24v 5.9 Cummins Fuel Line Diagram: Routing & Troubleshooting
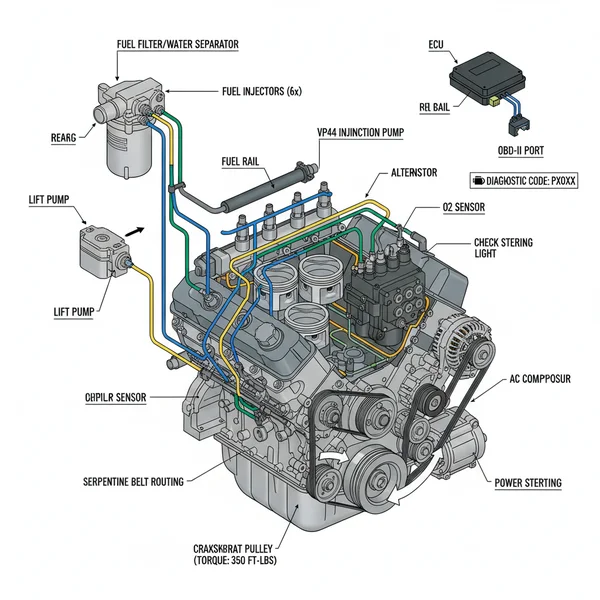
A 24v 5.9 Cummins fuel line diagram maps the path from the lift pump to the VP44 injection pump and high-pressure lines. It helps identify leak points, ensures correct torque spec application on fittings, and aids in diagnosing issues that trigger a check engine light or specific fuel-related diagnostic code.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Visualizes fuel flow from the tank to the fuel injectors.
- Identifying the VP44 injection pump and return line circuits.
- Maintaining prime and preventing air intrusion is critical for pump health.
- Use the diagram to trace supply vs. return lines during filter changes.
- Reference this when troubleshooting low fuel pressure or hard starting.
For owners of the second-generation Dodge Ram, understanding the 24v 5.9 cummins fuel line diagram is more than just a matter of curiosity; it is a vital part of maintaining one of the most legendary diesel engines ever produced. The transition from the mechanical P-pump of the 12-valve era to the electronically controlled Bosch VP44 injection pump on the 24-valve models introduced a new level of complexity to the fuel system. This article provides a comprehensive breakdown of the fuel delivery path, from the tank to the injectors, ensuring you can diagnose leaks, replace worn lines, or upgrade your system for better performance and reliability.
Detailed Breakdown of the 24v 5.9 Cummins Fuel System Components
The fuel system on the 24-valve 5.9L Cummins is divided into two primary sections: the low-pressure supply side and the high-pressure injection side. Navigating a 24v 5.9 cummins fuel line diagram requires identifying where these two systems meet and how the fuel returns to the tank to maintain cooling and lubrication.
The low-pressure side begins at the fuel tank. In the original factory configuration, a lift pump (either mounted on the side of the engine block or inside the fuel tank, depending on the specific manufacturing run) pulls fuel forward. This fuel travels through a 3/8-inch supply line toward the fuel filter housing. The filter housing is a critical junction point located near the intake manifold. Here, the fuel is cleaned and any water is separated before it enters the Bosch VP44 injection pump.
Once the fuel reaches the VP44, the engine’s ECU (Engine Control Unit) manages the timing and volume of the fuel delivery. The VP44 then pressurizes the fuel to several thousand PSI and distributes it through six individual stainless steel high-pressure lines. These lines are meticulously bent to ensure equal length, which is crucial for maintaining consistent injection timing across all cylinders. The fuel that isn’t injected into the cylinders—specifically the fuel used for cooling the pump and the excess from the injectors—is routed back to the tank through a return line manifold.
The diagram illustrates the flow from the tank (Blue) to the filter (Green), the high-pressure delivery (Red), and the return circuit (Yellow).
On these engines, the VP44 injection pump relies entirely on the fuel flow provided by the lift pump for both lubrication and cooling. If the supply pressure drops below 10 PSI, the injection pump can suffer internal damage, often leading to a “dead pedal” symptom.
Step-by-Step Guide to Interpreting and Installing Fuel Lines

Using a 24v 5.9 cummins fuel line diagram effectively requires a methodical approach to tracing the lines under the hood. Whether you are replacing a single leaking injector line or installing a complete aftermarket fuel system like a FASS or AirDog, follow these steps to ensure a successful installation.
Tools and Materials Needed
- ✓ 17mm and 19mm flare nut (crows foot) wrenches
- ✓ 3/4 inch open-ended wrench
- ✓ Clean, lint-free rags
- ✓ Replacement Viton O-rings for connector tubes
- ✓ Diesel fuel pressure gauge
Installation and Troubleshooting Steps
1. Safety First: Ensure the engine is cool and the battery is disconnected. Diesel fuel systems can hold residual pressure. Wear safety glasses to protect against high-pressure fuel spray.
2. Trace the Low-Pressure Supply: Start at the fuel filter housing. Identify the inlet line coming from the chassis. If you are upgrading your lines, this is where you will often replace the restrictive factory “banjo” bolts with high-flow fittings.
3. Inspect the VP44 Inlet: Follow the line from the filter housing to the side of the VP44 pump. This line is a common point for air leaks, which can cause hard starting.
4. Identify High-Pressure Lines: Look at the rear of the VP44. You will see six lines exiting in a circular pattern. These are numbered based on their firing order and cylinder position. Use the 24v 5.9 cummins fuel line diagram to ensure you are connecting the correct line to the corresponding injector port on the cylinder head.
5. Setting the Torque Spec: When tightening the high-pressure fuel lines, precision is key. The specific torque spec for the fuel line nuts at the injector is generally 28 ft-lbs. Over-tightening can crush the flare, while under-tightening leads to leaks.
6. Bleeding the Air: Once the lines are installed, you must bleed the air. Crack open the nuts on injectors 1, 3, and 4. Crank the engine in short bursts until fuel without air bubbles weeps from the nuts. Tighten them down and attempt to start the engine.
7. Verify ECU Communication: If the engine fails to start or stumbles, use an OBD-II scanner to check for any diagnostic code. Codes like P0216 often indicate that the timing in the VP44 is failing, often due to a lack of fuel pressure.
8. Final Inspection: Check for leaks around the fuel heater and the water-in-fuel sensor located on the filter housing. Also, ensure the lines are not rubbing against the accessory belt or the coolant flow hoses, as vibration can cause the lines to chafe over time.
Never use your hand to check for leaks while the engine is running. The high-pressure side of the 5.9 Cummins can produce enough pressure to inject diesel fuel directly through your skin, causing serious medical emergencies.
Common Fuel Line Issues & Troubleshooting

The most frequent problem encountered with the 24v 5.9 Cummins fuel system is air intrusion. Because the fuel system operates under vacuum in certain sections (before the lift pump), a small crack in a rubber hose or a loose fitting can pull air into the system without showing a visible fuel leak. This results in long cranking times or a “stumble” upon startup.
If your check engine light illuminates, always begin by checking the fuel pressure. A common diagnostic code for this platform is P0216 (Injection Timing Control Circuit Malfunction). While this often signals a failing VP44, it can also be triggered by severe fuel starvation caused by a clogged filter or a collapsed supply line.
Another area to watch is the front of the engine near the gear housing. While the Cummins uses a gear-driven system rather than a timing chain, the vibrations from the heavy-duty gears can cause the fuel line mounting brackets to vibrate loose. If these brackets fail, the high-pressure lines will eventually crack from harmonic resonance.
Pro Tips and Best Practices for Fuel System Longevity
To keep your 24v 5.9 Cummins running for hundreds of thousands of miles, maintenance of the fuel lines and associated components is non-negotiable.
Upgrade your factory banjo bolts to “high-flow” versions. The stock bolts have very small orifices that restrict fuel flow, especially when the engine is under load. High-flow bolts can increase the volume of fuel reaching the VP44, helping it stay cool.
1. Install a Fuel Pressure Gauge: This is the single most important modification for a 24v Cummins. Monitoring your pressure in real-time allows you to catch a lift pump failure before it destroys your expensive VP44 injection pump. Aim for a constant 15-18 PSI.
2. Use Quality Filters: Always use high-quality, 7-micron or 10-micron fuel filters. The tolerances inside the VP44 and the fuel injectors are incredibly tight. Even microscopic debris can cause internal wear or sticking injectors.
3. Address “Dead Head” Issues: If you notice your fuel lines vibrating excessively, check the plastic “blue” or “yellow” clips that hold the lines together. If these are missing, replace them immediately. These clips are designed to dampen the pulses sent through the lines by the injection pump.
4. Inspect for Corrosion: In regions where road salt is common, the steel fuel lines running along the frame rail are prone to rusting. Periodically inspect the lines from the tank to the engine. If you see pitting or heavy rust, consider replacing them with a stainless steel or nylon line kit to prevent a sudden breakdown.
By following the 24v 5.9 cummins fuel line diagram and adhering to these maintenance standards, you ensure that your engine receives the clean, high-pressure fuel it needs to deliver the torque and reliability the Cummins name is known for. Whether you are performing a stock repair or a high-performance upgrade, accuracy in your fuel line routing is the foundation of a healthy engine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 24v 5.9 Cummins fuel line diagram?
This diagram is a visual schematic illustrating the routing of fuel from the lift pump to the high-pressure lines. It details how diesel moves through the filter housing and injection pump. It is essential for mechanics diagnosing fuel delivery issues or identifying components like the return manifold and supply lines.
How do you read 24v 5.9 Cummins fuel line diagram?
Start by identifying the lift pump as the fuel source. Follow the supply lines toward the fuel filter housing and then to the VP44 pump. High-pressure lines lead to the injectors, while return lines head back to the tank. Arrows usually indicate the direction of fuel flow throughout the system.
What are the parts of 24v 5.9 Cummins fuel system?
The primary parts include the electric lift pump, fuel filter housing, VP44 injection pump, and six high-pressure fuel lines. Additionally, it contains a fuel return manifold, overflow valve, and banjo bolts. These components work together under ECU control to ensure precise fuel timing and delivery to the engine cylinders.
Why is torque spec important?
Using the correct torque spec on fuel line fittings and banjo bolts prevents leaks and avoids stripping delicate threads. Overtightening can crush seals or crack lines, while undertightening leads to air leaks. Precise torque ensures a high-pressure seal, which is vital for maintaining consistent rail pressure and engine performance.
What is the difference between supply and return lines?
Supply lines carry pressurized diesel from the tank toward the engine to provide power. Return lines carry excess fuel back to the tank to help cool the injection pump and lubricate the system. Distinguishing between them in a diagram is crucial for identifying where a potential fuel leak actually originates.
How do I use 24v 5.9 Cummins fuel line diagram?
Use the diagram to trace the physical path of fuel when troubleshooting a diagnostic code. If your OBD-II scanner indicates low pressure, identify all fittings between the pump and filter. Check these points for leaks or loose connections that might trigger a check engine light or other engine performance issues.