12 Volt RV Battery Hookup Diagram: Wiring & Setup Guide
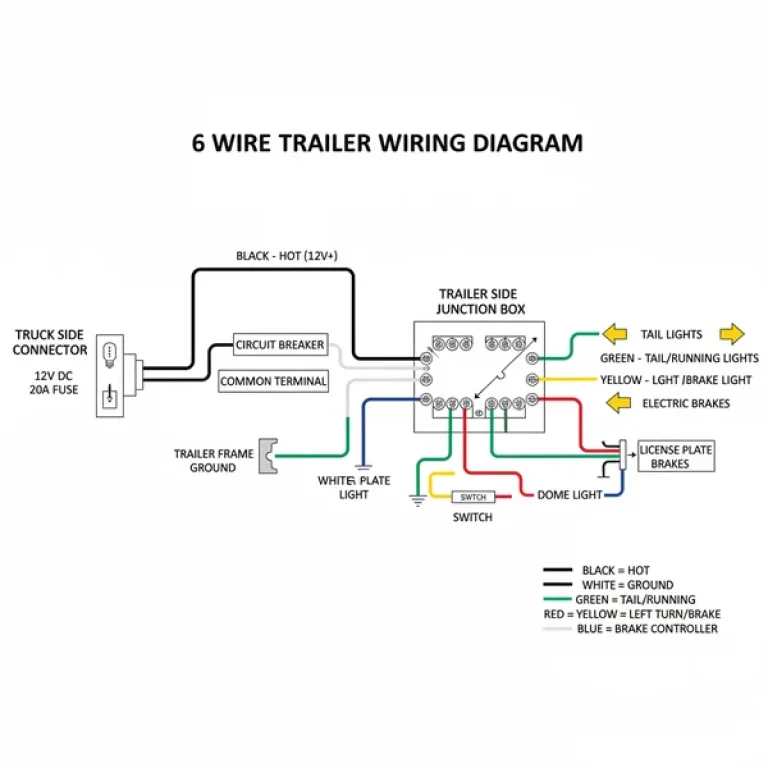
A 12 volt RV battery hookup diagram illustrates the wiring connections between your trailer battery, the 7-way RV blade connector, and the vehicle’s electrical system. It details how auxiliary power charges the battery while running lights, turn signals, and the brake controller receive necessary power for safe towing operations.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Provides a visual roadmap for wiring deep cycle batteries to the trailer’s electrical distribution center.
- Correctly identifying the RV blade 7-pin connector pins is essential for system functionality.
- Ensure proper grounding to prevent electrical shorts or failures in the signal lighting system.
- Use high-quality terminal connectors to maintain a stable 12V auxiliary power flow during travel.
- Consult this diagram when installing new batteries or troubleshooting lighting and charging issues.
Understanding the intricacies of a 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram is essential for any trailer owner looking to ensure a safe and functional towing experience. Whether you are installing a new system or troubleshooting an existing one, having a clear roadmap of how electricity flows from your tow vehicle to your trailer batteries is vital. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed breakdown of the wiring standards, color codes, and connection points necessary to power your auxiliary systems and safety features. By the end of this article, you will understand how the RV blade connector functions, how to wire an electric brake system, and how to maintain a steady charge for your house batteries while on the road.
Most modern trailers use a standard 7-way RV blade connector. While some smaller utility trailers use a 4-pin flat connector, the 7-way system is required for trailers equipped with electric brakes and internal 12-volt battery systems.
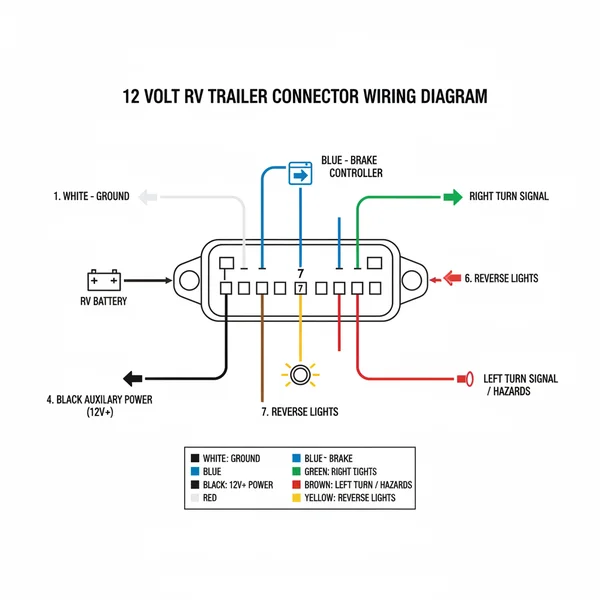
The core of any 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram is the 7-way trailer plug, often referred to as the RV blade connector. Unlike a simple flat connector that only handles basic lighting, the 7-way plug manages high-current tasks such as charging the RV battery and activating the electric brake magnets. The diagram typically displays a circular face with six flat blades surrounding a central round pin. Each position is strictly assigned to a specific function to ensure compatibility across different tow vehicles and trailers.
In a standard configuration, the center pin is usually reserved for the reverse lights, though in some custom setups it may vary. The surrounding blades are allocated for the ground pin, the left and right turn signal and brake light combinations, the running lights, the brake controller output, and the auxiliary power line. The auxiliary power line is particularly critical as it provides the 12-volt charge from the vehicle’s alternator to the RV’s house battery. This allows your refrigerator to run and your batteries to top off while you are driving.
– Insert AI diagram here
The color-coding in a 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram is generally standardized, but you should always verify with a multimeter. Typically, white represents the ground, black or red is used for auxiliary power, green handles the right turn signal, yellow handles the left turn signal, brown is for running lights, and blue is dedicated to the electric brake controller. Understanding these variations is crucial because older trailers or specific manufacturers may deviate from these “standard” colors. Always refer to the pin position on the plug rather than the wire color alone to avoid short circuits.
Never assume wire colors are correct without testing. Miswiring the auxiliary power to the ground pin can cause immediate melting of the harness or an electrical fire in the tow vehicle.
Step-by-Step Installation and Wiring Guide
Following a 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram requires a methodical approach to ensure every connection is secure and weather-resistant. Before beginning, gather high-quality wire strippers, a crimping tool, heat-shrink tubing, and a digital multimeter.
Step 1: Disconnect All Power Sources
Before touching any wires, disconnect the negative terminal of the RV house battery and ensure the tow vehicle is turned off. This prevents accidental shorts that could blow expensive fuses or damage the vehicle’s onboard computer. If your trailer has a solar setup, ensure the charge controller is also isolated.
Step 2: Mount the Connector Socket
Install the 7-way RV blade socket on the bumper or hitch of the tow vehicle. Ensure it is positioned where the trailer cord can reach it easily without being so loose that it drags on the ground. Use stainless steel hardware to prevent rust, which can eventually degrade the ground connection.
Step 3: Establish a Solid Ground
The ground pin is the most important part of the circuit. Without a clean ground, lights will flicker and the electric brake system will fail. Run a heavy-gauge white wire (usually 10 or 12 gauge) from the ground pin directly to the trailer frame. Clean the frame down to bare metal and use a ring terminal with a star washer to ensure a “bite” into the metal.
Step 4: Wire the Lighting Circuits
Connect the wires for the running lights, left turn signal, and right turn signal. In the 7-way system, the turn signals also act as the brake lights. Ensure these wires are tucked into a protective loom to prevent chafing against the trailer chassis.
Step 5: Connect the Electric Brake Lead
The blue wire is designated for the electric brake controller. This wire carries the modulated signal from the tow vehicle to the trailer’s brake magnets. It is vital that this wire is at least 12 gauge to handle the amperage required to stop a heavy trailer. Connect this to the “Brake” terminal on your RV blade plug.
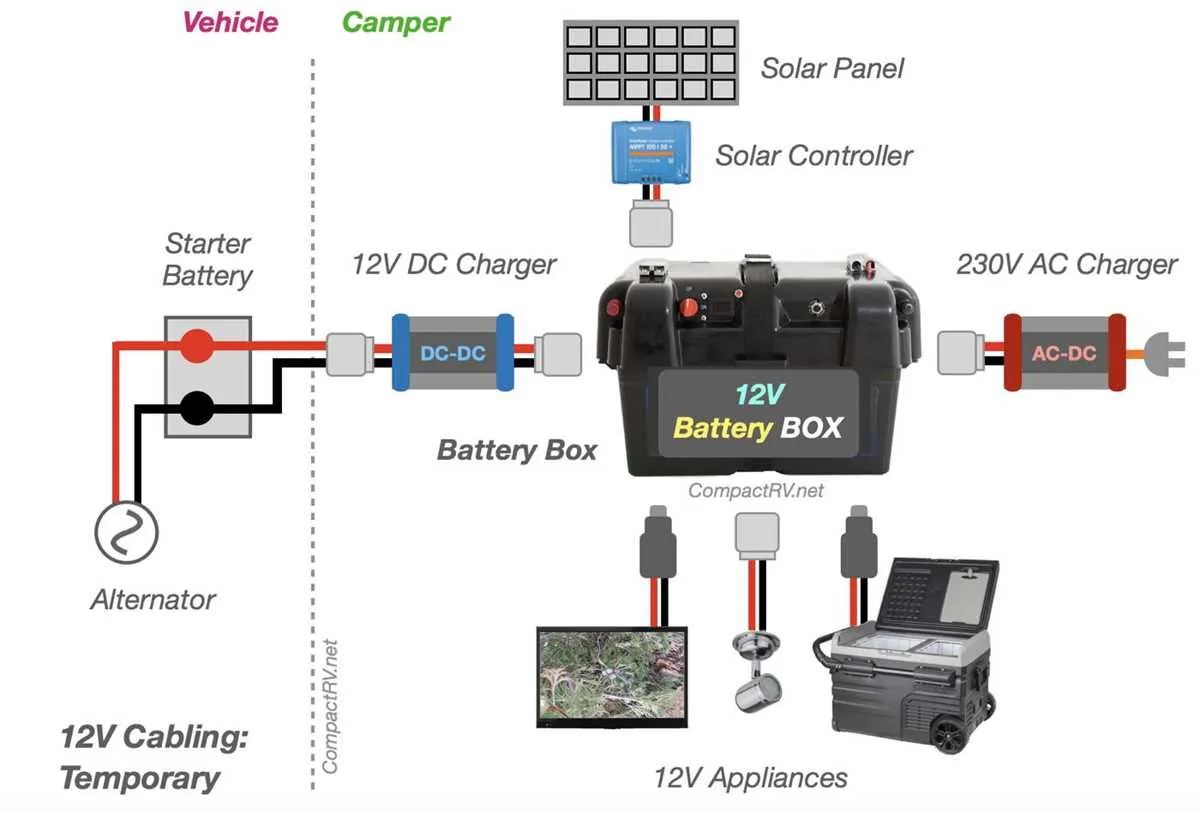
Step 6: Set Up the Auxiliary Power Line
The auxiliary power wire (typically black) connects the tow vehicle’s charging system to the positive terminal of the RV battery. You must install an in-line circuit breaker (usually 30 or 40 amps) near the battery source. This protects the system if the trailer battery tries to draw too much current from the alternator.
Use a 10-gauge wire for the auxiliary power and ground leads. Thicker wire reduces voltage drop, ensuring your RV battery receives a full charge even over long distances.
Step 7: Final Testing with a Multimeter
Once everything is connected, use a multimeter or a 7-way plug tester. Check for 12 volts at the auxiliary power pin and ensure the ground pin shows zero resistance to the frame. Have a partner sit in the tow vehicle to activate the turn signals and the brake controller manual override while you verify the output at the plug.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
Even with a perfect 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram, electrical issues can arise due to the harsh environment trailers inhabit. One of the most common problems is “phantom” lighting issues, where turning on the turn signal causes all the running lights to flash dimly. This is almost always a symptom of a weak ground pin connection. If the electricity cannot return through the ground wire, it will “backfeed” through other circuits to find a path to the frame.
Another frequent issue is the RV battery not charging while driving. This is often caused by a blown fuse in the tow vehicle’s engine bay. Many truck manufacturers do not install the auxiliary power fuse or relay at the factory; they are often found in a plastic bag in the glovebox. If the fuse is intact but no power reaches the plug, check for corrosion inside the RV blade connector. Moisture can cause green crust (copper oxidation) to form, which acts as an insulator and breaks the circuit.
Tips & Best Practices for RV Wiring

To maintain a reliable 12-volt system, you should treat the trailer-to-vehicle connection as a primary maintenance item. Electrical resistance increases with heat and corrosion, so keeping the pins clean is paramount.
- ✓ Apply Dielectric Grease: Use a small amount of dielectric grease on the blades of the plug. This excludes oxygen and moisture, preventing the corrosion that leads to signal loss.
- ✓ Verify Wire Gauge: Never use thin “automotive” wire for electric brake or auxiliary power lines. Stick to 10 or 12-gauge multi-strand copper wire for these high-load applications.
- ✓ Secure the Harness: Use UV-rated zip ties to secure the wiring harness every 12 to 18 inches along the trailer tongue. This prevents the wire from snagging on road debris.
- ✓ Check the Breakaway Switch: Ensure your 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram includes the breakaway switch. This safety device must be wired directly to the RV battery so that it can lock the brakes if the trailer detaches.
When choosing components, opt for a molded 7-way cord rather than assembling your own plug from loose wires. Molded cords are factory-sealed against the elements and are far less likely to suffer from internal shorts. If you must use a flat connector adapter for a smaller trailer, remember that it will not provide auxiliary power or support for a brake controller.
Investing time in understanding and implementing a proper 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram ensures that your trailer remains a safe, powered, and reliable home on wheels. Regular inspections of the ground pin and auxiliary power circuits will prevent the most common roadside headaches and keep your batteries ready for your next off-grid adventure.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram?
A 12 volt RV battery hookup diagram is a schematic showing how the house battery connects to the trailer’s systems. It highlights the paths for auxiliary power, the brake controller, and exterior lighting like turn signals, ensuring the battery charges while the towing vehicle provides essential safety signals.
How do you read 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram?
To read the diagram, start at the battery terminals and follow the color-coded lines to the junction box or 7-way RV blade connector. Look for specific labels such as ground, auxiliary power, and running lights to understand how electricity flows from the source to each component.
What are the parts of 12 volt rv battery hookup?
The primary parts include the deep cycle battery, a battery disconnect switch, an inline fuse or circuit breaker, and the 7-way RV blade plug. Additionally, it involves the wiring for the brake controller, turn signal circuits, and the converter that manages the trailer’s internal 12V distribution.
Why is auxiliary power important?
Auxiliary power is crucial because it allows the tow vehicle’s alternator to charge the RV battery while driving. This ensures that the house battery remains topped up for off-grid use and provides the necessary current for the breakaway switch to activate the brakes in an emergency.
What is the difference between running lights and turn signal wiring?
Running lights are wired to stay illuminated whenever the tow vehicle’s headlights are on, providing visibility. In contrast, turn signal wiring is connected to dedicated pins on the RV blade that pulse electricity only when the driver indicates a turn, signaling intent to other motorists on the road.
How do I use 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram?
Use the diagram as a reference guide during installation or repair to ensure every wire reaches its correct terminal. It helps identify which wire controls the brake controller or running lights, allowing you to test continuity and verify that the 12-volt system is properly grounded and fused.