48 Volt Golf Cart Wiring Diagram: Battery & Motor Setup
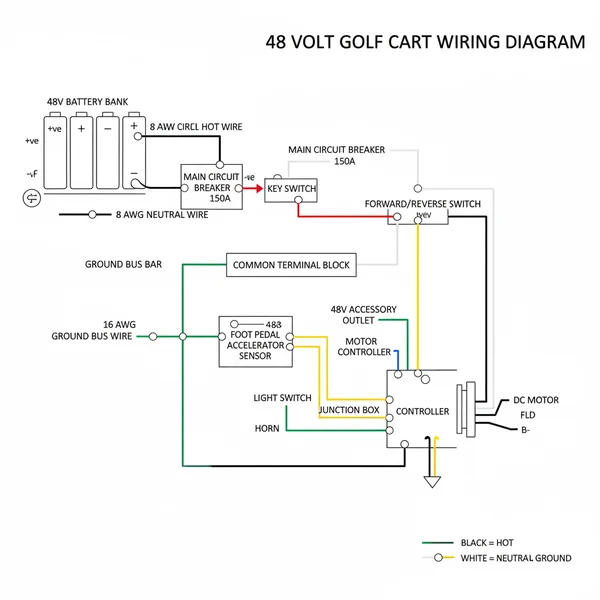
A 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram illustrates the series connection of six 8-volt or eight 6-volt batteries to generate high voltage. It maps the path from the main hot wire through the controller and motor, ensuring current returns via the ground wire. This schematic is essential for troubleshooting electrical issues or upgrading components.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides a visual map for connecting multiple batteries in a series configuration to reach 48V.
- Identify the main solenoid as the primary switching point for the high-voltage circuit.
- Ensure all connections are tight and corrosion-free to prevent high resistance and heat.
- Use the diagram to trace power from the ignition switch to the motor controller.
- Refer to this schematic when installing accessories or replacing the battery pack.
Maintaining or upgrading a high-voltage electric vehicle requires a clear understanding of its internal electrical architecture. If you are a DIY enthusiast or a golf cart owner, having access to a reliable 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram is the first step toward a successful repair or performance enhancement. This technical illustration serves as a blueprint, showing you exactly how the battery bank, motor, controller, and solenoid interact to move your vehicle. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the wiring paths, terminal connections, and safety protocols necessary to manage your golf cart’s power system effectively.
Most 48V systems utilize either six 8-volt batteries or eight 6-volt batteries connected in series. Always confirm your battery voltage before following a specific wiring schematic to prevent equipment damage.
Understanding the 48 Volt Golf Cart Wiring Diagram
The primary purpose of a 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram is to map the flow of electricity from the energy source to the drivetrain. In a standard setup, the “Main Positive” and “Main Negative” are the two most critical points. The diagram illustrates how individual batteries are linked in a series configuration to achieve the total required 48-volt output. For instance, in a series circuit, the positive terminal of one battery connects to the negative terminal of the next. This cumulative effect boosts the total voltage while keeping the amperage capacity the same as a single battery.
Beyond the battery bank, the diagram highlights the relationship between the speed controller and the solenoid. The solenoid acts as a heavy-duty relay, while the controller manages the amount of current sent to the motor based on pedal input. You will often see labels for specific terminals, such as the common terminal on the controller or the brass screw contacts on the solenoid. Color-coding is frequently used to distinguish between high-current power cables and low-current signal wires. For example, thick black or red cables usually represent the main power loop, whereas thinner wires may indicate the “traveler wire” pathways used in the Forward/Reverse switch or the key switch circuit.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: 48V Golf Cart Battery Series & Controller Schematic]
Diagram showing 6x8V batteries in series, connecting to a Solenoid, Motor Controller, and Motor (A1, A2, S1, S2 terminals).
In various models, such as those from Club Car, EZGO, or Yamaha, the specific routing might differ, but the core physics remain constant. You might encounter variations in how the ground wire is routed; some systems use a chassis ground, while most modern electric carts utilize a dedicated negative return to the battery bank to avoid frame electrolysis. Understanding these nuances through a visual diagram prevents “crossed wires” that could lead to a short circuit or controller failure.
Step-by-Step Guide to Interpreting and Installing Wiring

Reading a 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram can feel overwhelming at first, but following a logical sequence makes the process manageable. Whether you are replacing old cables or installing a new controller, use these steps to ensure accuracy.
-
✓ Step 1: Gather the Correct Tools and Materials
Before touching the electrical system, ensure you have a digital multimeter to verify voltage levels. You will need a set of insulated wrenches, terminal cleaning brushes, and high-quality cables of the correct gauge. For 48V systems, 4 AWG is standard, but 2 AWG is preferred for high-torque applications. -
✓ Step 2: Identify the Battery Configuration
Locate the “Main Positive” battery (where the cable goes to the solenoid) and the “Main Negative” battery (where the cable goes to the controller or charger port). Use the diagram to verify that the jumper wires between batteries are correctly alternating from positive to negative terminals. -
✓ Step 3: Wire the Solenoid and Controller
The solenoid usually has two large brass screw terminals and two smaller terminals. The diagram will show the hot wire from the battery bank connecting to one large terminal. The other large terminal connects to the controller’s “B+” post. Ensure the common terminal connections for the activation circuit are secure. -
✓ Step 4: Route the Motor Leads
The motor typically has four terminals labeled A1, A2, S1, and S2 (or F1, F2). Refer specifically to your 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram for your motor type (Series vs. Shunt/Sepex), as swapping these can cause the motor to spin backward or not at all. -
✓ Step 5: Install the Forward/Reverse (F/R) Switch
The F/R switch often utilizes a traveler wire to signal the controller which direction to send the current. Ensure the signal wires are not pinched and follow the diagram’s color codes to avoid reversing the pedal logic. -
✓ Step 6: Connect Accessory Wiring
If you are adding lights or a GPS, do not tap directly into a single 8V battery. Use a 48V-to-12V voltage reducer. The “hot wire” for the reducer should come from the main pack positive, and the neutral wire equivalent (the negative return) should go to the main pack negative.
Always switch the golf cart to “Tow” mode (if applicable) and disconnect the main negative cable before performing any work. 48 volts is enough to cause significant arcing and severe burns if a tool shorts across the terminals.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting with the Wiring Diagram

Even with a perfect installation, electrical components can fail over time. The most frequent problem users encounter is a “no-go” situation where the cart has full voltage but won’t move. In this case, the diagram helps you trace the signal path. You can use your multimeter to check if the “hot” signal is reaching the solenoid when the pedal is pressed. If the solenoid clicks but the cart doesn’t move, the 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram points you toward the high-amp cables or the controller output.
Another common issue is localized heat. If you notice a brass screw terminal on the solenoid or a battery post is melting, it indicates a loose connection or an undersized wire gauge. Resistance creates heat, and heat increases resistance, leading to a dangerous cycle. Use the diagram to ensure you haven’t accidentally bypassed a fuse or a circuit breaker. If you see smoke or smell ozone, immediately disconnect the main battery leads and seek professional help, as this indicates a direct short in the controller or motor windings.
Use a thin coat of dielectric grease or terminal protector spray on all brass and copper connections. This prevents the “white powder” corrosion that commonly disrupts the ground wire path in high-humidity environments.
Tips & Best Practices for 48V Systems
To maximize the lifespan of your wiring and batteries, consistency is key. Always use high-quality, fine-strand copper cables. While a standard neutral wire in a home might be solid core, golf carts require flexible, multi-strand cables to handle the vibrations of off-road or turf travel. When tightening nuts onto battery posts, use a torque wrench to meet the manufacturer’s specifications—over-tightening can strip the lead threads, while under-tightening causes the arcing issues mentioned earlier.
Regular maintenance should include a visual inspection of the entire wiring harness. Look for frayed insulation or wires that are rubbing against the frame. Ensure that your traveler wire connections to the micro-switches are tight and free of debris. If you are upgrading your motor or controller for more speed, you must also upgrade your wire gauge. Moving from 6 AWG to 2 AWG can significantly reduce “voltage sag,” giving your cart more punch during acceleration and climbing hills.
- ✓ Label Your Wires: Use heat-shrink labels to identify “Main Pos,” “Motor A1,” etc., for future troubleshooting.
- ✓ Avoid Mixed Batteries: Never mix brands, ages, or capacities in a 48V series string.
- ✓ Clean Terminals: A mixture of baking soda and water neutralizes acid and keeps the common terminal points clean.
In conclusion, mastering your 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram is the best way to ensure the longevity and safety of your vehicle. By understanding how the current flows from the batteries through the solenoid and controller to the motor, you gain the confidence to perform your own maintenance and upgrades. Keep your connections tight, your gauge appropriate for the load, and always prioritize safety when working with high DC voltages.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram?
It is a technical schematic showing how batteries, the motor, and the controller connect to power the vehicle. It details how the traveler wire facilitates communication between switches and how the hot wire delivers power from the battery bank to the main solenoid for distribution throughout the system.
How do you read 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram?
Start at the first battery’s positive terminal and follow the lines to the motor and controller. Identify symbols for switches and fuses. Notice how the ground wire completes the circuit back to the negative terminal, ensuring a continuous loop for electrical current to flow safely.
What are the parts of 48 volt golf cart?
Key parts include the battery bank, motor, speed controller, and solenoid. The common terminal on the ignition switch directs power to various accessories. Additionally, the charging port, forward/reverse switch, and heavy-gauge cables are vital components that must be wired correctly to ensure reliable performance.
Why is ground wire important?
The ground wire provides a safe return path for electrical current to the battery source. In a golf cart’s DC system, proper grounding prevents short circuits and protects sensitive electronic components, like the speed controller, from being damaged by voltage spikes or improper current flow.
What is the difference between traveler wire and common terminal?
A traveler wire is typically used in multi-way switch configurations to toggle power between points. In contrast, the common terminal serves as the main entry or exit point for current within a switch, acting as the bridge that connects the power source to the intended output circuit.
How do I use 48 volt golf cart wiring diagram?
Use the diagram to verify that your batteries are connected in series rather than parallel. Identify the neutral wire equivalents in charging circuits to ensure safety. It helps you pinpoint where a connection might be broken, allowing you to test specific wires with a digital multimeter accurately.