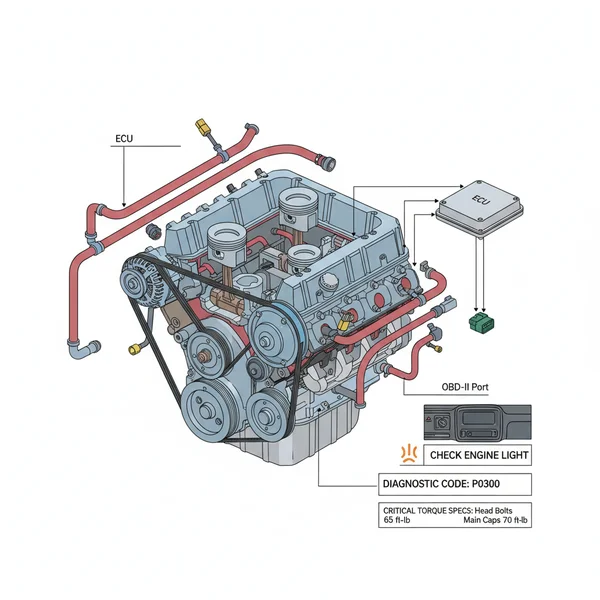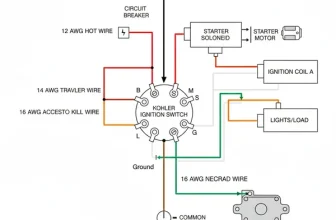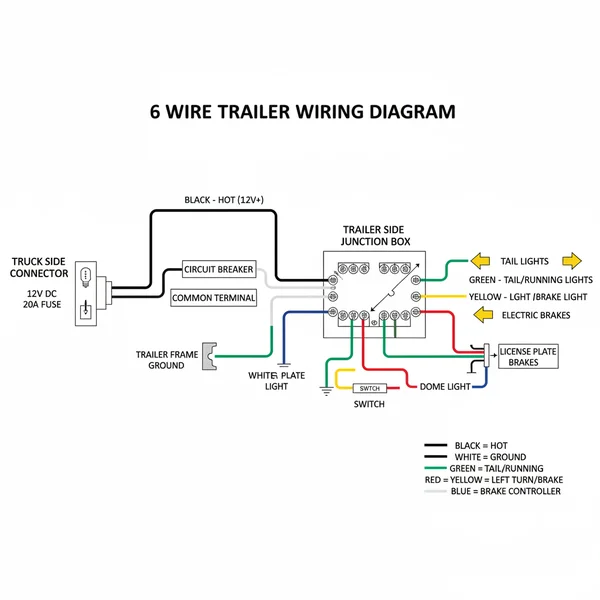
A 6 wire trailer wiring diagram maps out the connections for ground, tail lights, left turn/brake, right turn/brake, electric brakes, and a 12V hot wire battery lead. This setup provides essential lighting signals plus braking power and auxiliary charging for trailers, ensuring a secure electrical link between the towing vehicle and the trailer.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides standard lighting plus electric brakes and 12V power
- Correctly identifying the ground wire is vital for circuit completion
- Ensure wire gauges match the current load for brakes and power
- Use color-coding to simplify the matching process between vehicle and trailer
- Ideal for horse trailers or utility trailers needing independent braking
Towing a trailer safely requires a reliable electrical connection between your vehicle and the trailer. When you move beyond basic lighting and need to power electric brakes or auxiliary accessories, a 6 wire trailer wiring diagram becomes an essential tool. This specific configuration is common for mid-sized trailers, horse trailers, and campers that require more than just the four basic functions. Having an accurate 6 wire trailer wiring diagram ensures that your brake lights, turn signals, and electric brakes operate in harmony, preventing dangerous road conditions and legal issues. In this comprehensive guide, you will learn how to identify each wire, understand the color-coding standards, and successfully wire your own trailer plug to ensure consistent performance on the road.
A 6-way trailer connector adds two critical functions over the standard 4-way: a dedicated circuit for electric brakes and an auxiliary power line for battery charging or interior lights.
Understanding the 6 Wire Trailer Wiring Diagram
The 6 wire trailer wiring diagram typically describes a round connector, often referred to as a “6-pole round” plug. Unlike smaller flat connectors, this round housing is designed for durability and is frequently found on horse trailers and utility trailers. To read the diagram correctly, you must understand the function assigned to each pin within the connector. The pins are usually arranged in a circular pattern with one pin in the center and five surrounding it.
Inside the plug housing, you will find a brass screw for each connection point. These screws are designed to bite into the copper strands of your wiring to provide a low-resistance path for the electrical current. Each wire serves a specific purpose, and mixing them up can lead to malfunctions, such as your brakes engaging when you turn on your headlights.
Typical 6-Way Round Connector Pinout (Vehicle Side View)
The standard color-coding for a 6 wire system is as follows:
- ✓ White Wire: This is the ground wire. It is the most important wire in the system as it completes the circuit for every other function.
- ✓ Brown Wire: This controls the tail lights and running lights.
- ✓ Yellow Wire: This operates the left turn signal and left brake light.
- ✓ Green Wire: This operates the right turn signal and right brake light.
- ✓ Blue Wire: This is the dedicated circuit for electric trailer brakes.
- ✓ Red or Black Wire: This is the hot wire, used for auxiliary power such as interior lights or charging a battery.
It is important to note that while this is the standard, some manufacturers may vary their colors. Always refer to the labels on the common terminal block or the specific instructions provided with your trailer plug. Furthermore, the gauge of the wire is critical; the ground, brake, and auxiliary wires should typically be a heavier 10 or 12 gauge, while signal wires can be 14 or 16 gauge.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide

Following a 6 wire trailer wiring diagram step-by-step is the best way to avoid errors. Before you begin, ensure you have the necessary tools: wire strippers, a crimping tool, a multimeter for testing voltage, and electrical grease.
Always disconnect the vehicle battery before working on wiring to prevent accidental shorts or damage to your vehicle’s sensitive electronics.
Step 1: Preparation and Identification
Identify the six wires on both your vehicle and your trailer. If the colors do not match the standard diagram, use your multimeter to check which wire is which. For example, have a helper turn on the left signal while you check for 12V voltage on the vehicle wires. While residential systems use a traveler wire or neutral wire for complex switching, trailer systems are simpler DC circuits where each wire has a direct path to its load.
Step 2: Strip the Wires
Use your wire strippers to remove about half an inch of insulation from the end of each wire. Ensure the copper strands are clean and not frayed. If the copper is corroded (turning green), cut the wire back until you find shiny, clean copper to ensure a solid connection.
Step 3: Connect the Ground Wire
The white ground wire should always be connected first. In a 6-way plug, find the terminal marked “GD” or “WHT.” Loosen the brass screw, insert the wire, and tighten it firmly. A poor ground is the number one cause of trailer lighting failure, so ensure this connection is tight.
Step 4: Wire the Tail and Signal Lights
Connect the brown (tail), yellow (left turn), and green (right turn) wires to their respective terminals. In some setups, the yellow and green wires serve as both the turn signal and the brake light. These are often labeled “LT” and “RT” on the plug’s internal housing.
Step 5: Connect the Electric Brakes and Auxiliary Power
The blue wire is for your electric brakes. This wire carries significant current when the brakes are applied, so ensure the connection is robust. Finally, connect the red or black hot wire to the center terminal or the terminal marked “AUX.” This provides the 12V feed to the trailer’s auxiliary systems.
Step 6: Secure and Seal the Plug
Once all wires are connected to their respective brass screw terminals, slide the plug housing over the wire assembly. It is highly recommended to apply a small amount of dielectric grease to the terminals before closing the housing. This prevents moisture from causing corrosion and shorts inside the plug.
Step 7: Final Testing
Reconnect the vehicle battery. Using a trailer circuit tester or a multimeter, verify that each pin receives the correct 12V voltage when the corresponding vehicle function is activated. For the brake wire (blue), you will need to engage the manual override on your brake controller to see a reading.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting

Even with a perfect 6 wire trailer wiring diagram, problems can arise due to environmental factors or wear and tear. One of the most common issues is “dim lights,” which usually indicates a weak ground. Since the ground is the common terminal for all circuits, a loose white wire will cause the electricity to seek a return path through other bulbs, causing them to glow dimly or blink erratically.
Another frequent issue is a “short to ground,” where a hot wire touches the trailer frame. This will usually blow a fuse in the vehicle. If your electric brakes are not responding, check the blue wire for continuity. Unlike a residential neutral wire, which returns current in an AC system, the trailer’s frame often acts as the return path; if the trailer’s frame isn’t properly bonded to the connector’s ground, the brakes will fail to engage.
If you encounter intermittent power, check the pins on the vehicle side. They often spread apart over time. Use a small flathead screwdriver to gently spread the split-pins back open for a tighter fit.
Tips & Best Practices for Trailer Wiring
To ensure your wiring job lasts for years, follow these professional maintenance and installation tips. First, always use the correct wire gauge. Using wire that is too thin for the electric brakes or auxiliary power can cause the wire to overheat, leading to a drop in voltage and potential fire hazards. For the brake and power lines, 10 or 12-gauge wire is recommended, while 14 or 16-gauge is sufficient for the signal lights.
Maintenance is equally important. At the start of every towing season, inspect the brass screw connections inside the plug. Vibrations from the road can loosen these screws over time. If you live in an area where salt is used on the roads, clean the plug terminals regularly with electrical contact cleaner to prevent oxidation.
- ✓ Use Heat Shrink: When splicing wires, always use adhesive-lined heat shrink tubing rather than electrical tape to keep moisture out.
- ✓ Route Wires Carefully: Run wires through the interior of the trailer frame or through protective conduit to protect them from road debris.
- ✓ Grommets are Essential: Any time a wire passes through a hole in the metal frame, use a rubber grommet to prevent the metal from chafing through the insulation.
By following a clear 6 wire trailer wiring diagram and taking the time to secure your connections properly, you ensure that your towing setup is safe, legal, and reliable. Whether you are hauling a horse trailer or a heavy equipment hauler, a well-wired 6-way system provides the power and control needed for modern towing demands. If you ever feel overwhelmed or find that your vehicle’s factory wiring does not match the standard, do not hesitate to consult a professional auto electrician to avoid damaging your vehicle’s integrated computer systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 6 wire trailer wiring diagram?
A 6 wire trailer wiring diagram is a visual schematic used to connect a six-pole plug between a towing vehicle and a trailer. It typically includes circuits for running lights, left and right turn signals, electric brakes, a 12V hot wire for battery charging, and a dedicated ground wire.
How do you read 6 wire trailer wiring diagram?
To read a 6 wire trailer wiring diagram, match the color-coded lines to the corresponding terminals on the plug. Identify the central common terminal or ground, then trace the paths for brake signals and the auxiliary power line. Ensure each pin location matches the specific layout of your vehicle’s socket.
What are the parts of 6 wire trailer wiring?
The system consists of a six-pole connector housing, color-coded wires, and terminal pins. Key wires include the white ground wire, green and yellow signal wires, brown tail light wire, blue electric brake wire, and a red or black hot wire for constant 12V auxiliary power delivery to the trailer.
Why is ground wire important?
The ground wire is critical because it provides the return path for electrical current to the vehicle’s battery. Without a solid ground connection, the trailer lights may flicker or fail entirely. It acts similarly to a neutral wire in AC systems, completing the DC circuit safely for all components.
What is the difference between traveler wire and hot wire?
A hot wire provides constant 12V power to the trailer’s battery or interior lights. While a traveler wire is usually found in AC house wiring, in some custom trailer setups, it might refer to an auxiliary line used for specialized switching functions between different power sources or secondary lighting.
How do I use 6 wire trailer wiring diagram?
Use the diagram by stripping the wire ends and inserting them into the numbered ports of the trailer plug. Tighten the screws on the common terminal first, then follow the schematic to secure the signals, brakes, and power leads before testing the entire system with a multimeter or vehicle.