4.6 L V8 4.6 Ford Engine Diagram: Repair and Identification
The Ford 4.6 L V8 engine diagram illustrates the layout of internal components, vacuum lines, and electrical sensors. It helps owners identify parts like the fuel injectors and ignition coils, which are essential for resolving a check engine light by mapping physical locations to specific diagnostic codes for more efficient troubleshooting.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Map out sensor locations and vacuum routing effectively.
- Identification of ignition coils and fuel injectors is critical.
- Always refer to a specific torque spec for all critical engine bolts.
- Use a multimeter to verify electrical connections shown in the layout.
- Use this diagram when diagnosing misfires or emission system failures.
Understanding the layout of a 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram is essential for anyone performing maintenance or complex repairs on this iconic powerplant. Whether you are driving a legendary Mustang, a rugged F-150, or a dependable Crown Victoria, the Ford Modular engine family requires precision and an accurate visual reference to ensure parts are replaced correctly. Having the right diagram prevents costly mistakes, such as improper accessory belt routing or misidentifying critical sensors. In this guide, you will learn how to navigate the engine’s architecture, identify critical components like the timing chain and ECU, and apply technical specifications for a successful DIY project.
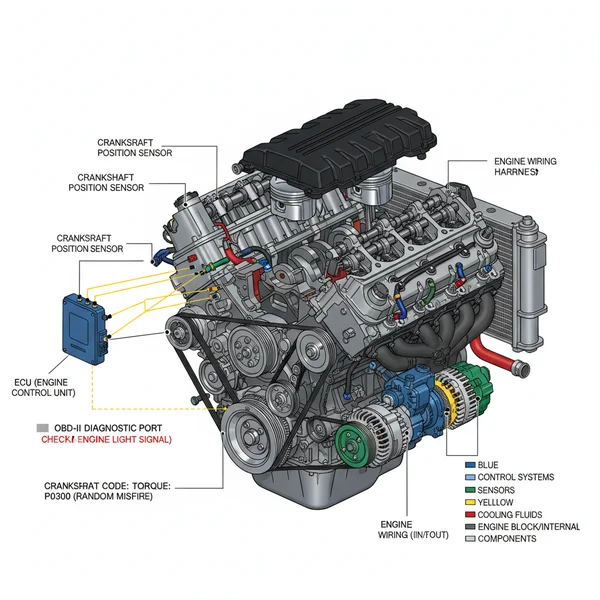
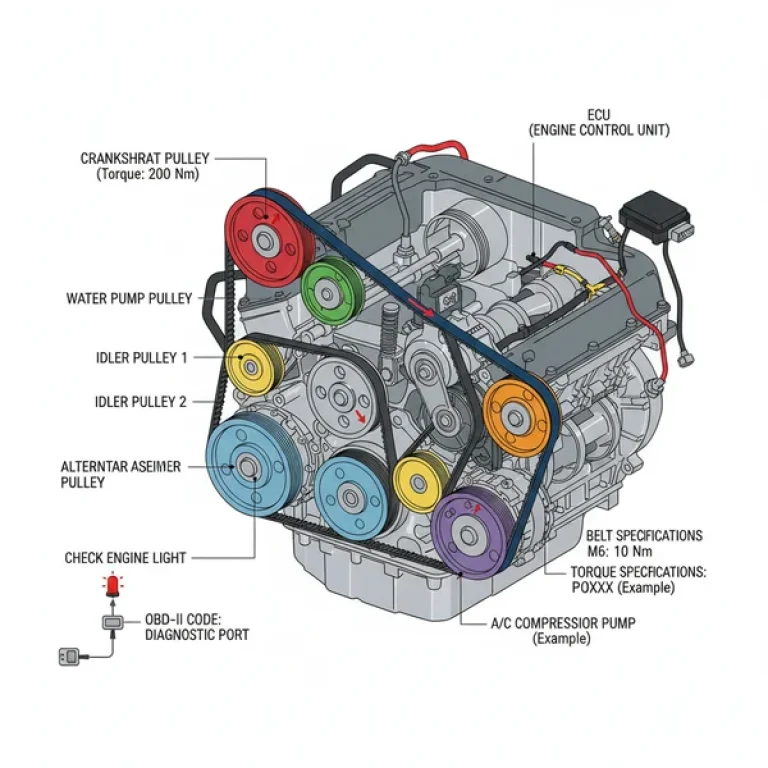
An engine diagram for the Ford 4.6L V8 serves as a roadmap for the mechanical and electronic landscape of the vehicle. These diagrams are typically categorized into several views: the front dress (accessory drive), the top-end (intake and fuel system), and the internal timing assembly. The front-end layout is dominated by the accessory belt, which winds around the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and the water pump. In most diagrams, the belt path is represented by a continuous looped line, showing exactly which side of the belt contacts each pulley.
Moving deeper into the engine’s anatomy, the timing chain diagram is perhaps the most critical for high-mileage engines. Unlike pushrod engines, the 4.6L Modular V8 uses an Overhead Cam (OHC) design, necessitating long, complex chains that synchronize the crankshaft with the camshafts. Visual breakdowns often use color-coding to highlight the timing marks on the chains and the corresponding dimples on the sprockets. This ensures the “timing” is perfect to prevent piston-to-valve contact.
The electronic side of the 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram focuses on the wiring harness and sensor locations. This includes the placement of the Electronic Control Unit (ECU), which acts as the brain of the engine, and the various sensors like the Mass Air Flow (MAF), Oxygen sensors, and Throttle Position Sensor (TPS). These diagrams are indispensable when you are chasing an elusive diagnostic code or trying to figure out why a specific component isn’t receiving power.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: A technical blueprint of a 4.6L V8 engine showing the accessory belt routing, intake manifold layout, spark plug locations, and timing chain configuration.]
The Ford 4.6L V8 was produced in 2-valve, 3-valve, and 4-valve configurations. While the block remains similar, the cylinder heads and intake manifolds vary significantly, so always ensure your diagram matches your specific valve count.
To effectively use a 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram for a repair or inspection, follow these systematic steps:
- 1. Identify the Specific Engine Variant: Before starting, check your VIN or the sticker on the valve cover. The 4.6L comes in “Romeo” and “Windsor” versions. While they look similar, they have different bolt patterns for the flywheel and different valve cover bolt counts.
- 2. Locate the OBD-II Port: For any modern diagnostic work, start by plugging a scanner into the OBD-II port (usually under the dashboard). If you have a check engine light, the scanner will provide a diagnostic code that corresponds to a specific system on your engine diagram.
- 3. Map the Accessory Belt Path: If you are replacing the alternator or water pump, use the diagram to note the tensioner’s position. Use a long-handled breaker bar to release tension and carefully slide the belt off. Referring to the diagram during reinstallation is the only way to ensure the water pump rotates in the correct direction.
- 4. Trace the Coolant Flow: Locate the thermostat housing and the heater core hoses on your diagram. This is vital when flushing the system or diagnosing an overheating issue. The 4.6L often develops leaks at the plastic intake manifold crossover, which is easily identified on a top-down diagram.
- 5. Verify the Firing Order: When replacing spark plugs or ignition coils (COP system), refer to the diagram for the correct cylinder numbering and firing order (1-3-7-2-6-5-4-8). Mixing these up will cause a severe misfire.
- 6. Locate the ECU and Main Harness: If you are dealing with electrical gremlins, find the ECU on your diagram. Usually located near the firewall or passenger kick panel, the diagram will help you identify which wire bundles lead to the fuel injectors versus the ignition system.
- 7. Reference Torque Specs: Every bolt on this engine, from the intake manifold to the cylinder head bolts, has a specific torque spec. Use your diagram to identify the bolt sequence (the order in which they must be tightened) to prevent warping components.
- 8. Inspect the Timing Chain Guides: If you hear a rattling sound from the front of the engine, consult the timing diagram. You will need to remove the front timing cover to see if the plastic guides have shattered, which is a common maintenance item for high-mileage Ford V8s.
For these tasks, you will need a standard set of metric sockets (8mm to 19mm), a quality torque wrench, an OBD-II code reader, and possibly a fuel line disconnect tool. Safety is paramount; always disconnect the negative battery terminal before working on the electrical system or fuel rails to prevent sparks or accidental fuel sprays.
The 4.6L engine uses “torque-to-yield” (TTY) bolts for the cylinder heads. These are one-time-use bolts that stretch when tightened. Never reuse these bolts, as they can snap or fail to provide proper clamping force.
Even with a high-quality 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram, certain issues are frequent visitors for owners of this engine. One of the most notorious problems is the “Check Engine Light” caused by a misfire. Often, this is due to moisture getting into the spark plug wells or a failing Ignition Coil-on-Plug (COP). A diagnostic code like P0301 through P0308 will tell you exactly which cylinder is at fault.
Another common issue involves the intake manifold. Many 4.6L engines featured a composite (plastic) intake manifold that is prone to cracking near the front coolant crossover. If you see coolant pooling in the engine “V” or near the front fuel injectors, your diagram will help you identify the specific gaskets and bolts needed for a manifold replacement. Furthermore, listen for “timing chain slap.” If the tensioners lose hydraulic pressure or the guides wear down, the chain can rub against the metal cover. If left unaddressed, this can lead to catastrophic engine failure. If the noise persists even after an oil change, it is time to consult your timing diagram and prepare for a teardown.
To prevent the famous “blown spark plug” issue on early 2-valve 4.6L engines, always use a torque wrench to tighten spark plugs to 11-13 lb-ft. Never “hand tighten” based on feel alone, as the aluminum threads are very delicate.
Maintaining a 4.6L Ford V8 is rewarding because of the engine’s inherent durability. To keep it running smoothly, always prioritize high-quality synthetic oil. These engines rely on oil pressure to operate the timing chain tensioners; using the wrong viscosity or low-quality oil can lead to premature timing system wear.
When replacing parts, try to stick with OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) components, especially for sensors like the MAF or O2 sensors. The ECU in the 4.6L is finely tuned to the voltage signals of OEM sensors, and aftermarket “cheap” alternatives often trigger a check engine light or cause poor idle. For cost-saving, consider purchasing your parts online from reputable wholesalers, but verify the part numbers against your 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram to ensure compatibility.
Lastly, keep your cooling system in top shape. The 4.6L runs best when the coolant flow is unobstructed. Every 50,000 miles, perform a coolant flush and inspect the accessory belt for cracks or glazing. If the belt shows wear, replace it immediately, as a snapped belt will cause an instant loss of power steering, cooling, and charging. By following these best practices and keeping a detailed 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram handy, you can easily push these engines past the 200,000 or even 300,000-mile mark with basic DIY skills.
Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the 4.6 L V8 4.6 Ford Engine Diagram: Repair And Identification
Identify the specific engine generation (2V, 3V, or 4V) to ensure the diagram matches your vehicle’s configuration.
Locate the primary electrical connectors and sensors that feed data into the OBD-II diagnostic system.
Understand how the vacuum lines route through the intake manifold to prevent common idling and stalling problems.
Connect the diagram’s sensor locations to any active diagnostic code retrieved from your vehicle’s scanner tool.
Verify that all bolts are tightened to the manufacturer’s recommended torque spec during the reassembly process.
Complete the repair by clearing the error codes and performing a test drive to ensure the engine runs smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram?
A 4.6 L V8 4.6 Ford engine diagram is a visual map showing the placement of mechanical parts and electrical sensors within the modular engine. It provides a detailed view of the intake manifold, cylinder heads, and timing components, which is vital for performing complex repairs or simple maintenance tasks.
How do you read 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram?
To read the diagram, start by orienting yourself with the front of the engine where the belt drive sits. Follow the lines representing vacuum hoses or electrical harnesses. Use the legend to identify symbols for the ECU and various sensors to understand how signals flow through the entire system.
What are the parts of 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine?
Key parts of this engine include the cast iron or aluminum block, overhead camshafts, and the sophisticated fuel injection system. It also features a complex cooling system and various sensors that communicate with the OBD-II system to monitor performance, fuel efficiency, and emission levels during standard vehicle operation.
Why is ECU important?
The ECU is crucial because it acts as the brain of the 4.6 Ford engine, managing air-fuel ratios and ignition timing. It monitors sensor data to optimize performance and triggers a diagnostic code if a fault occurs, allowing the driver to address issues before they cause significant mechanical damage.
What is the difference between 2V and 3V 4.6 engines?
The primary difference between the 2V and 3V Ford 4.6 engines lies in the cylinder head design and valve count. The 2-valve version is simpler for maintenance, while the 3-valve version offers improved airflow and variable cam timing, requiring more precise attention to the specific torque spec during assembly.
How do I use 4.6 l v8 4.6 ford engine diagram?
Use the diagram as a reference guide when troubleshooting a persistent check engine light or replacing worn components. By matching the diagram to the physical engine bay, you can quickly locate hard-to-find sensors or trace vacuum leaks that might be causing performance drops or poor idling issues.