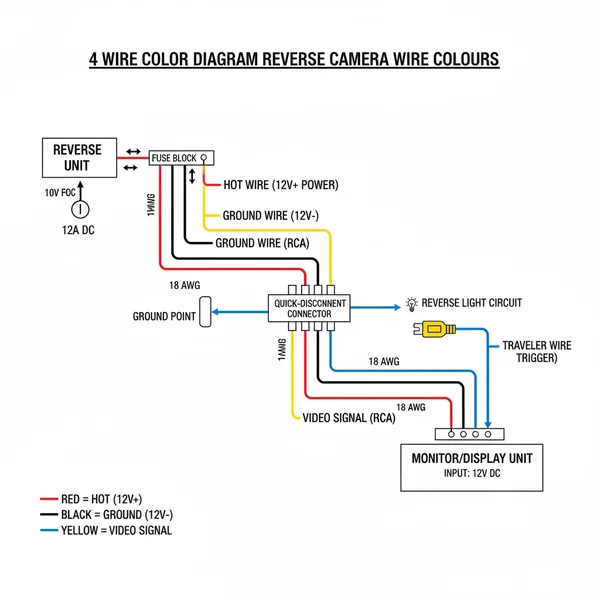
4 Wire Color Diagram Reverse Camera Wire Colours: Setup Guide
A standard 4-wire reverse camera uses Red for the 12V hot wire, Black for the ground wire, Yellow for video, and White or Green for the trigger signal. This configuration ensures the camera receives power from the reverse light circuit and transmits a clear video feed to the dashboard monitor.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Primary colors include red for power and black for ground
- The hot wire must connect to the 12V reverse light circuit
- Always use a multimeter to verify current before splicing
- The trigger wire acts as a signal path for the monitor
- Use this diagram when installing aftermarket backup cameras
Installing a backup system in your vehicle is one of the most effective ways to improve safety and visibility, yet the process often stalls when you are faced with a bundle of mysterious cables. Understanding the 4 wire color diagram reverse camera wire colours is the most critical step in ensuring your monitor displays a crisp, clear image the moment you shift into reverse. Having the correct diagram prevents blown fuses, damaged image sensors, and the frustration of a “no signal” screen. In this comprehensive guide, you will learn the standard functions of each color-coded wire, how to measure voltage correctly, and the best practices for integrating these components into your vehicle’s existing electrical system for a professional-grade installation.
Decoding the 4 Wire Color Diagram and Component Functions
When you unbox a standard 4-wire reverse camera, the wiring harness typically consists of four distinct colors: Red, Black, Yellow, and White (or sometimes Green). Each of these serves a specific role in delivering power and transmitting data. Understanding these roles is much like understanding a household light switch; while you won’t find a brass screw or a traveler wire in a DC automotive circuit, the logic of completing a circuit remains the same.
In a standard 4 wire color diagram reverse camera wire colours setup, the Red wire is your primary power lead, often referred to as the hot wire in electrical terms. This wire must be connected to a 12V power source that is energized when the vehicle is in reverse. The Black wire is the ground wire, which completes the circuit by connecting to the vehicle’s metal chassis. The Yellow wire is almost universally reserved for the Video Signal, carrying the visual data from the camera lens to the dashboard monitor. Finally, the White wire usually functions as the “Trigger” or “Reverse Signal” wire, which tells the monitor to automatically switch its display to the camera feed.
[ RED ] ——–> (+) 12V Reverse Light Power (Hot Wire)
[ BLACK ] ——> (-) Chassis Ground (Ground Wire)
[ YELLOW ] —–> (V) Video Output (RCA Center Pin)
[ WHITE ] ——> (T) Trigger / Reverse Sense Wire
*Note: Video Ground is often shared with Black wire.
DIAGRAM: Standard DC 4-Wire Configuration for Backup Cameras
It is important to note that variations exist. Some high-definition (AHD) cameras might use different internal shielding, but the core 4-wire logic remains consistent across 90% of aftermarket kits. While residential wiring uses a neutral wire to return current to the source, automotive systems use the entire metal frame of the car as the return path, which is why a solid connection for your ground wire is so vital for video clarity.
Unlike AC home electrical systems that use a common terminal for multiple connections, automotive DC systems require dedicated, isolated paths for video signals to prevent electromagnetic interference from the vehicle’s alternator and ignition system.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide

Properly implementing the 4 wire color diagram reverse camera wire colours requires a methodical approach. Follow these steps to ensure a clean installation.
1. Prepare Your Tools and Workspace
Before starting, gather a digital multimeter, wire strippers, electrical tape, zip ties, and a soldering iron or high-quality crimp connectors. Ensure you have the correct gauge of wire if you need to extend any leads; typically, 18 to 22 gauge is sufficient for the low current draw of a camera.
2. Identify the Reverse Light Power
Locate the wiring harness leading to your vehicle’s reverse lights. Use your multimeter to find the hot wire. Have an assistant put the car in reverse (with the parking brake engaged and engine off) and check for 12V voltage. Once identified, this is where your Red camera wire will connect.
3. Establish a Solid Ground
Find a clean, unpainted bolt on the vehicle’s chassis to serve as your ground point. In home wiring, you might see a brass screw on a receptacle for this purpose; in a car, a ring terminal secured to a chassis bolt is the equivalent. Connect the Black ground wire here.
4. Route the Video Cable
Run the Yellow video cable from the back of the vehicle to the dashboard. Avoid routing it near high-voltage components or large wire bundles to prevent “noise” or static in the video feed. This cable acts as the primary data traveler wire for your visual information.
5. Connect the Trigger Wire
The White wire must be connected to the “Reverse Indication” input on the back of your head unit or monitor. This signal tells the screen to stop displaying the radio or GPS and start showing the camera feed. Without this connection, you would have to manually switch the screen every time you back up.
6. Final Testing
Before reassembling your vehicle’s interior panels, start the engine and shift into reverse. Check for a clear image. If the image flickers, re-check your ground wire and ensure the voltage at the Red wire is a steady 12V-14V.
Never tap into a wire without testing it with a multimeter first. Modern vehicles use CAN bus systems where some wires carry sensitive data; tapping the wrong wire can cause computer errors or airbag deployment.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting

Even with a perfect 4 wire color diagram reverse camera wire colours map, problems can arise. The most frequent issue is a black screen or “No Signal” message. This is usually caused by a failure in the power circuit. If the camera isn’t receiving the proper voltage, the image sensor cannot boot up. Use a multimeter to verify that the Red hot wire is receiving at least 12V when the car is in reverse.
Another common problem is image distortion or “rolling lines” on the screen. This is often an indication of a poor ground wire connection. In DC electronics, the ground is just as important as the power. If the connection is loose or touching a painted surface, the circuit will be inefficient. Additionally, check for interference. If you have routed your video cable too close to the vehicle’s fuel pump or ignition coils, electromagnetic interference can degrade the signal.
Lastly, if the camera works but doesn’t turn on automatically, the White trigger wire is likely disconnected or tapped into the wrong source. This wire functions similarly to a common terminal in a multi-way switch; it needs to see a state change (from 0V to 12V) to trigger the monitor’s logic.
Tips & Best Practices for a Long-Lasting Setup
To ensure your reverse camera survives the elements and provides years of service, follow these professional tips:
- ✓ Use Heat-Shrink Tubing: Avoid using only electrical tape for exterior connections. Heat-shrink tubing provides a waterproof seal that prevents corrosion of the copper strands.
- ✓ Verify Wire Gauge: Use the appropriate gauge for extensions. Using wire that is too thin can cause a voltage drop over long distances, resulting in a dim or flickering image.
- ✓ Solder Your Connections: While crimp connectors are convenient, soldering your connections ensures they won’t vibrate loose over time, which is a common cause of intermittent camera failure.
- ✓ Add an Inline Fuse: For extra safety, place a small 3-amp or 5-amp inline fuse on the Red power wire. This protects your vehicle’s factory wiring in case the camera ever shorts out.
If your vehicle has a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal on the reverse lights—common in many European cars—your camera might flicker when the engine is running. To fix this, use a 12V relay to provide clean power directly from the battery, using the reverse light wire only as a trigger for the relay coil.
Mastering the 4 wire color diagram reverse camera wire colours allows you to take full control of your vehicle’s safety upgrades. By correctly identifying the hot wire, securing a reliable ground wire, and ensuring the video signal is shielded from interference, you can achieve a factory-quality installation. Remember that while car electronics share some conceptual DNA with home wiring—such as the need for completed circuits and proper voltage—the automotive environment requires extra attention to vibration and moisture protection. With these steps and tips, your new reverse camera will provide a clear view of the road behind you for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 4 wire color diagram reverse camera wire colours?
A 4 wire color diagram reverse camera wire colours guide illustrates how to connect the video signal, power, and ground leads. This diagram is essential for integrating an aftermarket camera with your car’s head unit, ensuring that the 12V hot wire correctly powers the lens while the ground wire completes the circuit.
How do you read 4 wire color diagram reverse camera wire colours?
To read this wiring diagram, identify the power source, ground, and video signal paths. The red line represents the positive feed, similar to a hot wire in AC. The black line indicates the ground wire, while the yellow and white lines represent the video data and the reverse trigger signal lines.
What are the parts of 4 wire color diagram reverse camera wire colours?
The main parts include the camera unit, the RCA video connector, the 12V power input, and the trigger wire. In this setup, the red wire is the hot wire, the black is the ground wire, and the white wire functions like a traveler wire, sending a signal to flip the screen.
Why is ground wire important?
The ground wire is critical because it provides a safe path for electrical current to return to the vehicle’s chassis. Without a solid ground connection, the camera may experience signal interference, flickers, or complete power failure. It acts as the DC equivalent to a neutral wire to complete the circuit loop.
What is the difference between traveler wire and trigger wires?
While a traveler wire is used in 3-way AC light switches, the reverse camera trigger wire serves a similar purpose by carrying a signal between two points. It notifies the head unit to switch the display to the camera view immediately when the driver shifts the vehicle into reverse gear.
How do I use 4 wire color diagram reverse camera wire colours?
Use this diagram to map out your cable routing from the rear bumper to the dashboard. Start by identifying your reverse light’s common terminal for power. Match the colors on your camera harness to the diagram to ensure the hot wire and ground wire are pinned in the correct locations.