost. Using a wire that is too thin (high gauge number) for the hot wire or the brake line causes a phenomenon called “voltage drop.” This means the trailer magnets receive less power than the controller is sending, resulting in poor braking performance. For runs longer than 20 feet, upgrading to a 10-gauge wire for the brake circuit is a highly recommended safety measure.
Finally, consider the quality of your components. Cheap, plastic 7-way sockets often crack or warp in extreme temperatures. Opting for a heavy-duty, glass-filled nylon or metal housing will provide better protection for the internal wiring. If you are frequently towing in salted winter conditions or near salt water, stainless steel mounting hardware is a must to prevent the common terminal from losing its connection to the vehicle frame.
By following a clear 7 pin brake controller wiring diagram and adhering to these installation standards, you create a towing environment that is safe for you and everyone else on the road. Proper wiring is not just about making things work; it is about ensuring they work every single time you hit the brakes in an emergency. Keep your connections tight, your wires protected, and your diagrams handy for a lifetime of trouble-free towing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a 7 pin brake controller wiring diagram?
A 7-pin brake controller wiring diagram is a technical schematic used to map the electrical connections between a vehicle’s cabin controller and the trailer plug. It identifies pins for turn signals, tail lights, reverse lights, auxiliary power, and the critical electric brake signal, ensuring safe communication between both systems.
How do you read a 7 pin brake controller wiring diagram?
Reading the diagram involves matching the wire colors or pin numbers to their specific functions. You start by identifying the ground wire and the hot wire for power. Then, follow the lines to see where the brake signal connects, ensuring each terminal on the plug matches the vehicle’s harness.
What are the parts of a 7 pin brake controller?
The main components include the controller unit, a dedicated wiring harness, and the 7-way plug. Internally, it features a common terminal for shared connections and utilizes various colored wires to handle specific tasks like sending the brake signal, powering lights, and maintaining a solid ground connection for safety.
Why is the ground wire important?
The ground wire is the most critical part of the circuit as it completes the electrical loop. Without a solid ground, the brake controller cannot send accurate signals, which may lead to intermittent braking or complete failure. It ensures that the hot wire and signals have a stable return path.
What is the difference between a hot wire and a neutral wire?
In 12V DC systems like trailer wiring, a hot wire carries positive current to power accessories, while the ground acts as the return. While a neutral wire is typically found in AC home wiring alongside a traveler wire, in trailers, the ground serves the primary return function for power.
How do I use a 7 pin brake controller wiring diagram?
Use the diagram to guide your installation by verifying each pin’s location on the trailer connector. Start by mounting the controller, then use the schematic to bridge the hot wire to the battery and the signal wire to the brake pedal switch, ensuring all connections are secure and fused.