12 Volt RV Battery Hookup Diagram: Wiring Instructions
A 12 volt RV battery hookup diagram illustrates how your trailer battery links to the RV blade connector and charging system. It ensures auxiliary power reaches appliances while coordinating turn signal and running lights. Proper wiring prevents electrical shorts and ensures the brake controller functions correctly for towing safety.
📌 Key Takeaways
- Identifies how the house battery connects to the vehicle’s charging system.
- The 7-way RV blade connector is the central hub for all trailer functions.
- Proper grounding is critical to avoid flickering lights or brake failure.
- Use color-coded wires to match standard industry schematics for easier repairs.
- Refer to this diagram when installing solar panels or dual-battery banks.
Understanding the electrical architecture of your recreational vehicle is essential for ensuring a safe and functional camping experience. Whether you are installing a new power system or troubleshooting a faulty connection, a 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram acts as the definitive roadmap for your trailer’s energy distribution. This diagram illustrates how the tow vehicle interacts with the trailer’s house battery, lighting, and safety systems. By following a standardized wiring scheme, you ensure that your auxiliary power charges correctly while driving and that your electric brakes respond instantly when needed. In the following sections, you will learn the specific pin configurations for various connectors, the importance of proper grounding, and how to maintain a reliable 12-volt circuit for all your off-grid adventures.
Most modern trailers use the 7-way “RV Blade” style connector. Unlike the simpler 4-flat connector, the 7-way plug allows for battery charging and electric brake control, which are vital for heavy trailers and long-distance towing.
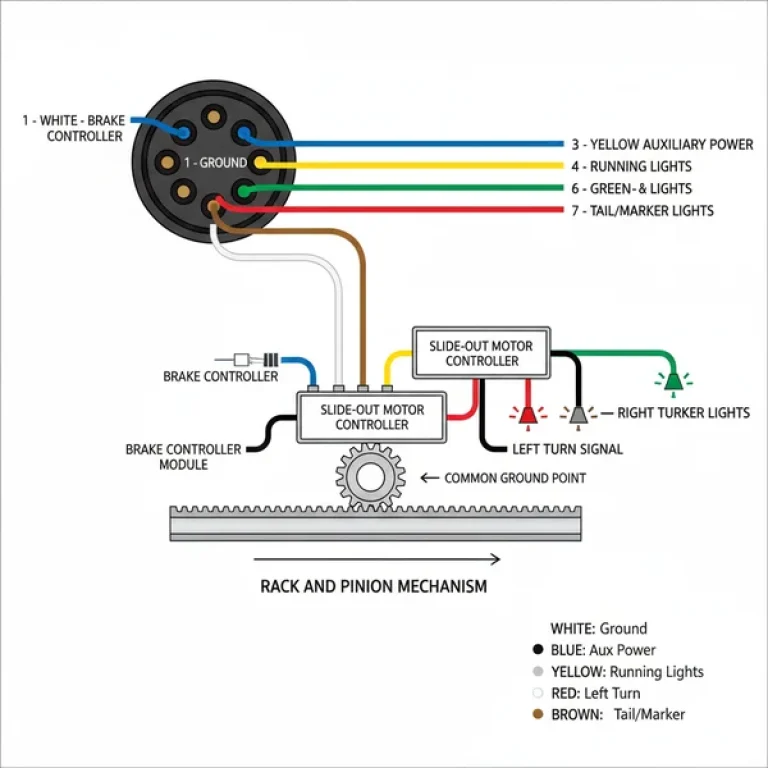
The 7-Way RV Blade Connector Breakdown
The most critical component of a 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram is the 7-way RV blade plug. This connector is the primary interface between the tow vehicle’s alternator and the trailer’s 12-volt system. Unlike a simple flat connector used for small utility trailers, the RV blade configuration carries high-amperage signals and dedicated power lines. Each blade within the circular housing has a specific assignment designed to keep your trailer legal and powered up.
At the center of the plug is usually the reverse light circuit, but the perimeter blades handle the heavy lifting. The “Auxiliary Power” pin is arguably the most important for RV owners, as it provides the +12V charge line that tops off your trailer’s house battery during transit. The “Ground Pin” is equally vital; without a solid return path to the vehicle chassis, the entire circuit will fail or behave erratically. The “Electric Brake” pin receives a modulated signal from the brake controller inside the cab, telling the trailer’s magnets how much force to apply during deceleration. Finally, the remaining pins control the running lights, left turn signal/brake light, and right turn signal/brake light.
[DIAGRAM_PLACEHOLDER: 7-Way RV Blade Wiring Schematic showing Pin 1: Ground (White), Pin 2: Electric Brakes (Blue), Pin 3: Tail/Running Lights (Brown), Pin 4: Battery Charge/Auxiliary (Black), Pin 5: Left Turn/Brake (Yellow), Pin 6: Right Turn/Brake (Green), Pin 7: Reverse Lights (Purple/Yellow)]
Variations do exist depending on the manufacturer. While most follow the industry standard colors (White for ground, Black for 12V hot), some older models or European imports may use different color coding. Always use a multimeter to verify the “hot” pin on your tow vehicle before finalizing your trailer-side wiring. This prevents accidental short circuits that could damage the expensive brake controller or the vehicle’s engine control module.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
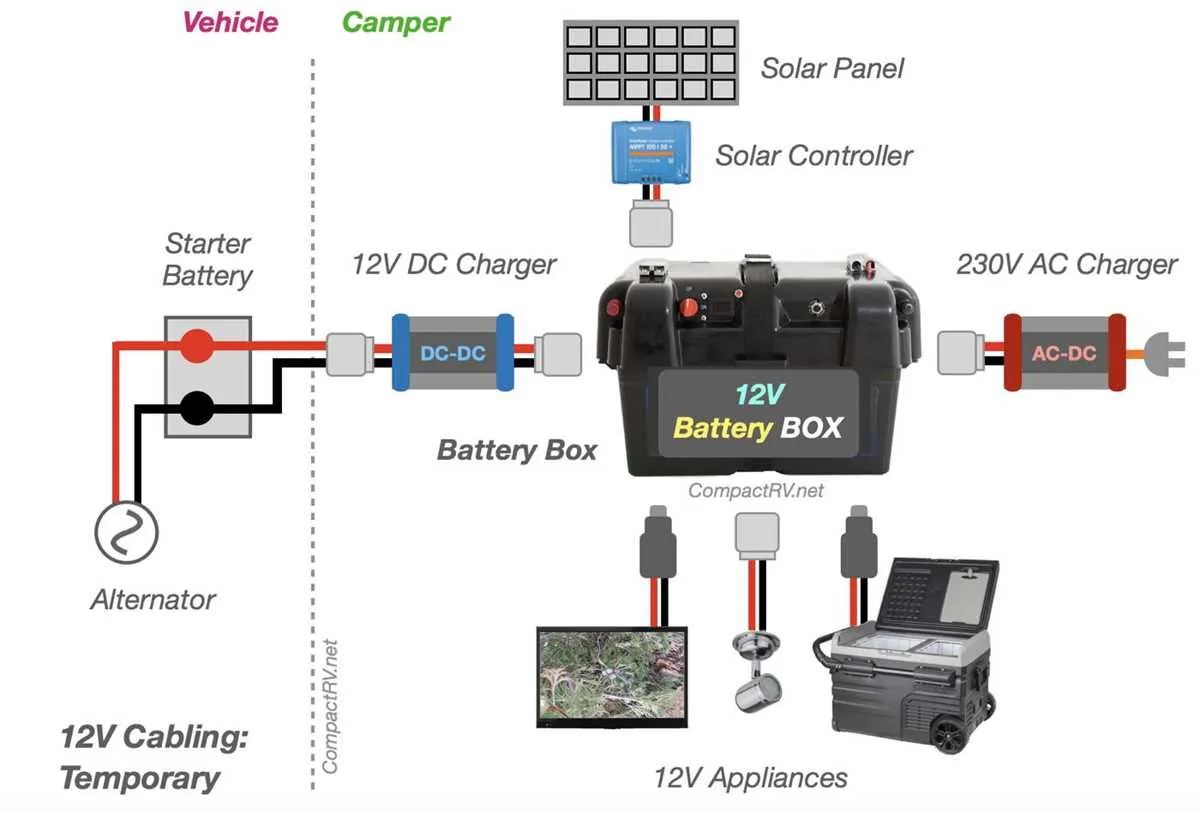
Wiring a trailer battery and connector system requires a methodical approach to ensure every circuit is protected and efficient. Follow these steps to implement a standard 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram on your trailer.
- Mount the Battery and Box: Begin by securing your 12-volt deep cycle battery in a protective, vented battery box on the trailer tongue. Ensure the box is bolted down and the battery cannot shift during travel.
- Establish a Solid Ground: Connect a heavy-gauge white wire (typically 10-gauge) from the negative (-) terminal of the battery directly to the trailer frame. Scrape away any paint or rust to ensure metal-to-metal contact. This serves as the foundation for the entire ground pin system.
- Install the Auxiliary Power Line: Run a black wire from the 7-way plug (Pin 4) to the positive (+) terminal of the trailer battery. You must install a 20-amp or 30-amp auto-reset circuit breaker on this line near the battery to protect against overcurrent. This allows the tow vehicle to charge the battery while driving.
- Connect the Brake Controller Lead: Locate the blue wire coming from your trailer’s electric brakes. Connect this to Pin 2 of the 7-way plug. This wire carries the signal that activates the braking magnets. Ensure these connections are waterproofed with heat-shrink tubing.
- Wire the Exterior Lighting: Connect the brown wire to the running lights, the yellow wire to the left turn signal, and the green wire to the right turn signal. Most trailers use a “split” system where the brake light and turn signal share the same filament/circuit.
- Integrate the Breakaway Switch: This is a critical safety step. Connect one wire of the breakaway switch to the positive (+) battery terminal and the other wire to the blue electric brake wire. If the trailer uncouples, the switch pulls, sending immediate 12V power from the house battery to the brakes.
- Final Connection and Testing: Once all wires are routed and secured with loom and zip ties, plug the trailer into the tow vehicle. Use a helper to check the turn signals, running lights, and brake lights. Finally, use a voltmeter to confirm that the trailer battery is receiving a charge from the vehicle alternator when the engine is running.
Never wire the breakaway switch directly to the tow vehicle’s power. It must be powered by the trailer’s onboard 12-volt battery to ensure it works even if the umbilical cord is severed during an accident.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting

Even with a perfect 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram, electrical gremlins can arise due to vibration, corrosion, and environmental exposure. The most frequent issue encountered by RVers is a “weak ground.” If your running lights flicker when you hit the turn signal, or if the electric brakes behave intermittently, the ground pin connection is likely corroded or loose. Because the trailer frame often acts as the return path, any rust at the grounding point will increase resistance and drop voltage.
Another common problem is a blown fuse on the tow vehicle side. Many modern trucks have dedicated fuses for the auxiliary power and trailer lights located in the engine bay fuse box. If your trailer battery isn’t charging despite a correct hookup, check the “Trailer Tow Charge” fuse. Additionally, if you notice your electric brakes are grabbing or not engaging at all, inspect the blue wire for “nicks” or abrasions where it passes through the trailer axle. If you cannot find the source of a total power failure after checking fuses and grounds, it may be time to use a 7-way circuit tester or consult a professional technician to check for internal wire breaks.
Tips and Best Practices for RV Wiring
To maintain a high-performing electrical system, quality components and proactive maintenance are your best allies. When selecting wire for your 12-volt system, always choose multi-strand copper wire rather than solid-core wire. Multi-strand wire is more flexible and resistant to the constant vibrations of road travel, preventing fatigue-related breaks over time.
- ✓ Use Dielectric Grease: Apply a small amount of dielectric grease to the pins of your 7-way plug and the flat connector. This prevents moisture from causing oxidation and ensures a clean connection every time you hitch up.
- ✓ Gauge Matters: For the auxiliary power and ground pin, use at least 10-gauge wire. Using thinner wire (like 14 or 16 gauge) will result in voltage drop, meaning your battery will never reach a full state of charge from the tow vehicle.
- ✓ Install a Junction Box: Instead of wire-nutting cables under the trailer frame, install a weatherproof 7-way junction box. This provides a clean, labeled area to connect your umbilical cord to the trailer’s internal wiring.
- ✓ Label Everything: Use a permanent marker or heat-shrink labels to identify wires. This makes future troubleshooting much faster if you need to replace a component or add a new accessory.
If you frequently transition between different trailers, keep a 7-way to 4-way flat connector adapter in your glovebox. This allows you to tow smaller trailers without auxiliary batteries or brakes without rewiring your vehicle’s main plug.
In conclusion, mastering your 12 volt rv battery hookup diagram is the key to a safe and worry-free journey. By ensuring your auxiliary power is fused, your ground pin is secure, and your electric brake controller is properly integrated, you protect both your equipment and your passengers. Regular inspection of the RV blade connector and maintaining your battery terminals will keep your system running efficiently for years to come. Remember that electrical work requires patience and attention to detail, but with the right diagram and tools, you can confidently manage your RV’s power needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a 12 volt RV battery hookup diagram?
This diagram is a visual schematic showing the electrical path between your trailer battery and the towing vehicle. It details how DC electricity flows to auxiliary power systems, the brake controller, and exterior lighting like your turn signal. It serves as a blueprint for safe installation and effective electrical troubleshooting.
How do you read a 12 volt RV battery hookup diagram?
To read this diagram, trace the lines from the battery terminals to the RV blade plug pins. Each color usually corresponds to a specific function, such as the white wire for ground or the blue wire for electric brakes. Follow the lines to understand the circuit flow clearly.
What are the parts of a 12 volt RV battery hookup?
The primary parts include the deep-cycle battery, a 7-way RV blade connector, inline fuses or circuit breakers, and various lighting circuits. It also incorporates the brake controller wire for safety, auxiliary power for interior devices, and the necessary wiring for the turn signal and running lights systems.
Why is auxiliary power important?
Auxiliary power is crucial because it allows the towing vehicle to charge the trailer battery while driving. This ensures that your RV remains powered up for lighting, refrigeration, and water pumps once you reach your campsite. It bridges the gap between the vehicle alternator and the trailer bank.
What is the difference between running lights and turn signal wiring?
Running lights are wired to stay illuminated whenever the towing vehicle’s headlights are on, providing visibility. In contrast, the turn signal wiring is an intermittent circuit that pulses power to specific bulbs. Both functions are handled through different pins on the standard 7-way RV blade connector system.
How do I use a 12 volt RV battery hookup diagram?
Use this diagram as a reference during the installation of a new battery or when adding electrical accessories. It helps you verify that each wire is connected to the correct terminal, preventing damage to the brake controller or auxiliary power systems. It is essential for any DIY electrical work.