5.3 Vortec Engine Parts Diagram: Identification and Repair
A 5.3 Vortec engine parts diagram visually maps the small-block V8’s internal and external components. It helps identify the intake manifold, cylinder heads, and the ECU managing performance. Use it to locate sensors when a diagnostic code triggers the check engine light or to find a specific torque spec.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Identify internal and external LS-based engine components accurately
- Locate critical sensors linked to the ECU for electrical repairs
- Ensure proper assembly using correct torque spec data provided
- Diagnose check engine light issues effectively using visual aids
- Essential reference for timing chain or manifold maintenance tasks
Whether you are performing a routine service or a complete overhaul, having a reliable 5.3 vortec engine parts diagram is an essential resource for any mechanic or DIY enthusiast. The 5.3L Vortec, part of General Motors’ legendary LS-based Small Block family, is known for its incredible durability and modular design. However, because these engines have been produced in various iterations—ranging from the early LM7 to the later LC9 and LMG versions—pinpointing the exact location of sensors, bolts, and internal components can be challenging without visual guidance. In this article, you will learn how to identify key components on a 5.3 Vortec, understand the routing of the accessory belt and coolant flow, and gain insights into the electrical connections that link your hardware to the ECU.
Breaking Down the 5.3 Vortec Engine Parts Diagram
The 5.3 Vortec engine is categorized by its “V” configuration, consisting of eight cylinders and a single camshaft located within the block (OHV design). When looking at a comprehensive 5.3 vortec engine parts diagram, the components are typically organized into three main sections: the top end, the bottom end, and the front-end accessory drive (FEAD).
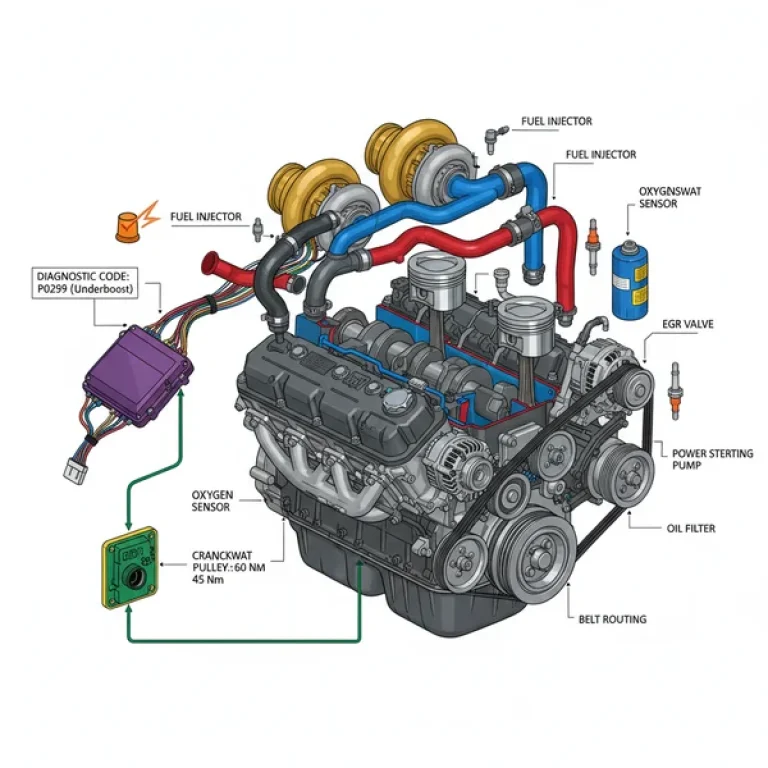
The top end of the diagram highlights the composite intake manifold, which is a signature feature of the Vortec line. This manifold houses the fuel rails and the eight individual fuel injectors. Directly behind the intake manifold, you will find the oil pressure sensor, a frequent point of maintenance. The cylinder heads sit beneath the valve covers, housing the rocker arms, pushrods, and valves.
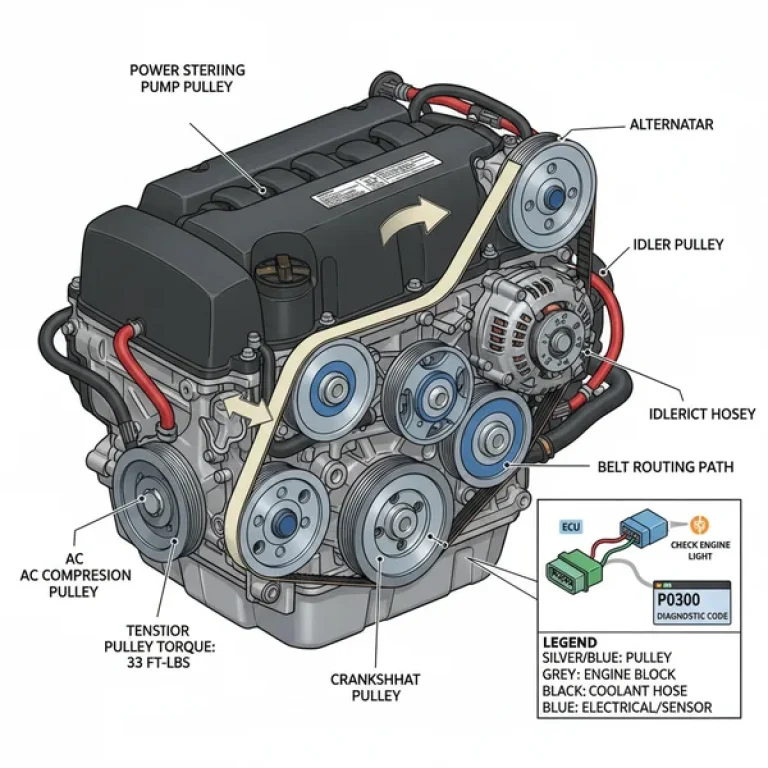
Moving to the front of the diagram, the focus shifts to the accessory belt system. This includes the alternator, power steering pump, water pump, and the A/C compressor. The diagram also illustrates the complex coolant flow path, starting from the radiator, through the thermostat housing located on the passenger side of the water pump, and into the engine block and heads.
In the bottom end of the diagram, you will see the crankshaft, the connecting rods, and the pistons. A critical area often searched for is the “valley cover,” located beneath the intake manifold. On older versions, this is where the knock sensors are hidden, while on newer versions equipped with Active Fuel Management (AFM), this area contains the solenoid manifold that controls oil flow to the lifters.
How to Use the Diagram for Repairs and Maintenance
Interpreting an automotive diagram requires a systematic approach. Follow these steps to ensure you are using the 5.3 vortec engine parts diagram correctly to facilitate your repair process.
- Identify Your Engine Generation: Before starting, determine if you have a Gen III (1999-2007) or Gen IV (2007-2014) engine. While the core 5.3 vortec engine parts diagram looks similar, certain sensors like the camshaft position sensor moved from the rear of the block (Gen III) to the front timing cover (Gen IV).
- Locate the Primary Component: Use the diagram to find the central part you are working on. For example, if you are replacing the water pump, find it on the front of the block. Notice how it connects to the thermostat housing and the various heater core hoses to understand the coolant flow.
- Cross-Reference with Torque Specs: Once you identify a part on the diagram, such as a cylinder head or a manifold, you must look up the specific torque spec for that component. For the 5.3 Vortec, most M8 bolts (like those on the intake) require roughly 89 lb-in, while cylinder head bolts require a complex “torque-to-yield” sequence.
- Trace the Electrical Path: Use the diagram to follow wiring harnesses back to the ECU (Engine Control Unit). This is vital if you are dealing with a sensor failure. The diagram will show you how the harness wraps around the back of the intake manifold.
- Verify the Accessory Belt Routing: If you have removed the serpentine belt, refer to the FEAD section of the diagram. It will show the exact “S” curve the accessory belt must follow around the pulleys to ensure the water pump rotates in the correct direction.
The 5.3 Vortec uses an “interference” design in some contexts, but more importantly, it utilizes a timing chain rather than a belt. The timing chain connects the crankshaft to the camshaft and is located behind the front timing cover. If this chain stretches, it can cause significant timing errors and diagnostic codes.
To perform these tasks, you will need a standard set of metric sockets (8mm to 24mm), a high-quality torque wrench, and potentially a fuel line disconnect tool if you are removing the intake manifold. Always wear safety glasses and ensure the engine is completely cool before opening the cooling system or touching the exhaust manifolds.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting with the 5.3 Vortec
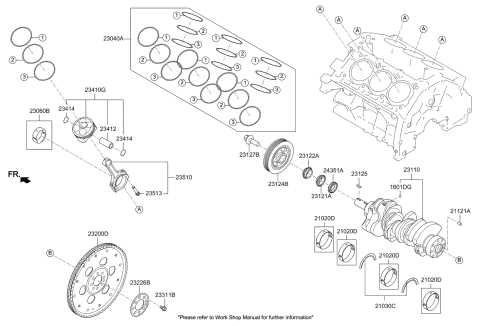
Even the most reliable engines face common failures. Using your 5.3 vortec engine parts diagram can help you isolate these issues when a check engine light appears on your dashboard. When the ECU detects a fault, it stores a diagnostic code that can be read via the OBD-II port located under the driver-side dash.
- ! Vacuum Leaks: Often caused by deteriorating intake manifold gaskets. The diagram helps you locate the specific bolts and the map sensor at the rear of the intake.
- ! Knock Sensor Failure: On Gen III engines, moisture gets trapped in the knock sensor wells in the “valley” under the intake. A diagram is necessary to see how to remove the manifold to reach these sensors.
- ! Oil Pressure Drops: Often caused by a clogged tiny screen located beneath the oil pressure sensor at the back of the block.
If you see a check engine light and pull a diagnostic code such as P0300 (Random Misfire) or P0332 (Knock Sensor Low Input), the diagram becomes your roadmap. It allows you to trace the wires and check for frayed insulation or loose connectors that might be sending false signals to the ECU. If you encounter deep internal knocking or consistent low oil pressure despite sensor changes, it may be time to consult a professional for a mechanical inspection of the rotating assembly.
Pro Tips and Best Practices for Maintenance
Maintaining a 5.3 Vortec ensures it can easily exceed 300,000 miles. Beyond just following the 5.3 vortec engine parts diagram for repairs, follow these professional best practices for long-term health.
Many electrical gremlins on the 5.3 Vortec are caused by poor grounds. Use your diagram to locate the ground straps on the back of the cylinder heads and the frame. Cleaning these connections can often clear “phantom” diagnostic codes.
Never reuse cylinder head bolts on this engine. They are “Torque-to-Yield” (TTY) bolts, meaning they permanently stretch when tightened. Reusing them can lead to head gasket failure.
- ✓ Use Quality Fluids: These engines prefer Dex-Cool coolant. Ensure your coolant flow is unobstructed by flushing the system every 50,000 miles.
- ✓ Check the PCV System: The Positive Crankcase Ventilation system is often overlooked. If the valve or hose (shown on the driver-side valve cover in your diagram) is clogged, it can lead to excessive oil consumption.
- ✓ Inspect the Harmonic Balancer: The main pulley on the crankshaft can wobble over time. Check its alignment with the rest of the accessory belt drive to prevent belt shredding.
- ✓ Stick to Torque Specs: Aluminum components like the cylinder heads and intake manifold can warp or crack if over-tightened. Always use a calibrated torque wrench.
In conclusion, understanding the 5.3 vortec engine parts diagram is the first step toward successful ownership and maintenance of one of the most popular engines ever built. By learning the locations of the ECU sensors, the path of the coolant flow, and the intricacies of the timing chain and accessory belt, you empower yourself to handle repairs with confidence. Whether you are clearing a check engine light via an OBD-II scanner or performing a weekend water pump replacement, let the diagram be your definitive guide to automotive success.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the 5.3 Vortec Engine Parts Diagram: Identification And Repair
Identify the main engine orientation and the primary component groups, such as the cylinder heads and intake.
Locate the specific sensor or mechanical part using the numbered legend corresponding to your diagnostic code.
Understand how the electrical wiring harnesses connect various sensors back to the central ECU.
Connect the diagram’s visual layout to the physical engine bay to verify component accessibility and tools needed.
Verify that every bolt follows the specific torque spec listed in the diagram to prevent leaks.
Complete the repair and use an OBD-II tool to clear the check engine light after installation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 5.3 Vortec engine parts diagram?
A 5.3 Vortec engine parts diagram is a visual schematic illustrating the layout of the General Motors 5.3L small-block V8. It highlights critical assemblies like the intake, block, and rotating assembly. It is indispensable for mechanics trying to identify specific part locations or routing during major engine overhauls.
How do you read 5.3 Vortec engine parts diagram?
To read the diagram, start with the main block as the central reference point. Follow the numbered callouts to the legend, which identifies each component. Distinguish between external bolt-ons, like the alternator, and internal parts. Pay attention to labels for sensors and electrical connectors wired directly to the ECU.
What are the parts of 5.3 Vortec engine?
Major parts include the cast-iron or aluminum block, cylinder heads, intake manifold, and rotating assembly. Vital electronic components include the ECU, fuel injectors, and ignition coils. Maintenance-heavy parts like the water pump, serpentine belt, and various sensors are also clearly labeled to assist in troubleshooting and routine repairs.
Why is the ECU important?
The ECU, or Engine Control Unit, acts as the brain of the 5.3 Vortec. It processes data from various sensors to manage fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions. When it detects a malfunction, it stores a diagnostic code and illuminates the check engine light to notify the driver immediately.
What is the difference between iron and aluminum blocks?
The primary difference is weight and durability. Iron blocks, common in older Silverado trucks, offer extreme strength for towing. Aluminum blocks, found in SUVs like the Tahoe, are lighter and improve fuel efficiency. Both share identical component layouts in most diagrams, making the parts identification process very similar.
How do I use 5.3 Vortec engine parts diagram?
Use the diagram to visually confirm part placement before starting a repair. It helps you locate sensors for testing with an OBD-II scanner when troubleshooting. Additionally, the diagram serves as a reference for reassembly, ensuring every gasket, bolt, and electrical connector is returned to its factory-specified location correctly.