48v Club Car Wiring Diagram 48 Volt: Troubleshooting Guide
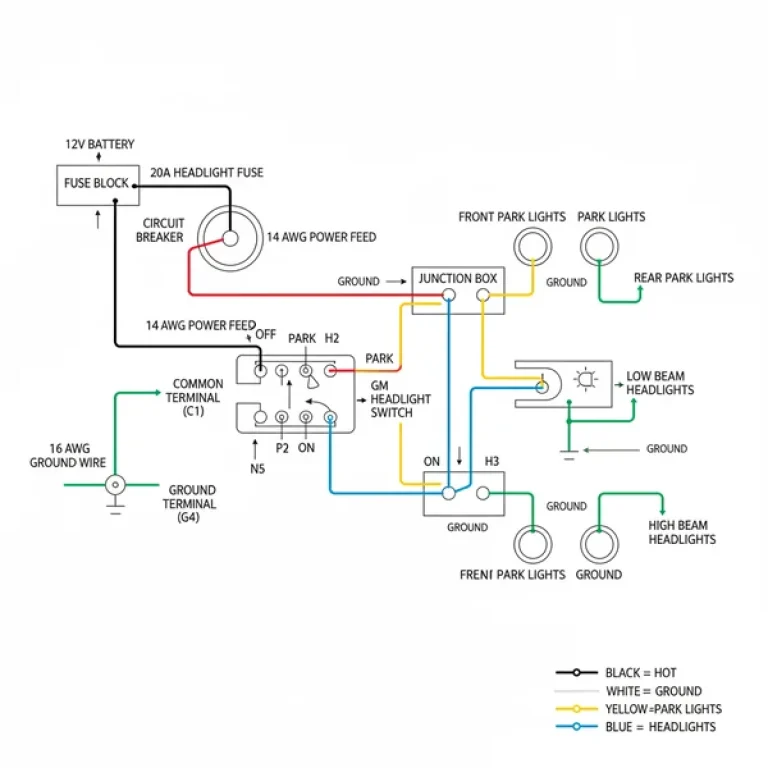
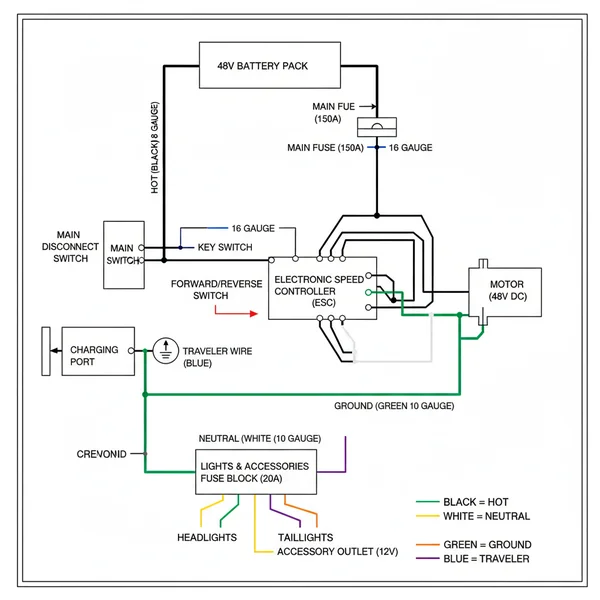
A 48v Club Car wiring diagram illustrates the series connection of your battery pack, tracing current from the hot wire through the solenoid to the motor. Identifying the common terminal and traveler wire ensures proper switch operation, while the ground wire maintains system safety and electrical stability across the chassis.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Map the electrical flow from batteries to the drive motor
- The solenoid is the most critical switching component to identify
- Always disconnect the main battery pack before touching any wires
- Use color-coding to distinguish traveler wires from main power leads
- Reference this diagram for battery replacement or controller upgrades
Maintaining a golf cart requires more than just checking the tire pressure; it demands a clear understanding of the electrical heartbeat under the seat. Whether you are troubleshooting a sudden loss of power or upgrading your vehicle for better hill-climbing torque, having a reliable 48v club car wiring diagram 48 volt is the most critical tool in your arsenal. These diagrams serve as a visual map, guiding you through the intricate network of batteries, controllers, and motors that define the modern electric vehicle. By following the correct schematics, you can ensure your cart operates safely, efficiently, and at peak performance. In this guide, you will learn how to identify every major component, trace current paths, and perform repairs like a professional technician.
Most Club Car 48-volt systems utilize either six 8-volt batteries or four 12-volt batteries connected in a series circuit to achieve the total required voltage. Always verify your battery configuration before consulting a specific wiring diagram.
Understanding the 48V Club Car Wiring Diagram Components
A comprehensive 48v club car wiring diagram 48 volt is more than just a series of lines; it is a representation of how high-amperage energy is converted into mechanical motion. The diagram typically begins at the battery bank, which acts as the primary reservoir of energy. In a standard 48V configuration, you will see the batteries linked in series. This means the positive terminal of one battery is connected to the negative terminal of the next, effectively stacking the voltage until the final 48V output is reached at the main positive and negative leads.
The diagram then branches out to several high-current components. The most prominent is the motor controller, often referred to as the “brain” of the cart. This device regulates the amount of voltage sent to the motor based on input from the accelerator pedal. You will notice large-gauge wires—usually 6-gauge or 4-gauge—connecting the controller to the solenoid and the motor. The solenoid acts as a heavy-duty relay, clicking into place to bridge the high-power circuit when you turn the key and press the pedal.
Another vital element in the diagram is the Forward/Reverse (FNR) switch. Depending on whether your cart is a “Series” or “Regen/IQ” model, the wiring at this switch will vary significantly. Series models use a mechanical lever that physically swaps heavy-gauge cables to reverse the polarity of the motor. IQ or Excel models use a smaller electronic rocker switch that sends a low-voltage signal to the controller, which then handles the direction change internally. The diagram will also illustrate the On-Board Computer (OBC), which monitors the flow of electricity during both use and charging to ensure the battery health is maintained.
Step-By-Step Guide to Reading and Implementing the Wiring

Interpreting a 48v club car wiring diagram 48 volt requires a methodical approach. Before you begin any physical work, you must gather the necessary tools: a high-quality digital multimeter, a set of insulated wrenches, a wire stripping tool, and replacement terminal ends.
Always flip the “Tow/Run” switch to the “Tow” position before touching any wiring. This de-energizes the controller and prevents accidental surges that can fry expensive electronic components.
- 1. Identify the Main Power Source: Start at the battery pack. Locate the main positive terminal (the one not connected to another battery) and the main ground wire or negative terminal. This is where your circuit begins and ends.
- 2. Trace the Solenoid Circuit: Follow the hot wire from the main battery positive to the large brass screw terminal on the solenoid. This is the primary entry point for high-voltage power.
- 3. Map the Controller Inputs: From the other large terminal on the solenoid, the wire usually proceeds to the B+ terminal on the controller. The diagram will show several smaller wires (often 16 or 18 gauge) entering a multi-pin connector on the controller; these are the signal wires for the throttle and key switch.
- 4. Locate the Traveler Wire for Accessories: If you are installing lights or a 3-way switch, you may encounter a traveler wire. While more common in home AC wiring, some specialized golf cart light kits use this logic. Ensure the traveler wire connects to the common terminal of the switch to allow multi-point control of the lighting system.
- 5. Verify Grounding: Identify the main ground wire path. Unlike a car, golf carts often do not use the chassis as a ground because it can cause corrosion. Instead, follow the dedicated negative cable back to the B- terminal on the controller or through the OBC.
- 6. Connect the Motor Leads: Finally, trace the wires from the controller (usually labeled A1, A2, S1, S2) to the motor. These wires must be the thickest gauge available to prevent heat buildup during acceleration.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting with the Diagram

When a Club Car fails to move, the wiring diagram becomes your diagnostic roadmap. One of the most frequent problems is a “clicked but no go” scenario. In this case, you use the diagram to identify the solenoid terminals. By testing the voltage at the hot wire side versus the output side, you can determine if the internal brass screw contact has failed. If the voltage does not transfer across the solenoid when activated, the component is faulty.
Another common issue involves “dead” batteries that are actually just victims of a loose ground wire or a failed neutral wire equivalent in the charging circuit. If the cart won’t charge, refer to the OBC section of your 48v club car wiring diagram 48 volt. Check the thin sensing wire that runs from the charger receptacle to the OBC; if this circuit is broken, the charger will never receive the signal to turn on.
If you see blue or white powder on your terminals, that is corrosion. It increases resistance and can mimic a wiring failure. Clean all terminals with a mixture of baking soda and water before replacing any components.
Persistent issues with speed or “shuddering” often point toward the MCOR (Motor Controller Output Regulator). The diagram will show the MCOR’s connection to the controller. Use your multimeter to check the resistance across these wires as you depress the pedal; a jumpy reading indicates a failing sensor rather than a wiring break.
Tips & Best Practices for 48V Systems
To maintain a healthy 48-volt system, wiring integrity is paramount. Always prioritize the gauge of your wires. For a standard cart, 6-gauge wire is sufficient, but if you have upgraded your controller for more speed or use the cart for heavy towing, upgrading to 4-gauge or even 2-gauge wiring will significantly reduce heat and improve the lifespan of your electronic components. High-quality copper cables with tinned ends offer the best resistance against the moisture often found in golf cart environments.
- ✓ Use Heat Shrink: Every time you replace a terminal, use marine-grade heat shrink with adhesive lining to seal the connection against oxygen and moisture.
- ✓ Torque Matters: Ensure every nut on a battery post or solenoid brass screw is torqued correctly. Loose connections create heat, which can melt battery posts or destroy controllers.
- ✓ Color Coding: Stick to standard color coding. Use red for hot wires and black for ground wires to avoid confusion during future repairs.
- ✓ Voltage Reducers: If you are adding 12V accessories like radios or LED bars, do not tap into just two batteries in the series. This creates an imbalance. Instead, use a 48V-to-12V voltage reducer as indicated in advanced wiring diagrams.
Regularly inspecting your wiring against the 48v club car wiring diagram 48 volt ensures that small vibrations haven’t rubbed the insulation off a wire, which could lead to a short circuit. By treating your wiring as a vital system rather than an afterthought, you extend the life of your batteries and ensure that your Club Car remains reliable for years to come. Remember, when in doubt, consult the diagram; it is the most accurate representation of how your vehicle was engineered to function. Understanding the relationship between the traveler wire, common terminal, and main power leads will empower you to handle almost any electrical challenge your golf cart presents.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the 48V Club Car Wiring Diagram 48 Volt: Troubleshooting Guide
Identify the main battery pack configuration and the primary positive terminal.
Locate the solenoid and verify the connection of the heavy-gauge hot wire.
Understand how the traveler wire links the forward/reverse switch to the controller.
Connect the ground wire from the negative terminal to the frame or motor.
Verify that each common terminal is securely tightened and free of corrosion.
Complete the circuit by checking the neutral wire path back to the battery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 48v club car wiring diagram 48 volt?
This diagram is a visual schematic representing the electrical system of a 48-volt Club Car golf cart. It details battery configurations, motor connections, and the paths of the hot wire and ground wire. It is essential for diagnosing power issues or installing new electrical accessories correctly without damaging components.
How do you read 48v club car wiring diagram 48 volt?
Start at the battery pack, following the main positive hot wire to the solenoid and controller. Look for lines representing the traveler wire between switches. Identify the neutral wire or common terminal connections to understand how current returns, ensuring you follow the flow from high to low potential points.
What are the parts of 48v club car wiring?
The system includes a battery pack, a solenoid for switching, an electronic speed controller, and the electric motor. It also features a forward/reverse switch, various fuses, and specific wiring like the traveler wire for multi-switch circuits and the essential ground wire for grounding the chassis or specific electronic components.
Why is common terminal important?
The common terminal serves as the shared connection point for multiple electrical paths within a switch or relay. In a 48v Club Car, it ensures that the controller receives the correct signal regardless of the switch position, allowing for seamless transition between forward, neutral, and reverse operations during vehicle use.
What is the difference between hot wire and traveler wire?
The hot wire carries the main 48V current from the power source to the components. In contrast, a traveler wire is used within the switching circuit, such as the forward/reverse assembly, to pass signals between different contact points, enabling precise control over the direction of the motor’s rotation and speed.
How do I use 48v club car wiring diagram 48 volt?
Use the diagram to verify that every connection matches the manufacturer’s specifications. Identify the location of the neutral wire and ground wire to prevent short circuits. It acts as a roadmap for testing voltage at specific points, helping you pinpoint failed components like solenoids or burnt-out motor speed controllers.